Synopsys Bundle
Who Really Owns Synopsys?
Understanding the ownership structure of a tech giant like Synopsys is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the market. Synopsys, a leader in electronic design automation, has a fascinating ownership story that impacts its strategic direction. Unraveling "Who owns Synopsys" provides invaluable insights into its governance, long-term vision, and potential for growth.
From its humble beginnings to its current status as a publicly traded company, the Synopsys SWOT Analysis reveals a dynamic evolution in its ownership. The composition of Synopsys shareholders, including major institutional investors, individual shareholders, and insiders, significantly influences the company's decisions. Delving into the Synopsys ownership structure helps uncover the forces driving its innovation and market performance, making it a critical area of focus for anyone interested in the Synopsys stock and the broader tech landscape.
Who Founded Synopsys?
The story of Synopsys's ownership begins in 1986. It was founded by Dr. Aart de Geus and a team of engineers. They spun out from General Electric's Microelectronics Center.
While the exact initial equity distribution isn't public, Dr. de Geus, as a co-founder and long-time CEO, held a significant stake. The company's initial focus was on logic synthesis technology. This was crucial for integrated circuit design.
Early backing likely came from venture capital firms and possibly angel investors. They recognized the potential of Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools. These investments were vital for research, development, and establishing a market presence. Vesting schedules ensured founder commitment.
Dr. Aart de Geus and a team of engineers from General Electric's Microelectronics Center founded the company. The team's expertise in chip design was key to the company's early success.
The company's initial focus was on logic synthesis technology. This was a critical part of designing integrated circuits. This technology helped automate and improve the chip design process.
Early investors likely included venture capital firms. These firms specialized in technology. Angel investors also recognized the potential of EDA tools.
The initial ownership structure aimed to secure technological leadership. It also ensured the commitment of the founding team. This was essential for long-term growth.
Early investments were crucial for funding research and development. They were also essential for establishing the initial market presence. These investments helped Synopsys grow.
Dr. Aart de Geus, as a co-founder and CEO, played a key role in shaping the company. He held a significant stake in the company. His leadership was vital.
Understanding
The founders, especially Dr. Aart de Geus, played a key role in the early success of the company. The initial investments and ownership structure were critical for growth.
- The company was founded in 1986 by Dr. Aart de Geus and a team of engineers.
- Early investors included venture capital firms and angel investors.
- The initial focus was on logic synthesis technology.
- The company is publicly traded with a market capitalization of around $80 billion as of May 2024.
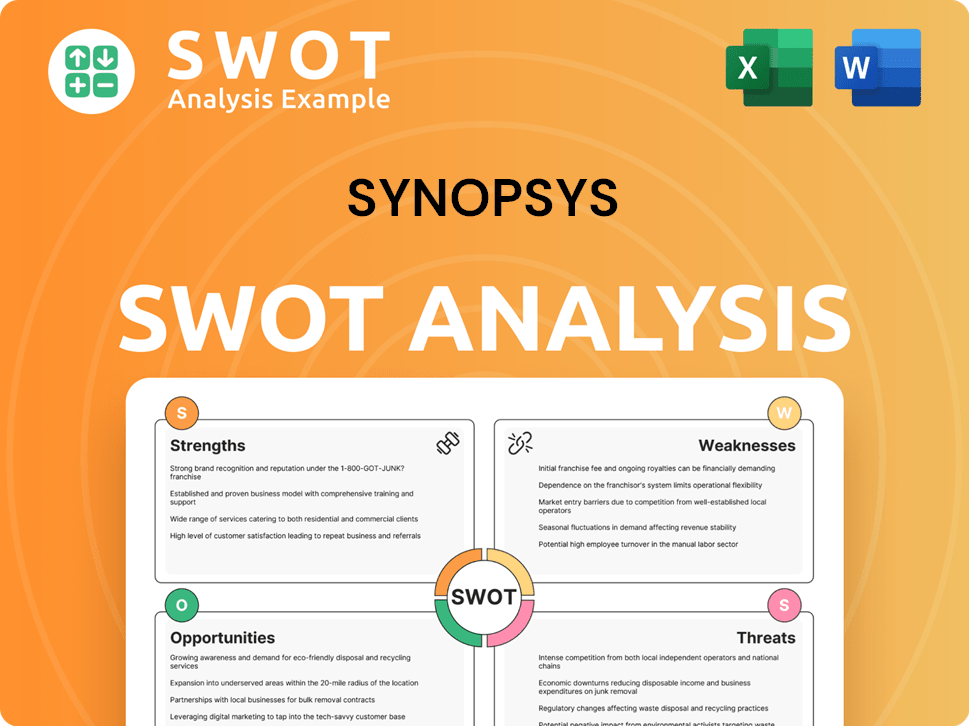
Synopsys SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Synopsys’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Synopsys's ownership structure is a story of growth, starting with its initial public offering (IPO) in 1992. This pivotal moment transitioned the company from private to public, opening its doors to a broader range of investors. The IPO was crucial, providing capital for expansion and strategic moves.
The ownership landscape of Synopsys has shifted significantly since its IPO. Institutional investors now dominate, holding the majority of shares. These include major players like The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street Corporation. Individual insiders, such as current and former executives, also maintain a stake, aligning their interests with the company's overall success. This structure has supported Synopsys's strategic growth in the EDA and IP markets.
| Key Event | Impact on Ownership | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Transitioned from private to public ownership, enabling access to wider investor base and capital. | 1992 |
| Growth and Acquisitions | Increased institutional ownership, reflecting market confidence and strategic expansion. | Ongoing |
| Insider Ownership | Alignment of interests between company leadership and shareholders. | Ongoing |
As of December 31, 2024, major institutional shareholders like Vanguard and BlackRock held substantial percentages of Synopsys's common stock. This reflects their investment in leading technology companies. The concentration of ownership among institutional investors and the presence of insider ownership highlight the company's stability and strategic direction. Understanding who owns Synopsys provides insight into its long-term strategy and market position.
The ownership of Synopsys is primarily held by institutional investors, with significant stakes held by Vanguard and BlackRock. Individual insiders also hold shares, aligning their interests with shareholders. This structure has supported Synopsys's growth in the EDA and IP markets.
- Institutional investors hold the majority of shares.
- Insider ownership aligns leadership with shareholder interests.
- The IPO in 1992 was a major turning point.
- The company's ownership structure supports its strategic growth.
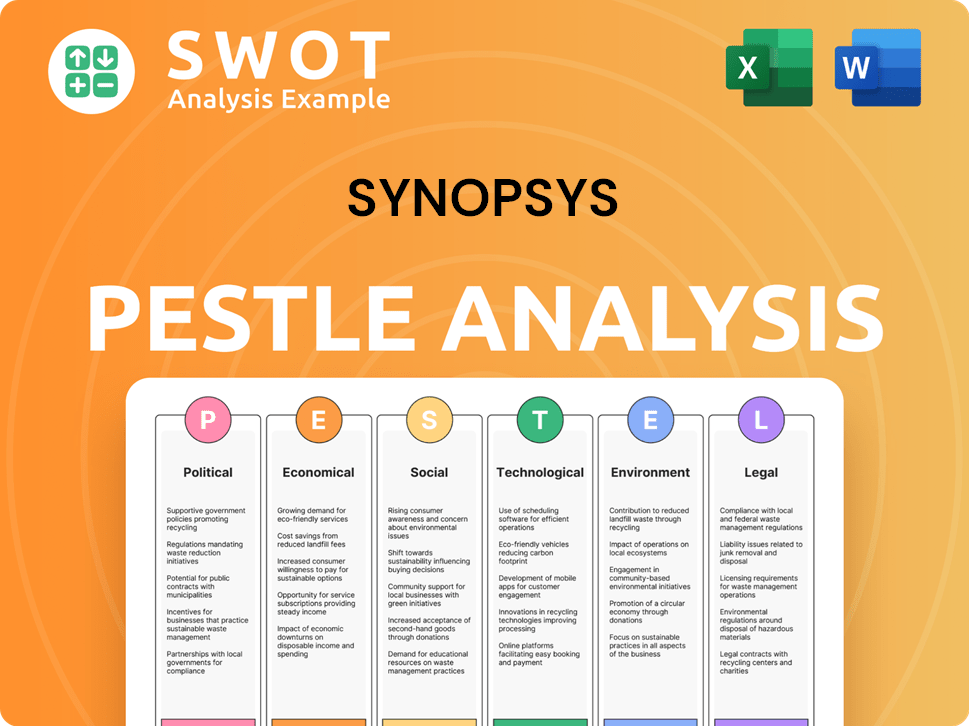
Synopsys PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Synopsys’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Synopsys, as of early 2025, is composed of a mix of independent directors and those with executive roles. This structure reflects a commitment to governance and oversight. Board members bring extensive experience in the technology and semiconductor industries. This experience is crucial for guiding the company's strategic direction and ensuring effective oversight of its operations. The board's composition is designed to promote accountability and align strategic decisions with long-term shareholder value.
While specific board seats are not directly tied to individual major shareholders, the board collectively represents the interests of all shareholders. This approach ensures that the board's decisions are made in the best interest of the company and its investors. The board oversees the company's strategic direction, risk management, and financial performance. This is a standard practice for publicly traded companies like Synopsys. The board's role is to ensure that the company operates in a responsible and sustainable manner, creating value for its shareholders.
| Board Member | Title | Relevant Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Aart de Geus | Chairman and CEO | Founder of Synopsys, extensive experience in EDA and semiconductor industries. |
| Trond Iversen | Lead Independent Director | Experience in technology and financial management. |
| Other Directors | Independent Directors | Diverse backgrounds in technology, finance, and corporate governance. |
The voting structure for Synopsys's common stock is generally one-share-one-vote. This means each share entitles its holder to one vote on shareholder matters. This structure ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares owned. There are no publicly disclosed special voting rights or founder shares that would give outsized control to specific individuals. Synopsys, like all public companies, is subject to potential proxy battles or activist investor campaigns. However, none have significantly impacted its recent decision-making as of early 2025. Understanding the Target Market of Synopsys is also crucial for understanding the company's strategic direction, which is influenced by the board.
Synopsys is a publicly traded company, so the ownership is distributed among various shareholders. The board of directors oversees the company's operations and represents the interests of all shareholders.
- The voting structure is one-share-one-vote.
- The board includes independent directors and executives.
- The board's decisions focus on long-term shareholder value.
- The company is subject to potential proxy battles.
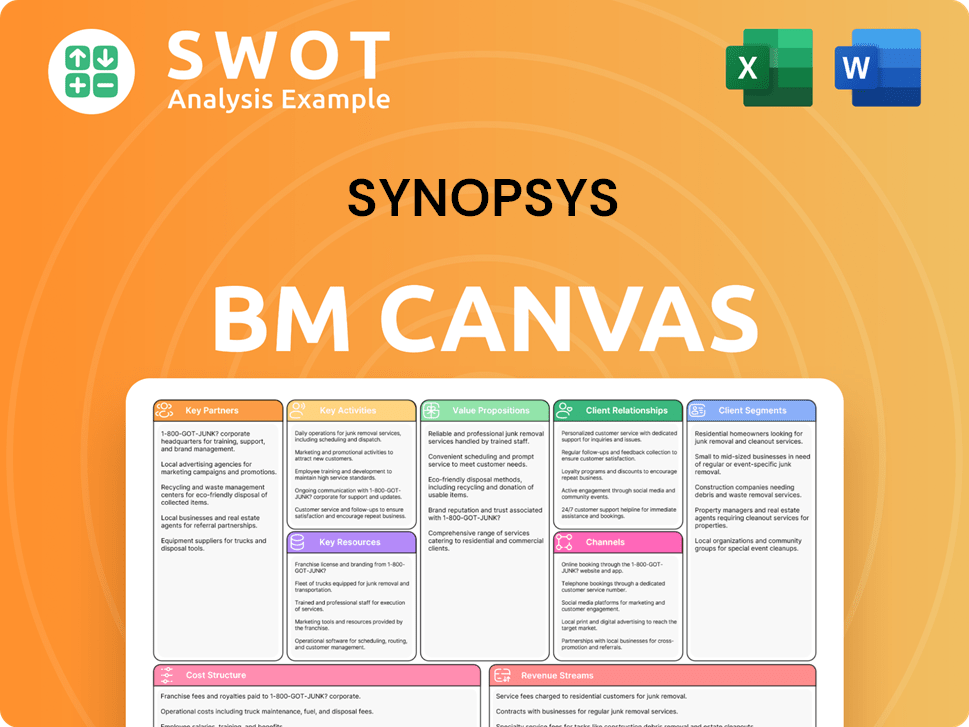
Synopsys Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Synopsys’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of the Synopsys company has been shaped by its robust growth and strategic moves. A key development influencing Synopsys ownership is the company's acquisition strategy, aimed at broadening its technology portfolio. The proposed acquisition of Ansys, announced in early 2024, is a significant event that could alter Synopsys's financial structure and potentially its shareholder base.
Consolidation within the software and semiconductor industries is a major factor driving changes in Synopsys shareholders. This often leads to increased institutional ownership as larger funds participate in such transactions. Share buyback programs also contribute to ownership shifts, incrementally increasing the proportional ownership of remaining shareholders. Founder dilution is a natural outcome for successful public companies, gradually reducing the original founders' percentage ownership as new shares are issued. The overall trend for Synopsys stock, aligning with the broader technology sector, is towards increased institutional ownership.
The primary focus of Synopsys has been on its growth strategy and market leadership, with no indications of planned privatization or major shifts in its core ownership strategy, beyond those influenced by market dynamics and strategic acquisitions. For more information on the company, consider exploring a detailed 0.
Synopsys owner has been influenced by strategic acquisitions and market dynamics. The Ansys acquisition, if completed, will significantly alter the financial structure. Institutional ownership is increasing, reflecting the company's stability.
Acquisitions, share buybacks, and founder dilution are key factors affecting the ownership structure. These elements contribute to a shift towards greater institutional ownership. The company's focus remains on growth and market leadership.
Synopsys Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Synopsys Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Synopsys Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Synopsys Company?
- How Does Synopsys Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Synopsys Company?
- What is Brief History of Synopsys Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Synopsys Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.