Target Bundle
Who Really Owns Target Corporation?
Understanding who owns a company is crucial for grasping its strategic direction and future prospects. Target Corporation's evolution from Dayton-Hudson to the retail giant we know today provides a fascinating case study in corporate ownership. This article explores Target's ownership structure, from its origins to its current status as a publicly traded entity. We'll uncover the key players shaping Target's destiny.
From its humble beginnings in 1902, Target SWOT Analysis reveals a dynamic shift in ownership. Examining Target's ownership history provides valuable insights into its corporate structure and the influence of Target shareholders. As a publicly traded company, understanding who controls Target and the impact of major investors is essential for anyone interested in Target Corporation stock ownership. This analysis will also look at the role of Target executives and the board of directors.
Who Founded Target?
The genesis of Target Corporation's ownership traces back to George Dayton, who acquired Goodfellow Dry Goods in June 1902. This pivotal acquisition established the foundation for a retail empire. The company's evolution, marked by name changes to Dayton's Dry Goods Company in 1903 and The Dayton Company in 1910, reflects its growth trajectory.
The launch of the original Target store in 1962 was a collaborative effort. John F. Geisse conceived the upscale discount retail model, while Douglas Dayton, then CEO of the Dayton Corporation, served as the first president of the Target store subsidiary. Early years saw the Target stores operating at a loss, but by 1965, the company reported its first gain, with sales reaching $39 million.
In 1967, the parent company, the Dayton Corporation, was renamed and went public, listing on the New York Stock Exchange. This move facilitated expansion beyond Minnesota. Later, in 1969, the Dayton Company merged with the J.L. Hudson Company to form the Dayton-Hudson Corporation, becoming the 14th largest retailer in the United States. This merger broadened the ownership base further.
The initial ownership structure of Target Corporation was significantly influenced by the Dayton family, who maintained a crucial role in shaping the company's vision and strategy for several decades. While the precise equity splits for the founders aren't publicly detailed, the Dayton family's influence was paramount. The company's transformation from a private entity to a publicly traded corporation in 1967 marked a significant shift in its ownership structure, broadening its base to include public shareholders. For a deeper dive into the company’s past, check out this Brief History of Target.
- George Dayton, as the founder, held a significant ownership stake, shaping the company's initial establishment and development.
- John F. Geisse and Douglas Dayton co-founded the original Target retail store in 1962.
- The 1967 IPO allowed the company to expand beyond Minnesota.
- The Dayton family played a crucial role in the company's vision and strategy for decades.
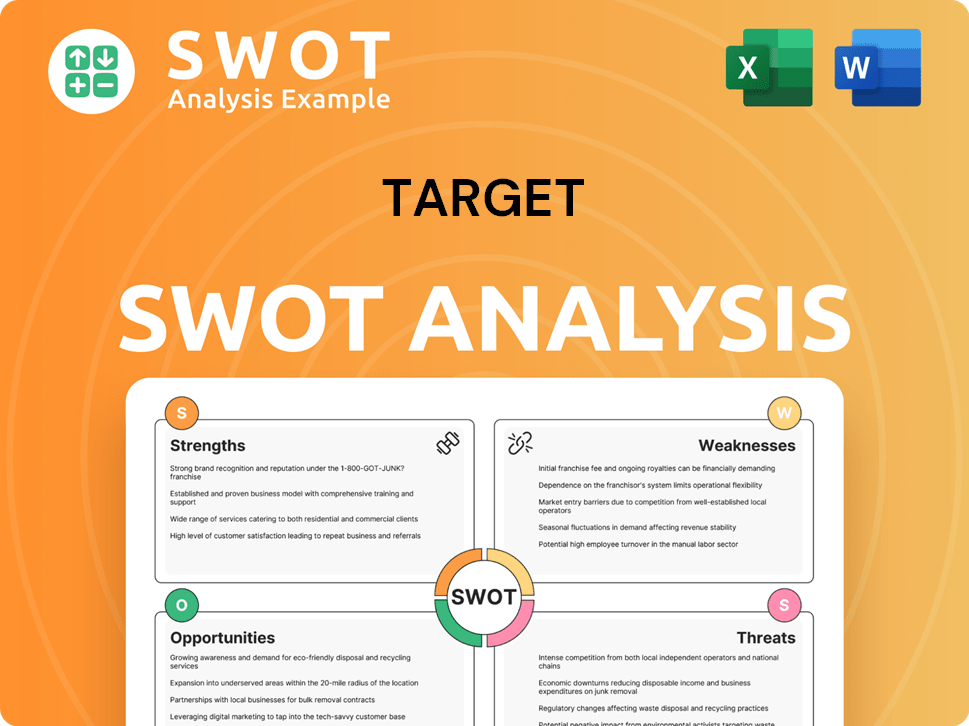
Target SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Target’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Target Corporation's ownership reflects its growth from a family-founded business to a publicly traded retail giant. Initially established as Goodfellow Dry Goods in 1902 by George Dayton, the company's trajectory shifted significantly with the opening of the first Target store in 1962. The parent company, then known as the Dayton Corporation, went public in 1967, marking the beginning of a transition towards broader ownership. This initial public offering (IPO) on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) was a crucial step in shaping its future ownership structure.
Further changes occurred in 1969 when the Dayton Company merged with the J.L. Hudson Company, forming the Dayton-Hudson Corporation, which managed multiple department store chains. By 1975, Target had become the primary revenue generator for Dayton-Hudson. The growing importance of the Target brand led to the official renaming of the company to Target Corporation in January 2000, solidifying its identity and focus. These strategic moves have significantly impacted the company's ownership, paving the way for institutional investors to become the dominant shareholders.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Goodfellow Dry Goods founded | 1902 | Family-controlled |
| First Target store opens | 1962 | Expansion of the business |
| Dayton Corporation IPO | 1967 | Publicly traded, wider ownership |
| Dayton-Hudson Corporation formed | 1969 | Diversification of holdings |
| Target Corporation renamed | 2000 | Focus on the Target brand |
Today, Target's ownership is largely dominated by institutional investors. As of May 2025, these investors collectively hold approximately 82% to 84.38% of the outstanding shares. Key institutional shareholders include The Vanguard Group, holding 44,836,356 shares as of March 31, 2025, State Street Corp with 35,207,075 shares, and BlackRock, Inc. with 35,043,629 shares as of March 31, 2025. Individual shareholders, including Target executives like CEO Brian C. Cornell and COO John J. Mulligan, own around 1% of the shares. The remaining shares are held by retail investors. The institutional holdings remained relatively unchanged at 83.72% in May 2025, reflecting stability in the company's ownership structure.
Target Corporation is a publicly traded company, primarily owned by institutional investors.
- The Vanguard Group, State Street Corp, and BlackRock, Inc. are major shareholders.
- Individual shareholders and retail investors hold a smaller percentage.
- The company's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its founding.
- Understanding Target's ownership is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
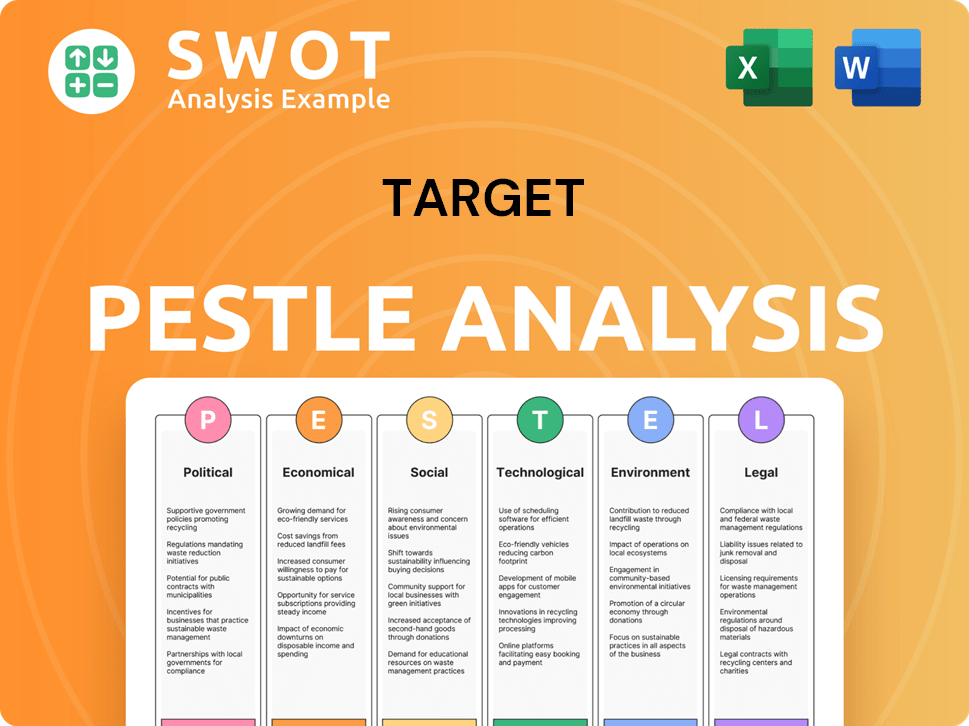
Target PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Target’s Board?
The current board of directors at Target Corporation oversees the company's governance, utilizing a voting structure that emphasizes proportional rights. At the Annual Meeting of Shareholders held on June 11, 2025, all 12 nominees were elected to the board for a one-year term. While specific details on which board members directly represent major shareholders or founders are not publicly itemized, the board includes both independent directors and those with executive roles within the company. Brian C. Cornell serves as both the chairman and CEO, a position he has held since 2014.
The board's composition reflects a commitment to diverse expertise and perspectives, essential for guiding a major retail corporation. The board is responsible for major decisions, including the oversight of the company's strategic direction, risk management, and executive compensation. Understanding the board of directors is key to understanding Target ownership and how decisions are made at the highest level within Target Corporation.
| Board Member | Title | Key Role |
|---|---|---|
| Brian C. Cornell | Chairman and CEO | Leads the board and oversees overall company strategy. |
| Independent Directors | Various | Provide independent oversight and expertise. |
| Executive Directors | Various | Bring operational expertise and insights. |
The voting structure for Target Corporation's common stock is based on a one-share-one-vote principle. Each share of common stock is entitled to one vote on all matters, including the election of directors. The company does not have dual-class shares or other arrangements that would grant outsized control to specific individuals or entities through special voting rights, golden shares, or founder shares. There is no cumulative voting for the election of directors. Shareholders owning 10% or more of Target's outstanding stock have the right to call a special meeting of shareholders. Additionally, a shareholder or group of up to 20 shareholders owning 3% or more of Target common stock continuously for at least three years may nominate and include director nominees in the company's proxy materials, up to the greater of 20% of the Board or at least two directors. If you want to learn more about the company's market, you can read about the Target Market of Target.
The board of directors is crucial for overseeing the company's strategy and operations.
- The voting structure is one share, one vote, ensuring equitable voting rights for all Target shareholders.
- Major shareholders have the power to call special meetings and nominate directors.
- The board includes a mix of independent and executive directors, providing diverse perspectives.
- Who owns Target is a key question, and understanding the board is essential to answering it.
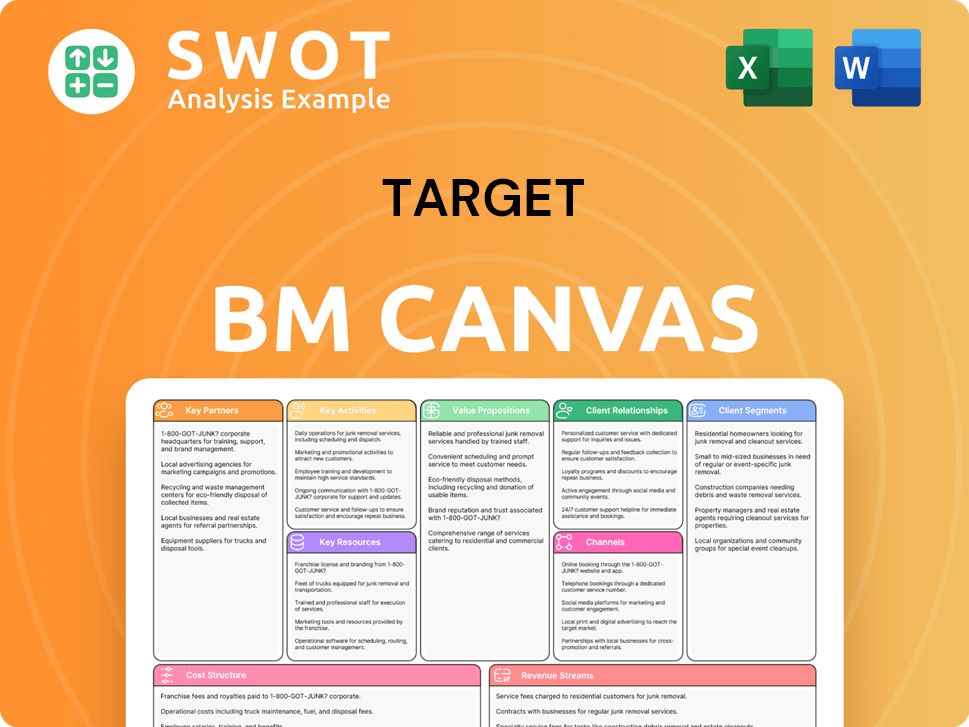
Target Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Target’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of Target Corporation has remained largely consistent, with institutional investors holding a significant majority. As of May 2025, institutional investors control approximately 83.72% of Target's outstanding shares. This indicates a stable and concentrated institutional ownership, with major players like Vanguard Group Inc., State Street Corp, and BlackRock, Inc. continuing to be the largest institutional shareholders. This ownership structure reflects the company's established position in the retail market and its appeal to large-scale investors seeking stable returns.
Target has consistently returned capital to shareholders through share buybacks. In the first quarter of fiscal year 2025, the company repurchased 2.2 million shares, valued at $251 million. At the end of Q4 2024, around $8.7 billion remained under its existing share repurchase program, initially authorized in August 2021. The company's buyback yield is 3.1% for the last twelve months, with a peak of 7.0% in January 2022. These actions highlight Target's commitment to enhancing shareholder value through direct financial returns.
| Ownership Category | Percentage (May 2025) | Key Shareholders |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Approximately 83.72% | Vanguard Group Inc., State Street Corp, BlackRock, Inc. |
| Insider Holdings | Approximately 0.15% | Brian C. Cornell |
| Public/Other | Remaining Percentage | Various individual and smaller institutional investors |
The current CEO of Target, Brian C. Cornell, has been in his role since 2014, ensuring leadership continuity. The company's focus on strategic initiatives, including enhancing customer experience and strengthening digital capabilities, is crucial for adapting to the evolving retail landscape. Furthermore, Target continues to invest in AI technology and plans to open around 20 new stores in 2025, demonstrating its commitment to both physical and digital growth. Understanding the Growth Strategy of Target helps to grasp how the company navigates market dynamics.
Target repurchased 2.2 million shares in Q1 2025, totaling $251 million. The company has approximately $8.7 billion remaining under its existing share repurchase program.
Brian C. Cornell has been the Chairman and CEO since 2014, ensuring continuity in leadership. Insider holdings are relatively stable, with a slight decrease to 0.15% in May 2025.
Target announced a 1.8% increase in its quarterly dividend. This marks its 54th consecutive year of annual dividend growth.
Target is focused on improving customer experience and strengthening digital capabilities. The company is integrating physical stores and digital channels.
Target Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Target Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Target Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Target Company?
- How Does Target Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Target Company?
- What is Brief History of Target Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Target Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.