Casey's General Stores Bundle
How Did Casey's General Stores Become a Convenience Store Giant?
From a single store in 1968, Casey's General Stores has transformed into a powerhouse in the convenience store industry. This journey showcases how a focus on small towns and communities fueled remarkable growth. Offering a unique blend of fuel, groceries, and freshly prepared foods, especially its famous pizza, has set Casey's apart.

Today, with over 2,600 Casey's General Stores SWOT Analysis locations across 17 states, primarily in the Midwest and South, Casey's stands as the third-largest convenience store chain. Understanding the brief history of Casey's General Stores reveals the strategic decisions that propelled its expansion from a regional enterprise to a major national presence, including its early years and the evolution of its business model. The company's consistent performance, even during economic downturns, highlights its resilience and understanding of its customer base, making it a compelling case study in retail success, including its impact on communities.
What is the Casey's General Stores Founding Story?
The story of Casey's General Stores began on August 14, 1968, in Boone, Iowa. Founded by Donald Lamberti, the company aimed to fill a gap in the market by bringing modern convenience to smaller communities. This marked the start of what would become a significant player in the convenience store industry.
Lamberti, drawing on his experience as an Area Supervisor for a major oil company, saw an opportunity to create a one-stop shop. His vision included offering essential goods, gasoline, and prepared foods to rural populations. This approach contrasted with the prevailing retail trends of the late 1960s.
The initial focus of Casey's company was on providing convenience and value in areas lacking larger supermarkets or gas stations. The first store in Boone, Iowa, was quickly followed by a second in Ames. Lamberti's background in the oil industry was crucial in establishing the gasoline component of the convenience stores. The name 'Casey's General Stores' came from Lamberti's initials, 'C.A.S.', reflecting the company's commitment to 'Convenience and Service.' The early funding came from bootstrapping and personal connections, a pragmatic approach that allowed the business to take root.
The founding of Casey's General Stores was driven by recognizing an unmet need in smaller communities and leveraging industry experience to create a successful business model. The company's initial focus on convenience and value, combined with a strategic approach to expansion, set the stage for its future growth.
- Casey's General Stores was founded on August 14, 1968, by Donald Lamberti.
- The initial business model targeted underserved, smaller communities.
- The first store was in Boone, Iowa, with a second in Ames.
- Lamberti's experience in the oil industry was key to fuel distribution.
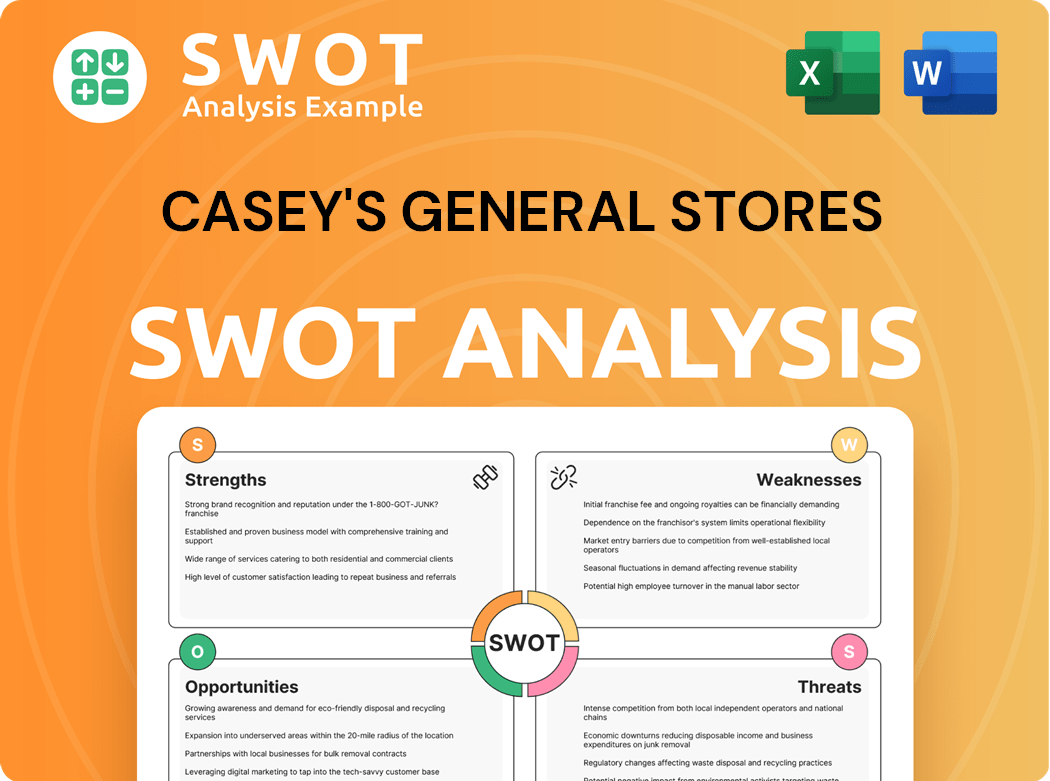
Casey's General Stores SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Casey's General Stores?
The early growth of Casey's General Stores was marked by careful expansion and strategic decisions. Following its initial establishment in Iowa, the company focused on expanding its presence across the Midwest. This strategic approach, coupled with innovative offerings, laid the foundation for its future success. The
Casey's history
is one of consistent growth and adaptation.The company's early expansion focused on small towns and rural communities, aligning with its business model. Early offerings included staple groceries, prepared foods, and gasoline. The integration of prepared foods, like donuts and sandwiches, quickly became a key differentiator for
Casey's company
.By 1977,
Casey's locations
had expanded to 118 stores. The introduction of pizza in 1980 significantly boosted its appeal and revenue. This strategic move helped solidify its position in the market and contributed to its sustained growth. TheCasey's gas stations
and stores became community hubs.The 1980s and 1990s saw accelerated expansion through organic growth and acquisitions. The company went public in 1983, fueling further expansion. New states, including Illinois, Missouri, and Kansas, were entered during this period. Strategic shifts included a continuous emphasis on prepared foods and operational efficiencies.
By 2000,
Casey's pizza
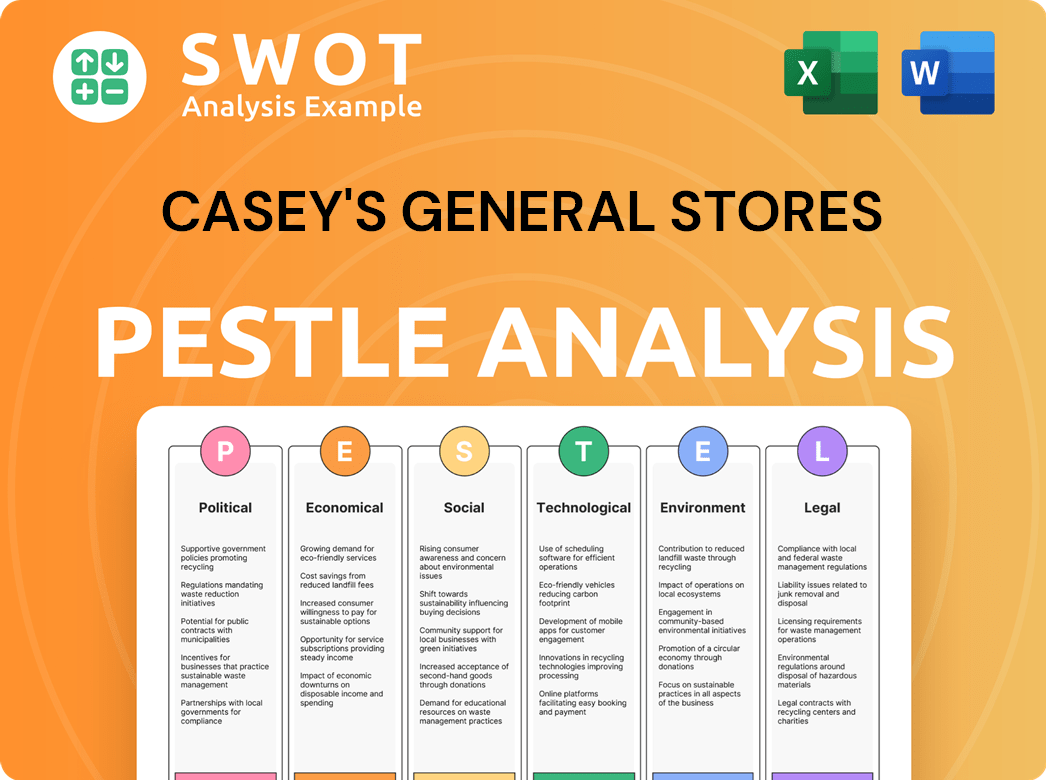
had over 1,200 stores, establishing it as a major regional player. The company filled a retail void in many small towns, often becoming a community hub. The focus on prepared foods and operational efficiency was crucial. As of fiscal year 2024, Casey's reported revenues of approximately $16.3 billion, highlighting its robust financial performance.Casey's General Stores PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Casey's General Stores history?
Throughout its history, Casey's General Stores has achieved numerous milestones, demonstrating its growth and adaptability within the convenience store industry. These achievements reflect the company's commitment to innovation and its ability to meet evolving consumer needs, solidifying its position in the market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1959 | Founder, Don Lamberti, opens the first store in Des Moines, Iowa, laying the foundation for the future of Casey's. |
| 1984 | Casey's introduces made-from-scratch pizza, transforming its business model and establishing itself as a food destination. |
| 1990s | The company expands rapidly, increasing its store count and solidifying its presence in the Midwest. |
| 2000s | Casey's continues its expansion, including strategic acquisitions and the integration of advanced technologies. |
| 2017 | Casey's launches its mobile app, enhancing customer experience and streamlining operations. |
| 2024 | Casey's Rewards loyalty program reaches over 8 million members, driving customer engagement and repeat business. |
Casey's has consistently embraced innovation to stay ahead in the competitive convenience store market. A key innovation was the introduction of made-from-scratch pizza, which set it apart from competitors and attracted customers seeking fresh food options. The company also pioneered the use of technology, including point-of-sale systems and loyalty programs, to improve operational efficiency and enhance customer service.
Introduced in 1984, this transformed Casey's into a food destination, differentiating it from traditional convenience stores. This move significantly boosted sales and customer traffic, establishing a strong brand identity.
Casey's was an early adopter of point-of-sale systems and loyalty programs, improving operational efficiency and customer experience. This technological advancement helped streamline transactions and gather valuable customer data.
Launched in 2017, the mobile app enhanced customer experience and streamlined operations. The app provided convenient ordering, payment options, and loyalty program integration.
The loyalty program, Casey's Rewards, has grown to over 8 million members as of early 2024, driving significant engagement and repeat business. This program fosters customer loyalty and provides valuable data for targeted marketing.
Partnerships with fuel suppliers have been critical to operational success, ensuring a reliable supply chain. These collaborations help maintain competitive pricing and consistent product availability.
Casey's continuously refines its prepared food offerings, including donuts and subs, to meet changing consumer preferences. This focus on fresh, high-quality food keeps customers returning.
Throughout its history, Casey's has faced various challenges, including economic downturns and increased competition. The 2008 financial crisis presented significant headwinds, but the company's resilient business model helped it weather the storm. More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic presented unique operational challenges, but Casey's adapted by enhancing its digital ordering capabilities and reinforcing its commitment to community service.
Casey's has consistently managed the impact of fluctuating fuel prices, which can affect profitability. The company employs strategies to mitigate these risks, such as hedging and competitive pricing.
Increased competition from larger retail chains has required Casey's to continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings. The focus on prepared foods and customer service helps maintain a competitive edge.
Economic downturns, such as the 2008 financial crisis, have presented challenges, but Casey's resilient business model and focus on essential goods helped it weather the storm. The company's ability to adapt has been crucial.
The COVID-19 pandemic presented unique operational challenges, but Casey's adapted by enhancing its digital ordering capabilities and reinforcing its commitment to community service. This adaptation demonstrated the company's flexibility.
Supply chain disruptions, particularly during the pandemic, required Casey's to manage inventory and ensure product availability. Strong supplier relationships and efficient logistics were key.
Changing consumer behaviors and preferences require Casey's to continuously adapt its offerings and services. The company's focus on innovation and customer experience helps it stay relevant.
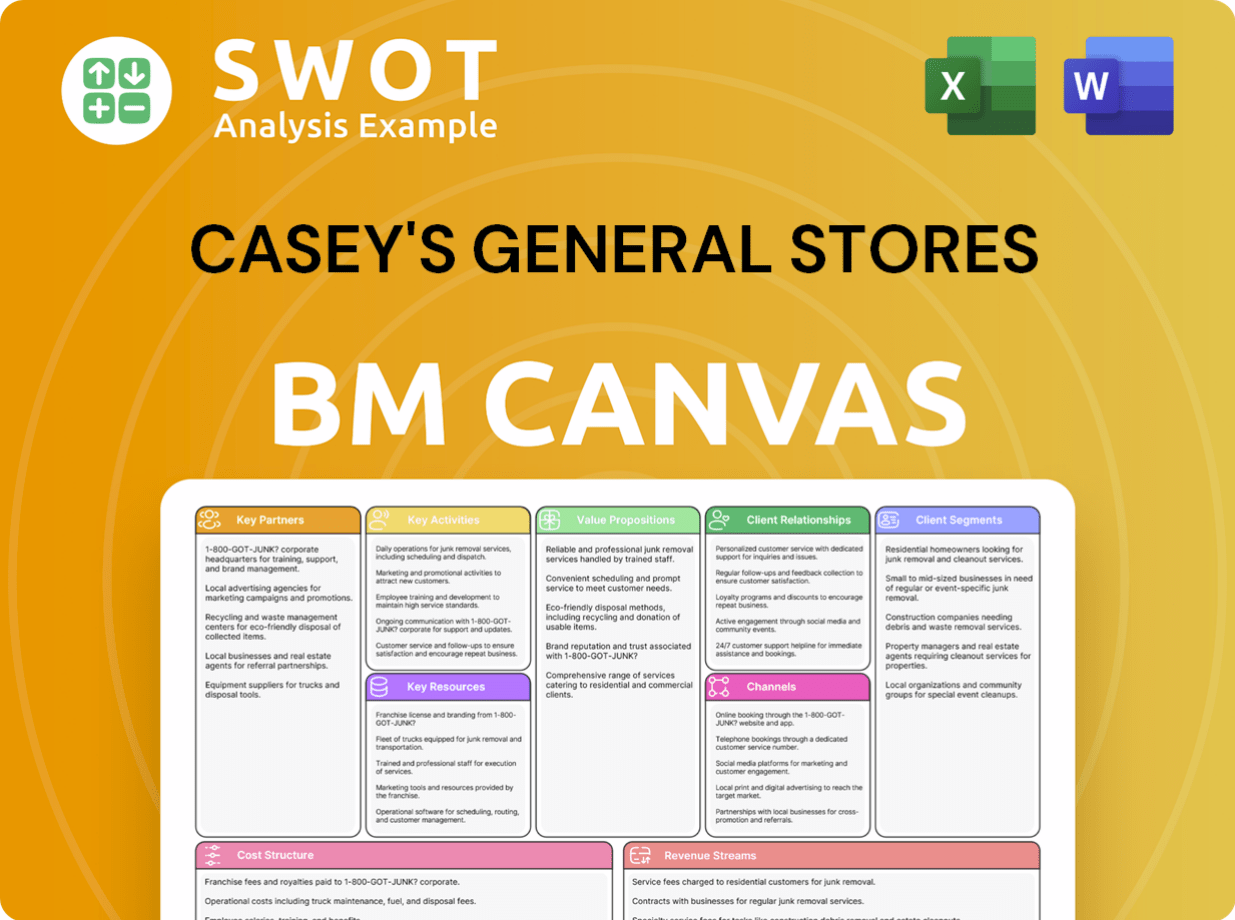
Casey's General Stores Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Casey's General Stores?
The brief history of Casey's General Stores is a story of consistent growth and strategic adaptation. From its humble beginnings in 1968, the company has evolved significantly, marked by key milestones such as going public in 1983 and the introduction of its famous pizza in 1980. The company has expanded its reach and services, particularly with the launch of its mobile app in 2017 and the Casey's Rewards program in 2019. Acquisitions, like the 2021 purchase of Buchanan Energy, have also played a role in the expansion of Casey's locations. By 2023, Casey's had exceeded 2,600 stores across 17 states, and in early 2024, the company reported strong financial results.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1968 | Donald Lamberti opens the first Casey's General Store in Boone, Iowa. |
| 1980 | Casey's begins selling its popular made-from-scratch pizza. |
| 1983 | Casey's General Stores goes public, listing on NASDAQ. |
| 2000 | The company operates over 1,200 stores. |
| 2010 | Casey's fends off a hostile takeover bid, reaffirming its independent growth strategy. |
| 2017 | Launches its mobile app, enhancing digital ordering and customer convenience. |
| 2019 | Introduces the Casey's Rewards loyalty program, rapidly accumulating millions of members. |
| 2021 | Acquires Buchanan Energy, adding 94 stores and expanding its footprint. |
| 2023 | Exceeds 2,600 store locations across 17 states. |
| 2024 | Casey's reports strong financial results, with net income increasing 15% to $145.7 million in the third quarter of fiscal year 2024. |
Casey's is focused on continued strategic growth, aiming to reach 3,000 stores by 2026. This expansion will involve organic growth and targeted acquisitions, particularly in its core Midwestern and Southern markets. The company will continue to seek opportunities to increase its number of Casey's locations.
The company plans to enhance its prepared food offerings, leveraging its strong brand recognition in pizza and other fresh items. Casey's will focus on expanding its menu and improving the quality of its food products to attract more customers. This is a key part of Casey's business model.
Digital transformation remains a key initiative, with continued investment in its mobile app, online ordering, and loyalty program. These efforts are designed to drive customer engagement and operational efficiency. Casey's is committed to staying ahead of digital trends.
Casey's aims to optimize its fuel sales and continue to be a community hub, aligning with the growing trend of convenience stores evolving into essential local service providers. The company recognizes the importance of community involvement. Casey's gas stations remain a vital part of the business.
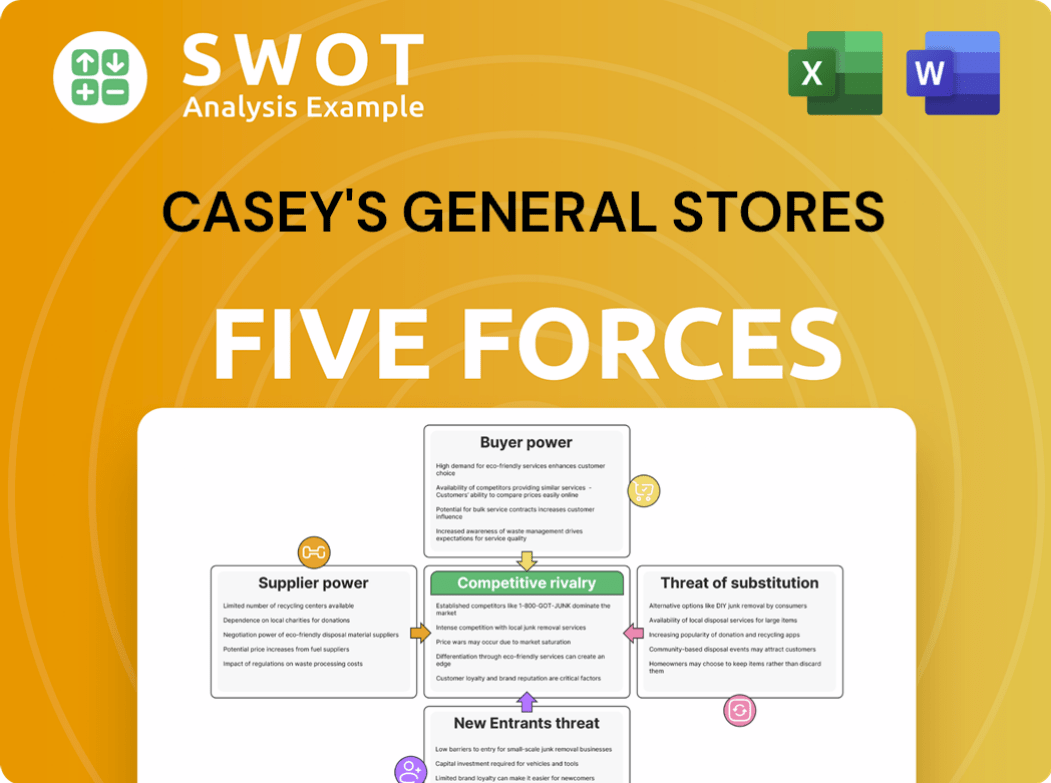
Casey's General Stores Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Casey's General Stores Company?
- How Does Casey's General Stores Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Brief History of Casey's General Stores Company?
- Who Owns Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Casey's General Stores Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.