Legal & General Group Bundle
Who Really Owns Legal & General Group?
Understanding the Legal & General Group SWOT Analysis is crucial for grasping its competitive position, but have you ever wondered about the power structure behind this financial giant? Legal & General's ownership structure dictates its strategic direction, influencing everything from investment decisions to its global footprint. Unraveling the intricacies of who owns Legal & General provides unparalleled insight into the company's future.

The recent sale of Legal & General's US insurance business, announced in February 2025, underscores the dynamic nature of its ownership and strategic focus. This shift, coupled with the company's substantial assets under management, highlights the importance of examining Legal & General shareholders, its structure, and the influence of its major investors. This analysis will explore the evolution of Legal & General ownership, from its founding to its current status as a publicly traded company, providing a comprehensive view of its governance and strategic direction.
Who Founded Legal & General Group?
The Legal & General Life Assurance Society, now known as Legal & General Group, was established in 1836. It was founded by a group of six London lawyers, marking the beginning of what would become a significant player in the financial sector. Understanding the initial ownership structure provides insight into the company's early vision and strategic direction.
The founders of Legal & General were Sergeant John Adams, Basil Montagu, W. C. L. Keene, Kenyon S. Parker, J. H. R. Chichester, and George L. Baker. Adams was elected as the chairman during the inaugural board meeting in June 1836. The company aimed to raise £1 million through stock sales, a target it achieved by 1839. Initially, share ownership was limited to members of the legal profession.
The first life insurance policy was issued in October 1836 to solicitor Thomas Smith. The founders' focus on life assurance reflected the favorable conditions for the life insurance industry in Britain during a period of population growth and increasing personal income. While specific details regarding equity splits or early agreements among the founders are not readily available, the company's early structure set the stage for its future growth.
The founders' backgrounds and the initial focus on the legal profession shaped the early Legal & General structure. The company's capitalization goal was achieved within a few years. The early success was indicative of the growing demand for financial products during the 19th century. To further understand the competitive environment, consider the Competitors Landscape of Legal & General Group.
- Founders: Sergeant John Adams, Basil Montagu, W. C. L. Keene, Kenyon S. Parker, J. H. R. Chichester, and George L. Baker.
- Initial Capitalization: £1 million, achieved by 1839.
- Shareholder Restriction: Initially limited to members of the legal profession.
- First Policy: Issued in October 1836 to Thomas Smith.
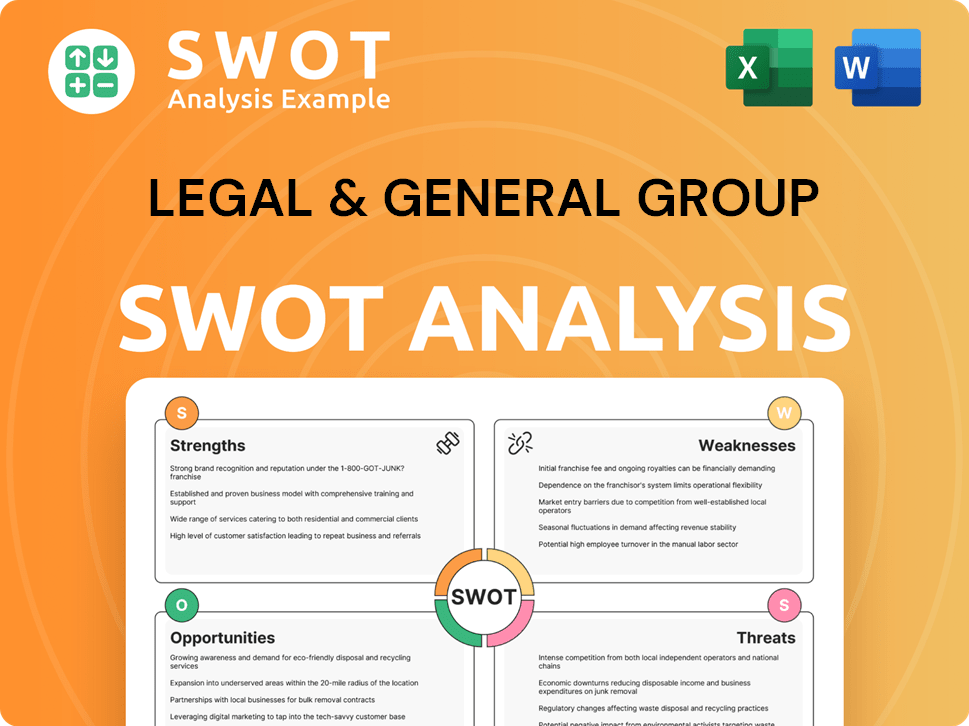
Legal & General Group SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Legal & General Group’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of Legal & General Group has evolved significantly since the 1970s, when it became a wholly owned division of the Legal & General Group. The company was formally incorporated as a Public Limited Company on February 27, 1979. This transition marked a pivotal moment, setting the stage for its listing on the London Stock Exchange and its inclusion in the FTSE 100 Index. The company's structure has since been shaped by its status as a publicly traded entity, influencing its shareholder base and governance practices.
Legal & General Group Plc's market capitalization provides insights into its valuation. As of March 18, 2025, the market capitalization was £14.6 billion. Looking at the broader trends, as of June 10, 2025, the market capitalization reached £14.74 billion, although it had decreased by 1.50% over the previous year. Furthermore, as of May 16, 2025, the market cap was €16.61 billion. These figures reflect the company's performance and market perception.
| Metric | Details | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization (March 18, 2025) | £14.6 billion | March 18, 2025 |
| Market Capitalization (June 10, 2025) | £14.74 billion (1.50% decrease YoY) | June 10, 2025 |
| Market Capitalization (May 16, 2025) | €16.61 billion | May 16, 2025 |
The ownership structure of Legal & General Group Plc is primarily institutional. As of December 31, 2024, institutions held approximately 89.6% of the shares, which amounted to over 5.1 billion shares. The general public held 7.24% of the shares, while employee share schemes accounted for 2.29%. Individual insiders held a smaller stake of 0.149%. This distribution highlights the significant influence of institutional investors on the company's direction. Understanding the Legal & General ownership structure is key to grasping its strategic direction.
Major institutional shareholders play a crucial role in Legal & General's governance and strategy. BlackRock, Inc. held 298,315,445 ordinary shares, representing 4.989% of the capital as of December 31, 2024. Other significant investors include The Vanguard Group, Inc., State Street Global Advisors, Inc., and Aviva Investors Global Services Ltd.
- Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance Company (MYL) acquired voting rights to 294,664,836 ordinary shares, representing 4.999912% as of March 3, 2025.
- Morgan Stanley (MS) held over 5% of voting rights through financial instruments as of February 7, 2025, with its interest at 5.287326% as of February 28, 2025.
- Legal & General Investment Management (LGIM) actively engages on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues.
- LGIM uses its voting rights to support or raise concerns regarding governance and business strategies.
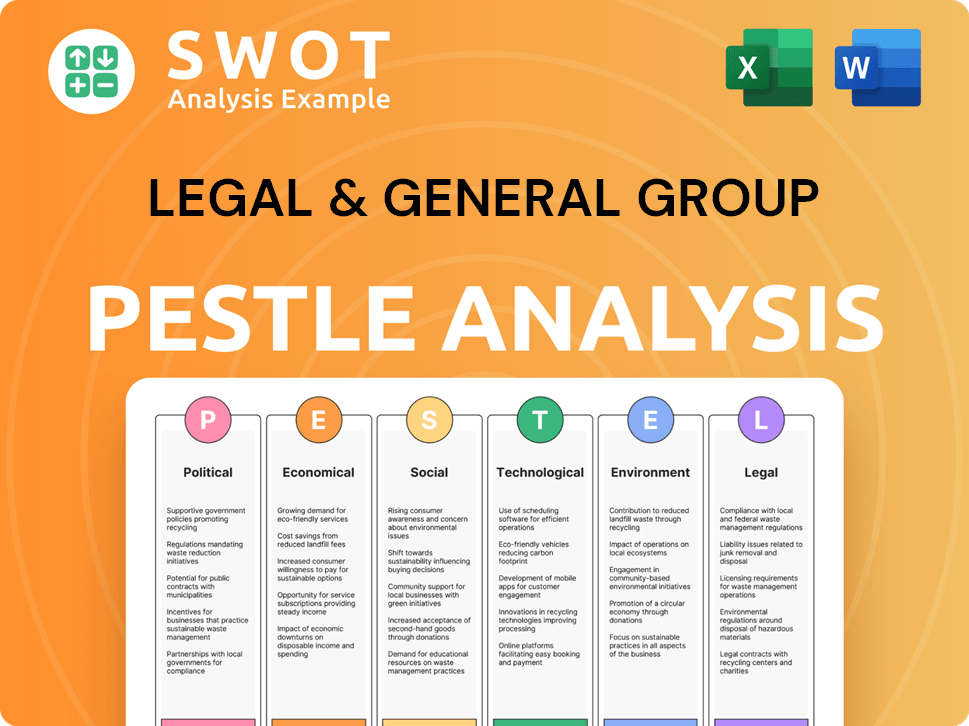
Legal & General Group PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Legal & General Group’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Legal & General Group Plc oversees the company's strategic direction. Sir John Kingman serves as Chairman, and António Simões is the CEO, who took over in 2023. Other directors include Lesley Mary Samuel Knox, Henrietta Caroline Baldock, Nilufer Kheraj, Carolyn Johnson, and Philip Arthur John Broadley. This board structure is crucial for the company's governance and operational oversight.
The composition of the board reflects a mix of experienced professionals, ensuring diverse perspectives in decision-making. The board's role includes setting strategic objectives, monitoring performance, and ensuring compliance. The board's decisions are pivotal in shaping the company's future, with each director contributing to the overall governance framework. The board also plays a key role in representing the interests of Legal & General shareholders.
| Board Member | Position | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sir John Kingman | Chairman | Oversees board activities |
| António Simões | CEO | Chief Executive Officer since 2023 |
| Lesley Mary Samuel Knox | Director | |
| Henrietta Caroline Baldock | Director | |
| Nilufer Kheraj | Director | |
| Carolyn Johnson | Director | |
| Philip Arthur John Broadley | Director |
The voting structure at Legal & General Group Plc generally follows the 'one-share-one-vote' principle. This means that each share carries equal voting rights, ensuring that shareholder control aligns with their economic interests. Decisions at board meetings are made through resolutions, with ordinary resolutions requiring over 50% approval and special resolutions often needing at least 75% approval. The Board unanimously recommends shareholders to vote in favor of all resolutions. For those interested in the company's origins, you can find more information in the Brief History of Legal & General Group.
Legal & General's Annual General Meeting (AGM) allows shareholders to exercise their voting rights. The company does not have dual-class shares or special voting rights. LGIM, a major institutional investor, votes against board directors if remuneration is not supported for two consecutive years.
- One-share-one-vote principle ensures equal voting rights.
- AGMs provide a platform for shareholder voting.
- LGIM actively monitors and votes on remuneration.
- Shareholders can vote in person or electronically.
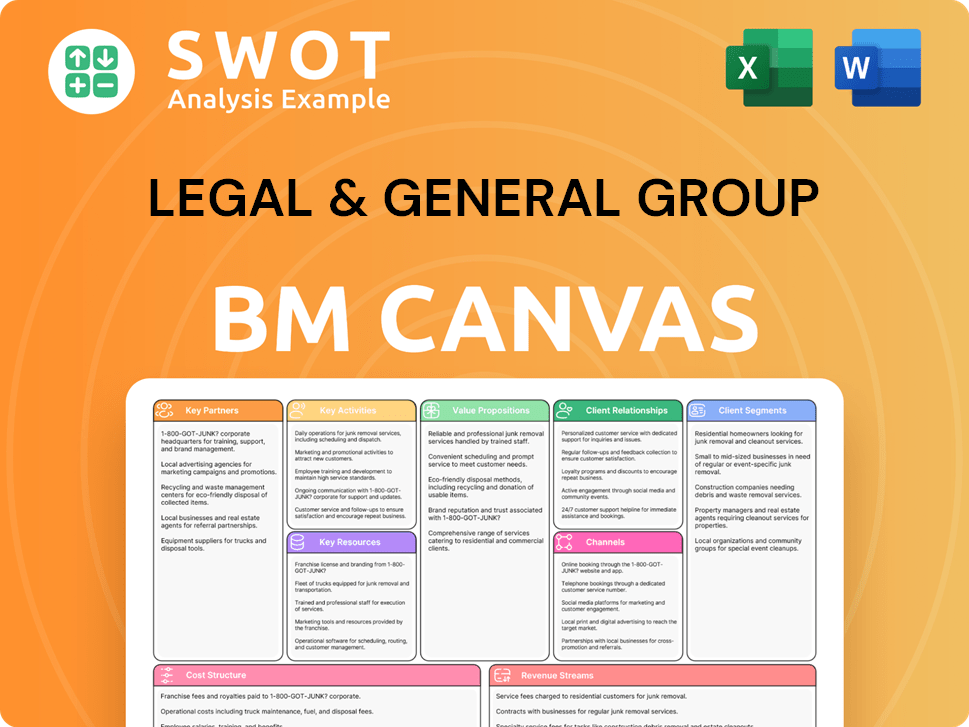
Legal & General Group Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Legal & General Group’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership profile of Legal & General Group has been shaped by significant strategic shifts. A major development in February 2025 was the agreement to sell its US insurance business to Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance Co for $2.3 billion, with the transaction expected to conclude by the end of 2025. This move is part of CEO António Simões' strategy to focus on core businesses like asset management and the UK retail sector. As part of this deal, Meiji Yasuda will also acquire a 5% equity stake in Legal & General.
In September 2024, Legal & General agreed to sell its UK homebuilder, Cala Group, for £1.35 billion. These strategic decisions are designed to return more capital to shareholders, with the company aiming to return over £5 billion through dividends and buybacks between 2024 and 2027. Legal & General announced a £500 million share buyback for 2025, increasing from £200 million in 2024. These actions reflect a concerted effort to optimize the company's portfolio and enhance shareholder value.
Institutional investors hold a significant portion of Legal & General's shares. As of December 31, 2024, institutions owned 89.6% of the company's shares, reflecting a broader trend in the investment landscape. Growth Strategy of Legal & General Group includes a focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues, with Legal & General Investment Management (LGIM) actively engaging with companies to promote responsible investment practices. This approach underscores the influence of institutional investors and the growing importance of ESG factors in investment decisions.
The sale of the US insurance business to Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance Co for $2.3 billion, expected to close by the end of 2025, is a pivotal move. This transaction allows Legal & General to concentrate on its core strengths.
Institutional ownership remains dominant, with institutions holding 89.6% of shares as of December 31, 2024. This highlights the influence of institutional investors. LGIM actively engages on ESG matters.
Legal & General is committed to returning capital to shareholders. The company plans to return over £5 billion through dividends and buybacks between 2024 and 2027. A £500 million share buyback is planned for 2025.
The sale of Cala Group for £1.35 billion in September 2024 is another strategic move. These divestments support the company's focus on core business areas and capital allocation.
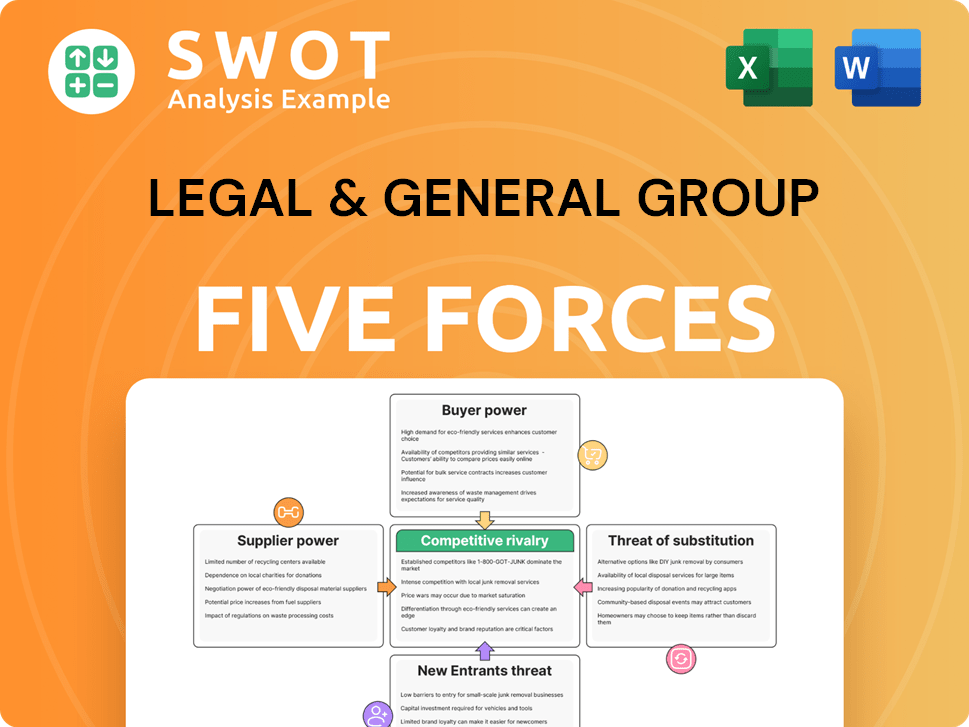
Legal & General Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Legal & General Group Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Legal & General Group Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Legal & General Group Company?
- How Does Legal & General Group Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Legal & General Group Company?
- What is Brief History of Legal & General Group Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Legal & General Group Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.