Aramco Bundle
How did Aramco rise to become a global energy titan?
Uncover the captivating Aramco SWOT Analysis and journey through the pivotal moments that shaped the Saudi Arabian Oil Company. From its humble beginnings in the Arabian desert to its current status as the world's largest oil producer, Aramco's story is a testament to strategic foresight and unwavering ambition. Discover how this company transformed Saudi Arabia and reshaped the global oil industry.

The Aramco history is a narrative of transformation, beginning with the discovery of oil in Dhahran in 1938, a turning point that propelled Saudi Aramco into the global spotlight. Initially a joint venture, the Aramco company evolved from an American-led exploration to a state-owned enterprise, playing a central role in the oil industry Saudi Arabia. This evolution, marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts, highlights the enduring impact of this energy giant on both the region and the world, offering a compelling case study in the history of oil.
What is the Aramco Founding Story?
The Aramco history began on May 29, 1933, with a concession agreement between the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the Standard Oil Company of California (SoCal). This agreement led to the formation of the California Arabian Standard Oil Company (CASOC), a subsidiary of SoCal, later known as Chevron. The primary aim was to explore and develop oil reserves in Saudi Arabia, driven by the growing demand for oil in the United States for both national security and industrial growth.
The initial challenge was to locate commercially viable oil reserves in the vast Saudi Arabian desert. Drilling operations commenced in 1935. The discovery of the Dammam No. 7 well, also known as 'Prosperity Well,' in 1938, marked a pivotal moment. This discovery provided the first crude oil product. Texaco joined as a partner in 1936, strengthening the venture. The early focus was on oil exploration and production due to the increasing global demand for energy.
The early exploration efforts were primarily funded by Standard Oil of California. The cultural and economic context, with the rising global demand for energy, significantly shaped the company's early focus on oil exploration and production. The Growth Strategy of Aramco highlights the company's evolution and its impact on the global oil industry.
The founding of the Saudi Arabian oil company, Aramco, was a strategic move driven by the need for oil.
- 1933: Concession agreement signed between the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and SoCal.
- 1935: Drilling operations began in Saudi Arabia.
- 1936: Texaco joined as a partner.
- 1938: Discovery of the Dammam No. 7 oil well.
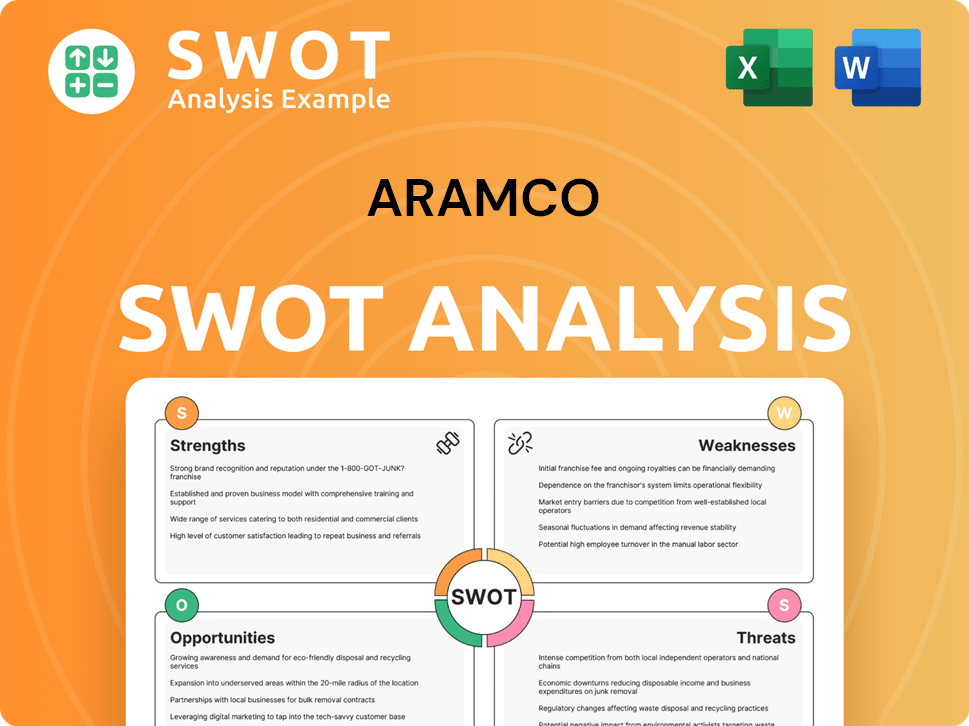
Aramco SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Aramco?
Following the discovery of commercial oil in 1938, the Arabian American Oil Company, later known as Aramco, experienced significant expansion. This period saw a rapid increase in crude oil production and a substantial expansion of its distribution capabilities. The company's growth was marked by major infrastructural developments and strategic shifts in ownership, shaping its evolution into a global energy leader. This early growth laid the foundation for the modern Saudi Arabian Oil Company, or Saudi Aramco.
Crude oil production surged, reaching 500,000 barrels per day by 1949. This rapid increase necessitated significant investments in infrastructure and logistics. The company's ability to efficiently extract and transport oil was crucial to its early success within the oil industry Saudi Arabia.
A key milestone was the completion of the Trans-Arabian Pipeline (Tapline) in 1950, spanning 1,212 kilometers. This pipeline was the longest in the world at the time, linking eastern Saudi Arabia to the Mediterranean Sea. This significantly reduced the cost and time of exporting oil to Europe, boosting Aramco's global presence.
In 1951, Aramco discovered the Safaniyah field, which became the world's largest offshore oil field. By 1958, crude oil production surpassed 1 million barrels in a calendar year. These discoveries were pivotal in establishing Aramco's dominance in the history of oil.
The company moved its headquarters from New York to Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, in 1952, while maintaining a New York office. In 1961, Aramco began processing liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). The Marketing Strategy of Aramco played a crucial role in its early growth.
The Saudi government started acquiring stakes in the 1970s. By 1973, the government held a 25% interest, increasing to 60% in 1974. By 1980, the Saudi government achieved 100% ownership. This transition marked a shift from a foreign-owned consortium to a fully state-owned entity, setting the stage for its transformation into an integrated petroleum enterprise.
In 1988, the company was officially renamed the Saudi Arabian Oil Company, or Saudi Aramco. This change reflected its status as the kingdom's national oil company. This renaming solidified its role in the oil industry Saudi Arabia and its impact on Saudi Arabia's economy.
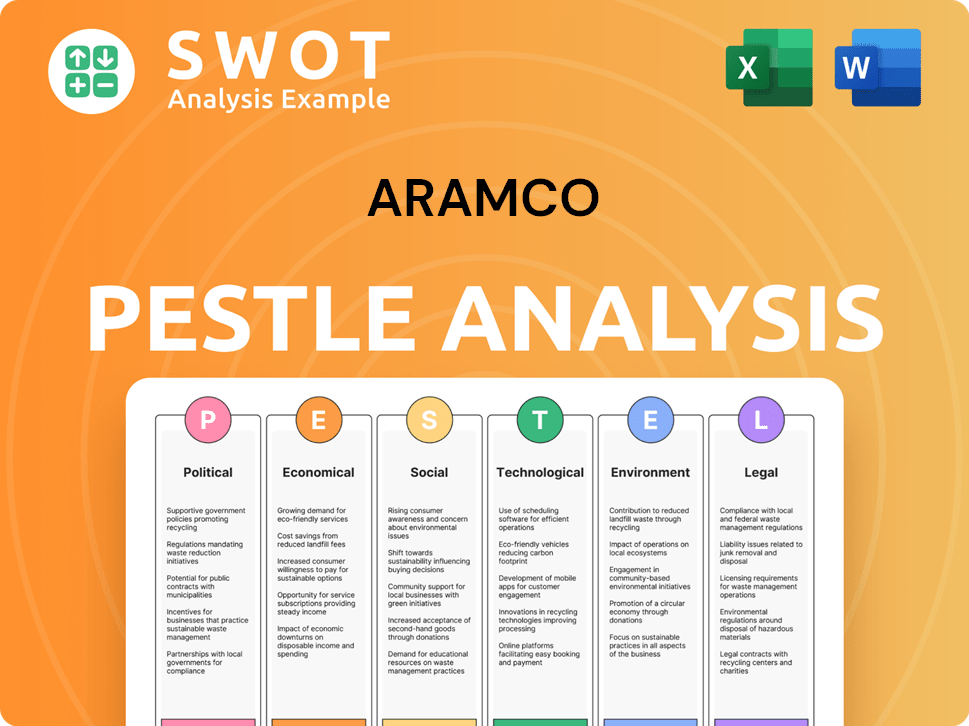
Aramco PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Aramco history?
The Aramco company has a rich history marked by significant milestones that have shaped the oil industry in Saudi Arabia and globally. From its early exploration days to its current status as a leading energy provider, Aramco's history is filled with pivotal moments that have defined its trajectory.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1975 | Launched the Master Gas System, a major gas project. |
| 1989 | Established Star Enterprise with Texaco in the U.S. for refining and marketing. |
| 1992 | Acquired a 35% stake in SsangYong Oil Refining Company (now S-Oil Corporation) in Korea. |
| 1994 | Acquired a 40% stake in Petron, a refiner in the Philippines. |
| 1996 | Acquired a 50% stake in Motor Oil (Hellas) Corinth Refineries and Avinoil. |
| 2000 | Established Aramco Gulf Operations, managing Saudi Arabian petroleum interests in the Offshore Neutral Zone. |
| 2003 | Completed the Haradh Gas Plant. |
| 2019 | Completed the world's largest initial public offering (IPO). |
| 2025 | Commissioned a breakthrough renewable energy storage system for gas operations in May 2025. |
Saudi Aramco has consistently pushed the boundaries of the oil industry through technological advancements and strategic initiatives. The company's commitment to innovation is evident in its investments in sustainable energy solutions and its efforts to reduce its carbon footprint, as detailed in Revenue Streams & Business Model of Aramco.
The Master Gas System was a major innovation, capturing and utilizing natural gas that was previously flared, improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Strategic joint ventures, such as Star Enterprise, expanded Aramco's global reach and market presence, enhancing its refining and marketing capabilities.
The IPO in 2019 was a groundbreaking moment, raising over $25 billion and valuing the company at $1.7 trillion, attracting foreign capital and supporting Saudi Arabia's economic transformation.
The commissioning of a renewable energy storage system for gas operations in May 2025 demonstrates Aramco's commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
Investments in research and development for sustainable alternatives to oil, such as lithium production, and partnerships with carbon capture initiatives, showcase Aramco's focus on environmental responsibility.
Acquisitions, like the 25% stake in Unioil Petroleum and the 50% stake in Blue Hydrogen Industrial Gases Company in Q1 2025, signify strategic expansion in downstream value chains and low-carbon energy.
Despite its achievements, Aramco's journey has not been without its challenges. The company faces ongoing issues related to market volatility and the transition to sustainable energy sources, requiring strategic adjustments to maintain its position in the oil industry.
In Q1 2025, the company reported a net profit of $26.01 billion, a 4.6% decrease from Q1 2024, primarily due to lower oil prices and higher operating costs.
Aramco has strategically adjusted its dividend policy, forecasting a total dividend of $85.4 billion in 2025, a nearly 30% drop from the $124.25 billion paid in 2024, reflecting a shift towards balancing shareholder payouts with rising capital investments.
The company is actively addressing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) concerns, investing heavily in research and development for sustainable alternatives to oil, and partnering with carbon capture initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint.
The need to balance shareholder payouts with significant capital investments in natural gas expansion and infrastructure presents a financial challenge.
Geopolitical instability and international relations can impact oil prices and Aramco's operations, adding complexity to its strategic planning.
The global shift towards renewable energy sources poses a long-term challenge, requiring Aramco to diversify its portfolio and invest in sustainable alternatives.
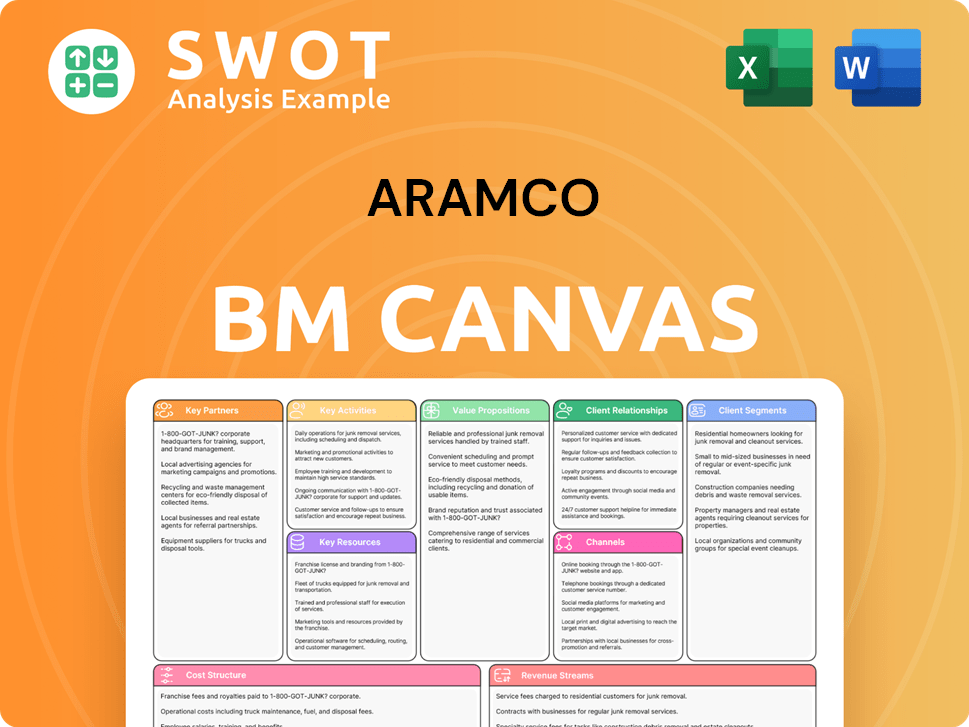
Aramco Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Aramco?
The Owners & Shareholders of Aramco have witnessed a remarkable journey marked by pivotal moments in the global oil industry. The evolution of the Saudi Arabian Oil Company, or Aramco, from its inception to its current status as a global energy giant is a story of strategic partnerships, technological innovation, and significant economic impact. This history showcases the company's adaptation to changing market dynamics and its forward-looking strategies.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1933 | The concession agreement was signed between Saudi Arabia and Standard Oil Company of California (SoCal), leading to the formation of California Arabian Standard Oil Company (CASOC). |
| 1938 | The first commercial oil field was discovered at Dammam No. 7. |
| 1944 | CASOC was renamed Arabian American Oil Company (Aramco). |
| 1949 | Crude oil production reached 500,000 barrels per day. |
| 1950 | Completion of the Trans-Arabian Pipeline (Tapline) occurred. |
| 1951 | The Safaniyah field, the world's largest offshore oil field, was discovered. |
| 1973 | The Saudi government acquired a 25% stake in Aramco. |
| 1975 | The Master Gas System was launched. |
| 1980 | The Saudi government achieved 100% ownership of Aramco. |
| 1988 | The company was officially renamed Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco). |
| 2019 | Aramco launched its Initial Public Offering (IPO). |
| 2024 | Net income reached $106.2 billion. |
| Q1 2025 | Net income of $26.01 billion was reported. |
| May 2025 | Aramco announced the commissioning of a breakthrough renewable energy storage system for gas operations. |
Aramco aims to increase its gas output by 60% by 2030 compared to 2021 levels. This strategic move is part of its broader plan to diversify its energy portfolio and meet rising global demand for natural gas.
The company plans to invest between $52 billion and $58 billion in capital expenditures in 2025. A significant portion of this investment will be directed towards expanding natural gas opportunities.
Aramco targets producing 2.5 million tonnes of blue ammonia annually by 2030. This initiative leverages its gas reserves and carbon capture and storage infrastructure, positioning it as a leading clean energy exporter.
Aramco is making significant investments in lithium production. This move aligns with the global shift towards sustainable energy and aims to meet the surging demand for lithium, a key component in batteries.
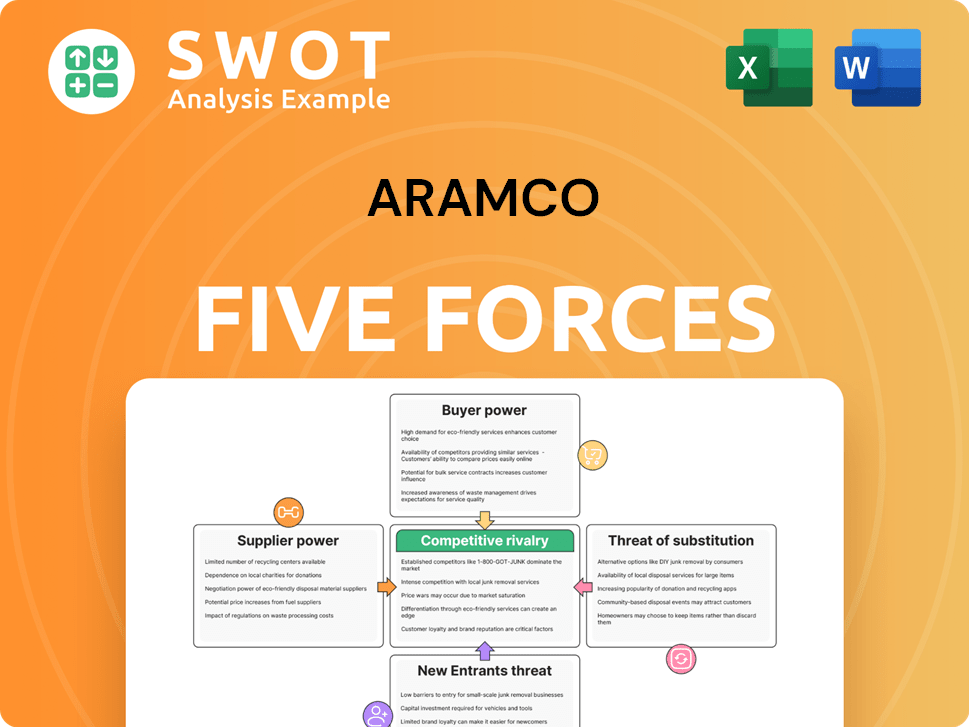
Aramco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Aramco Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Aramco Company?
- How Does Aramco Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Aramco Company?
- What is Brief History of Aramco Company?
- Who Owns Aramco Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Aramco Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.