Vector Bundle
Who Really Controls Vector Company?
Uncover the secrets behind Vector Company's ownership and its impact on New Zealand's critical infrastructure. Understanding the Vector SWOT Analysis is key to grasping the company's strategic direction. This deep dive explores the company's evolution, from its inception to its current market position, revealing the key players shaping its future.

Knowing 'Who owns Vector Company' is essential for anyone invested in New Zealand's energy and telecommunications sectors. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Vector Company ownership, examining its history and the influence of its major shareholders. We'll explore the company's management structure, its legal structure, and how these elements affect its operational decisions. Whether you're an investor or a business strategist, this information is crucial for making informed decisions about Vector Company.
Who Founded Vector?
The story of Vector Company's ownership begins in the early 1990s with the restructuring of New Zealand's electricity sector. Unlike typical startups, Vector didn't have individual founders in the traditional sense. Its roots are in the Auckland Electric Power Board, which set the stage for its commercial existence.
In 1993, the Auckland Electric Power Board was corporatized and rebranded as Vector Limited. This marked a significant shift in how the company was structured and operated. The initial ownership was mainly held by the Auckland Energy Consumer Trust (AECT), now known as Entrust.
Entrust was created to hold shares in Vector on behalf of electricity consumers in Auckland, Manukau, and parts of Papakura and Franklin. This setup ensured that the benefits of the electricity network mainly went back to the consumers within its service area. This unique model is a key part of understanding Vector Company's history.
At the start, Entrust owned 100% of Vector. This reflected a public utility model where consumers indirectly owned the infrastructure through the trust. There were no individual equity splits among 'founders' as the company emerged from a public utility rather than a private venture.
Early agreements focused on Entrust's mandate to manage assets for the long-term benefit of beneficiaries. These included mechanisms for dividend distribution to consumers, which was a key aspect of the company's operations.
This foundational ownership structure significantly shaped Vector's early strategic direction. The focus was on network reliability, community service, and stable returns for its beneficiaries rather than maximizing shareholder value for private individuals.
The initial structure of Vector, with Entrust as the primary shareholder, established a unique model of ownership. This model prioritized the interests of electricity consumers in the Auckland region. This approach has influenced Vector's operational and strategic decisions from its inception. Understanding the historical context is essential for grasping the current Vector Company ownership structure.
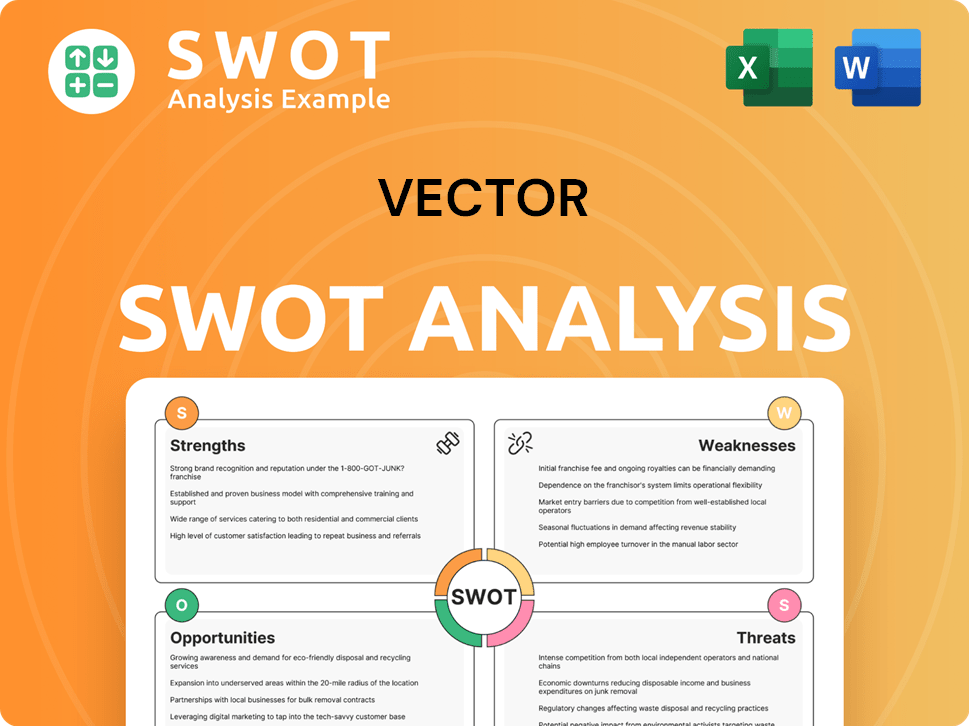
Vector SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Vector’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Vector Company has seen significant changes since its corporatization. A key event was the Initial Public Offering (IPO) in 1998, which introduced public shareholders to the company. This move, which allowed a portion of Vector's shares to be traded publicly on the New Zealand Exchange (NZX), was a pivotal moment in its ownership evolution. The IPO diversified ownership beyond the Auckland Energy Consumer Trust (Entrust), marking a shift towards a more public structure.
As of early 2025, the ownership landscape of Vector Company is characterized by a dominant shareholder and a publicly traded minority. The Auckland Energy Consumer Trust (Entrust) is the largest shareholder, holding approximately 75.1% of the company's shares. The remaining shares are held by a diverse group of public shareholders. This structure balances Entrust's community-focused objectives with the market's demands for financial performance. Understanding Revenue Streams & Business Model of Vector provides further insight into the company's operations.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Corporatization | Early 1990s | Transition from a municipal entity to a corporate structure. |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | 1998 | Partial listing on NZX, introduction of public shareholders. |
| Ongoing | 2024-2025 | Entrust maintains majority ownership; public shares held by institutional and individual investors. |
The major shareholders in Vector Company include Entrust, holding a significant majority stake, and a variety of institutional and individual investors who hold the remaining public shares. This ownership structure influences Vector's strategic decisions, balancing long-term community interests with the need for financial growth. The company's investments in new technologies, such as smart meters and electric vehicle charging infrastructure, reflect this balance.
Vector Company's ownership structure is primarily defined by the Auckland Energy Consumer Trust's substantial shareholding and public shareholders.
- The IPO in 1998 was a significant event, introducing public ownership.
- Entrust's majority stake ensures community-focused objectives are considered.
- Public shareholders include institutional and individual investors.
- The ownership structure influences strategic decisions and investments.
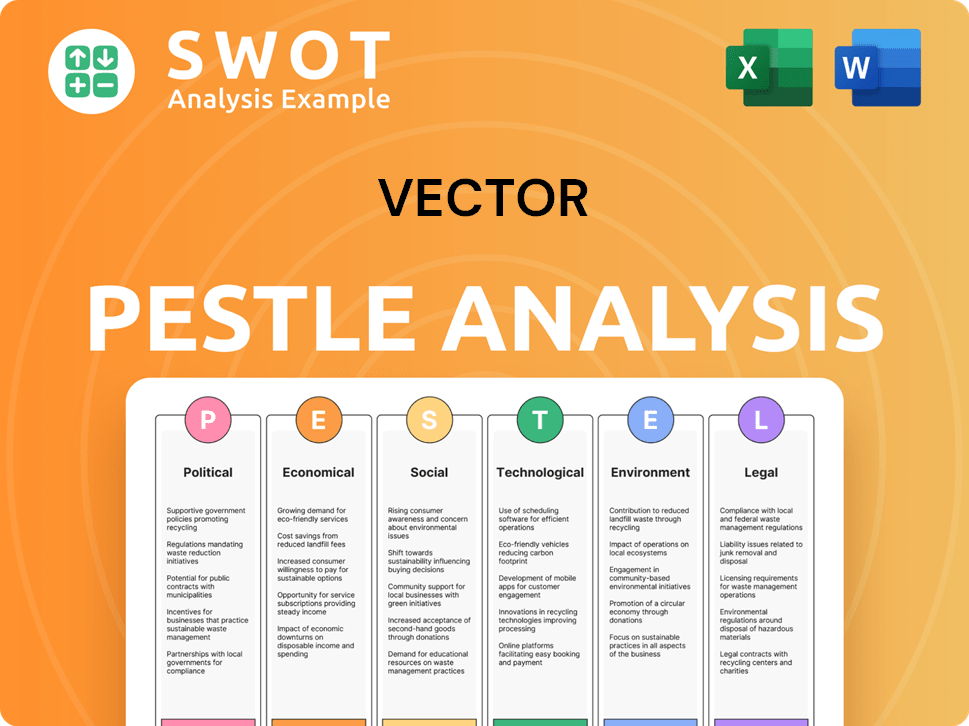
Vector PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Vector’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of Vector Limited is pivotal in representing the interests of its diverse ownership. The board typically includes directors representing major shareholders, like Entrust, and independent directors. The Chair of Entrust often holds a board position, linking the trust's strategies with the company's governance. Independent directors ensure balanced perspectives and uphold good corporate governance, providing oversight of executive management decisions. The Target Market of Vector is influenced by these strategic decisions.
The board's composition and influence are significant due to the ownership structure. The board is responsible for overseeing the company's strategic direction, including major capital expenditures, acquisitions, and dividend policies. The board's decisions are crucial for balancing long-term infrastructure investments with shareholder returns.
| Board Member | Role | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| [Name - To be updated] | Chair | Entrust |
| [Name - To be updated] | Director | Independent |
| [Name - To be updated] | Director | Independent |
Vector operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for its ordinary shares. Entrust's significant holding of approximately 75.1% gives it substantial voting control. This allows Entrust to determine the board's composition and influence key strategic decisions. There are no publicly disclosed special voting rights or golden shares, so Entrust's interests largely guide the company's direction. Recent governance activities focus on balancing infrastructure investment needs with shareholder returns, especially regarding dividend distributions.
Entrust, with approximately 75.1% ownership, has significant voting power. This impacts the composition of the board and key strategic decisions.
- The board includes directors representing major shareholders and independent directors.
- Independent directors ensure balanced perspectives and good corporate governance.
- The one-share-one-vote structure means voting power is proportional to shareholding.
- Recent governance focuses on balancing infrastructure investments and shareholder returns.
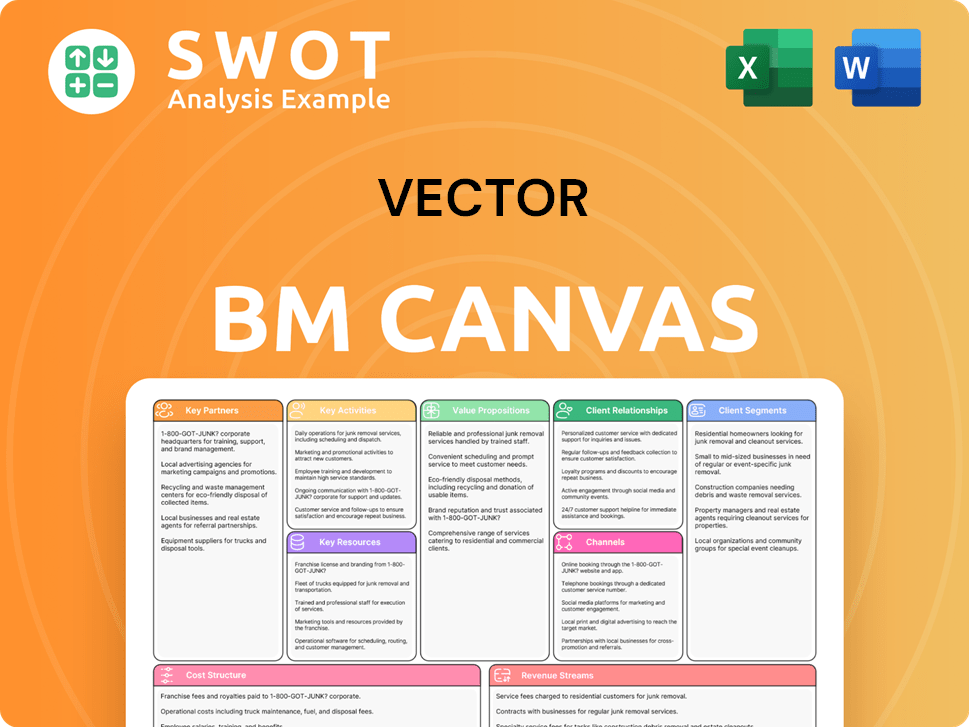
Vector Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Vector’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past three to five years (2022-2025), the ownership structure of Vector has remained relatively stable. The majority ownership continues to be held by Entrust. This stability is a key characteristic of the company's ownership profile, providing a solid foundation for its operations. While there haven't been significant changes in the controlling ownership, Vector has been active in capital management and strategic investments.
These activities, including investments in infrastructure upgrades and new energy solutions, indirectly influence the company's financial performance and its appeal to public shareholders. The company's focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors and the interest from institutional investors in stable assets also play a role. For further insights into the company's origins, you can explore the Brief History of Vector.
| Ownership Category | Approximate Percentage (2024-2025) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Entrust | 60-70% | Majority shareholder, providing stability. |
| Public Shareholders | 30-40% | Subject to market trends and investor sentiment. |
| Other Institutional Investors | Variable | May include pension funds and other long-term investors. |
Leadership changes, such as CEO appointments, are common and can influence strategic direction, but typically occur within the existing ownership framework. Public statements from Vector and analysts generally reinforce the stability of its ownership structure. This stability is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the company's focus on its core utility services and sustainable growth.
Entrust's continued majority ownership provides a stable foundation. This stability supports long-term strategic planning and investment in critical infrastructure. The stable ownership structure is a key factor in attracting and retaining investors.
Publicly traded shares are subject to broader market trends and investor sentiment. ESG factors and institutional investor interest influence Vector's performance. Capital management and strategic investments impact share trading volumes.
Leadership changes can influence the company's strategic direction. The company is focused on its core utility services and sustainable growth. Ongoing investments in infrastructure are a key priority.
Capital raising activities and dividend policies affect investor sentiment. The company's financial reports provide detailed ownership information. Share prices and annual reports offer insights into financial performance.
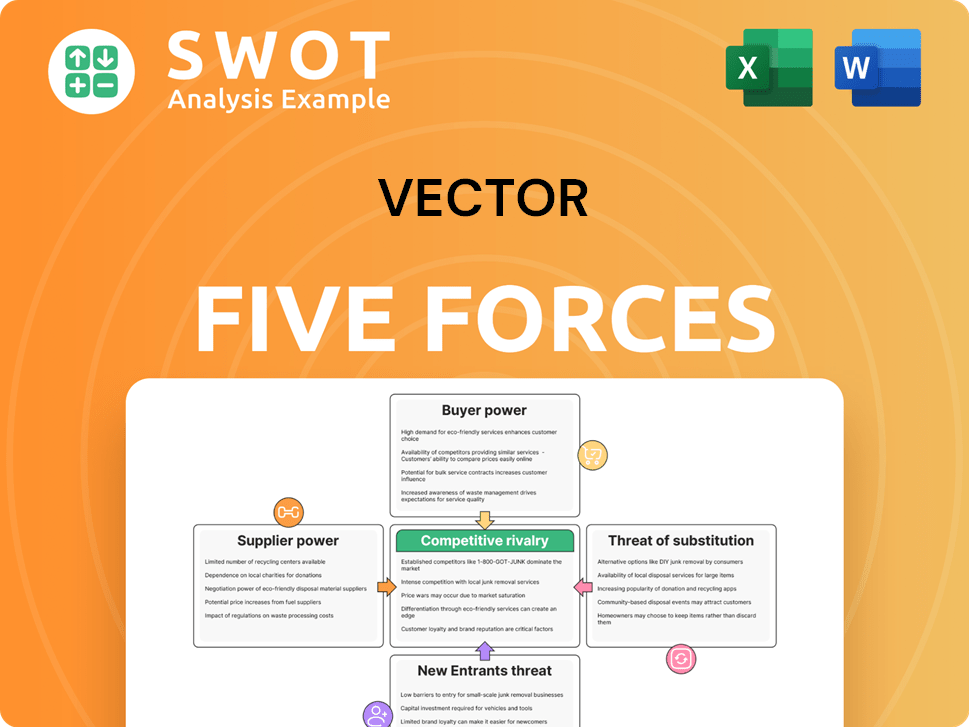
Vector Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Vector Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Vector Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Vector Company?
- How Does Vector Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Vector Company?
- What is Brief History of Vector Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Vector Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.