Casey's General Stores Bundle
Who Really Owns Casey's General Stores?
Ever wondered who steers the ship at one of America's largest convenience store chains? Understanding Casey's General Stores SWOT Analysis ownership is crucial for grasping its strategic moves and future potential. From its humble beginnings to its current market dominance, Casey's story is a fascinating study in corporate evolution. Knowing who owns Casey's unlocks insights into its governance, financial performance, and long-term vision.

Delving into Casey's ownership reveals a journey from a family-founded business to a publicly traded entity, significantly impacting its operational strategies. The evolution of Casey's ownership, from the founders to the current major shareholders, provides a clear picture of its growth and adaptation. This exploration of Casey's parent company and its stakeholders helps investors and analysts understand the forces shaping its future, including its stock performance and strategic decisions. Knowing who owns Casey's is key to understanding its place in the competitive landscape, including its market share and how it stacks up against its competitors.
Who Founded Casey's General Stores?
The foundation of Casey's General Stores was laid in 1968 by Don Lamberti. He transformed an old service station into the first convenience store in Boone, Iowa. This marked the beginning of a company that would grow to serve numerous communities.
While the exact details of the initial equity distribution are not publicly available, Lamberti's role as the founder suggests his primary ownership in the early stages. His vision set the stage for the company's focus on small towns, a core element of its business model.
The early ownership structure likely involved Lamberti and a small group of initial investors. These investors might have included family members or close associates, a common pattern for new businesses. As the company expanded, it would have used reinvested earnings and potentially local bank financing to support its growth.
The early ownership of Casey's General Stores was primarily held by its founder, Don Lamberti. The company's expansion was fueled by reinvested earnings and local financing. There is no information about significant early ownership disputes, indicating a stable founding period under Lamberti's leadership.
- Casey's ownership was concentrated with Don Lamberti in the initial phases.
- The company's expansion relied on reinvested profits and local financing.
- The early years were marked by a stable leadership period.
- The focus was on providing essential services to underserved rural communities.
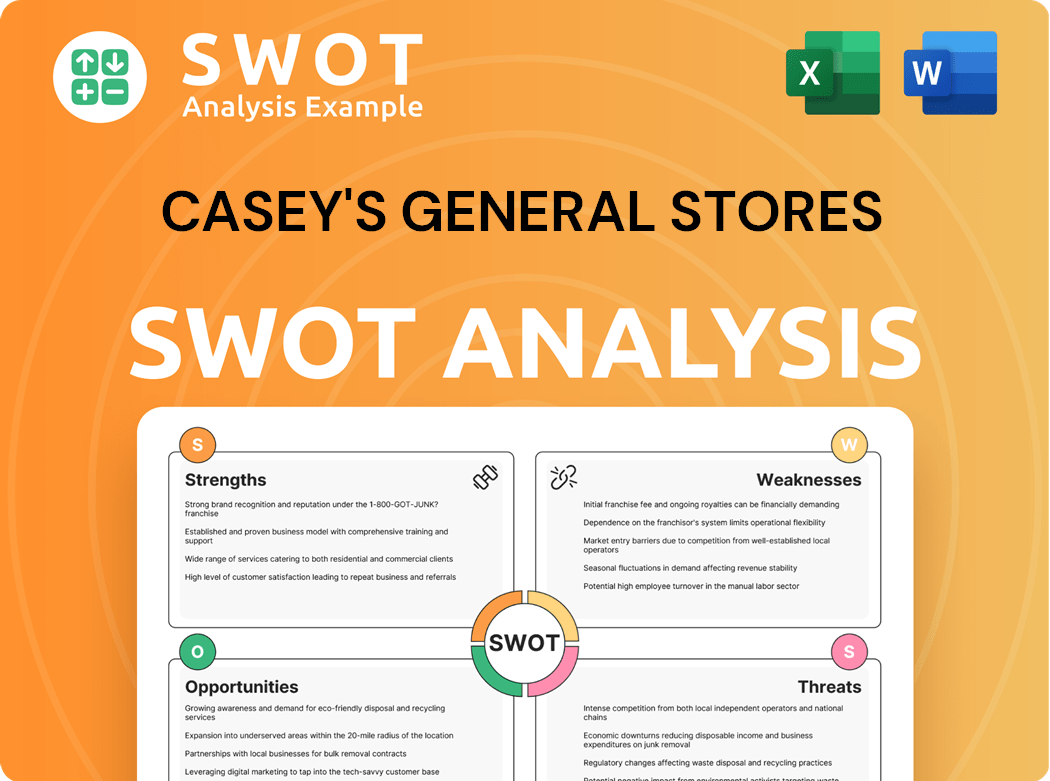
Casey's General Stores SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Casey's General Stores’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Casey's General Stores ownership reflects its journey from a privately held entity to a publicly traded corporation. A pivotal moment in Casey's history was the initial public offering (IPO) on October 12, 1983. This transition enabled the company to broaden its shareholder base and secure capital for expansion. The IPO marked a significant shift, moving away from a founder-led model to one with a more diverse ownership structure.
Over time, Casey's ownership has transformed, with institutional investors now holding a substantial portion of the shares. This shift towards institutional ownership has influenced corporate governance and a focus on shareholder value, typical of publicly traded companies. The change in ownership structure has been a key factor in shaping the company's strategic direction and operational practices.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | October 12, 1983 | Transitioned from private to public ownership, enabling broader shareholder base and access to capital. |
| Institutional Investment Growth | Ongoing | Increased influence of institutional investors on corporate governance and strategic decisions. |
| Shareholder Base Diversification | Ongoing | Shift from founder-led to a widely held public company, with significant holdings by institutional investors. |
As of early 2025, major institutional investors hold a significant portion of Casey's stock. Vanguard Group Inc. holds approximately 11.8% of shares, while BlackRock Inc. owns around 10.3%. State Street Corp. holds roughly 4.7% of the outstanding common stock. These figures, derived from recent SEC filings and financial reports, highlight the dominance of institutional investors. The high level of institutional ownership underscores the company's status as a mature, publicly traded entity. For more insights into Casey's General Stores, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Casey's General Stores.
Casey's General Stores went public in 1983, which was a turning point in its ownership structure.
- Institutional investors, such as Vanguard and BlackRock, are major shareholders.
- The shift to public ownership has influenced corporate governance.
- Understanding who owns Casey's is crucial for investors.
- The company's ownership structure reflects its growth and maturity.
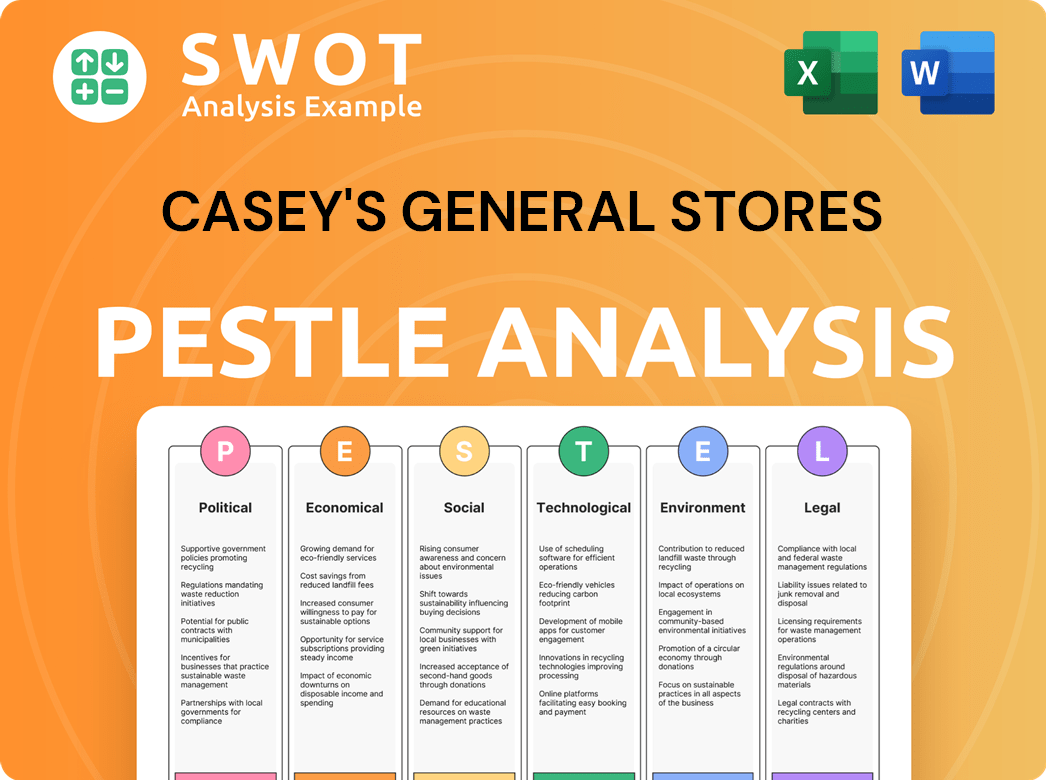
Casey's General Stores PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Casey's General Stores’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of Casey's General Stores includes a mix of independent directors and those with executive roles within the company. This structure aims to provide a balance between internal expertise and external oversight. The board's composition reflects a commitment to sound governance, with members bringing diverse experience from retail, finance, and operational backgrounds. This diverse expertise helps guide the company's strategic direction and ensures accountability.
The board's structure is designed to support the company's long-term goals. The presence of independent directors is crucial for providing unbiased oversight and representing the interests of all shareholders. This setup helps maintain a stable and effective governance framework, allowing Casey's to focus on its business objectives. The company's governance practices are generally stable, without significant public proxy battles or activist investor campaigns in recent years.
| Board Member | Title | Relevant Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Darren Rebelez | President and CEO | Extensive experience in the convenience store and restaurant industries. |
| William J. Wallin | Lead Independent Director | Experience in finance and corporate governance. |
| David L. Flitman | Director | Experience in retail and operations. |
Casey's operates under a one-share-one-vote structure, meaning each common share typically carries one vote. This approach ensures a relatively democratic voting process among shareholders. There are no publicly known special voting rights or founder shares that would grant outsized control to any single individual or entity. This structure supports equitable representation and decision-making within the company. For more insights, check out the Marketing Strategy of Casey's General Stores.
Casey's General Stores is a publicly traded company, with a governance structure designed for shareholder equity.
- The board includes independent directors and executives.
- The company uses a one-share-one-vote system.
- The governance structure is stable, supporting long-term strategic initiatives.
- The leadership team is focused on growth and operational excellence.
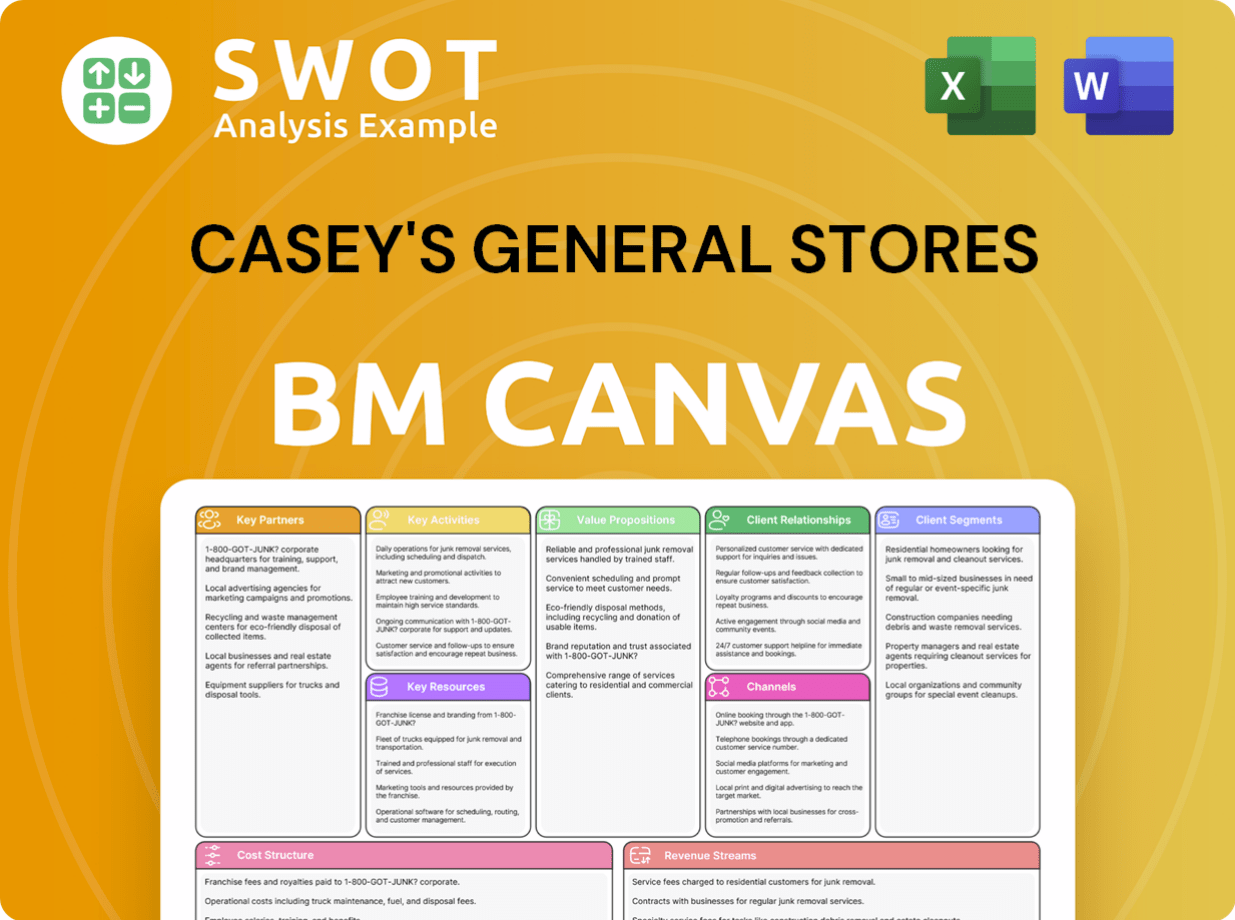
Casey's General Stores Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Casey's General Stores’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership structure of Casey's General Stores has remained relatively stable, with no significant changes in its fundamental ownership profile. The company has, however, continued its strategy of growth through acquisitions. A notable example is the November 2023 acquisition of 63 convenience stores from EG America for approximately $220 million. Such strategic moves can lead to minor shifts in institutional holdings, though the core ownership remains consistent.
Industry trends also indirectly influence the Casey's ownership landscape. The convenience store sector is experiencing increased consolidation, and there's a growing emphasis on prepared foods and digital engagement. These factors contribute to broader shifts in institutional ownership. The company has maintained its focus on organic growth, strategic acquisitions, and enhancing customer experience. As of May 2024, the company's market capitalization is approximately $12.5 billion, reflecting its continued strong performance and investor confidence.
The Casey's parent company has not announced any plans for CEO succession or potential privatization. This suggests a commitment to its public listing and current strategic direction. The absence of such announcements indicates a continued focus on long-term value creation for shareholders. The company's financial performance remains robust, with consistent revenue growth and a solid track record of profitability. For the fiscal year 2024, Casey's reported revenues of over $16 billion, demonstrating its strong market position and operational efficiency.
Strategic acquisitions, like the EG America deal, can lead to minor adjustments in institutional holdings. These changes are a natural part of growth, but they don't fundamentally alter the ownership structure. These moves reflect a commitment to expanding the company's footprint and market share.
Consolidation and digital engagement are key trends in the convenience store sector. These trends indirectly impact ownership patterns through increased institutional investment. This reflects a broader shift towards passive investing via index funds and ETFs.
No plans for CEO succession or privatization have been announced. This indicates a continued commitment to the current strategic direction. The focus remains on organic growth, strategic acquisitions, and enhancing customer experience. This focus is designed to provide long-term value.
Casey's continues to demonstrate strong financial performance, with consistent revenue growth. The company's market capitalization is approximately $12.5 billion (May 2024). Revenues for fiscal year 2024 exceeded $16 billion, showcasing its solid market position.
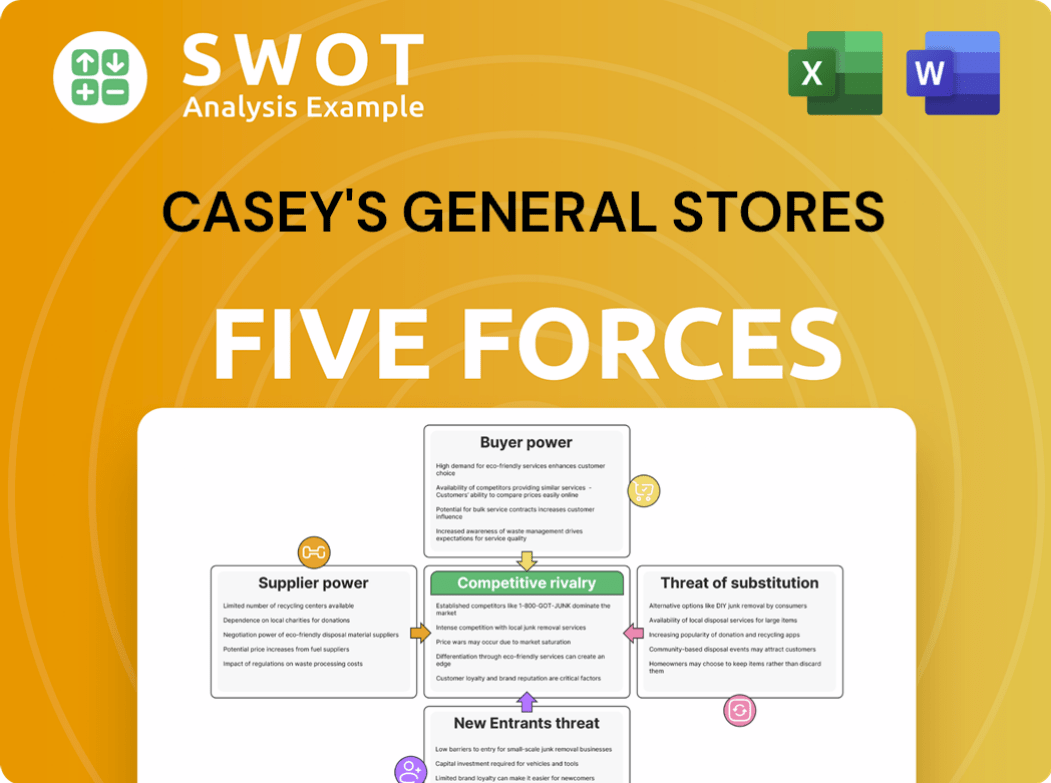
Casey's General Stores Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Casey's General Stores Company?
- How Does Casey's General Stores Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Brief History of Casey's General Stores Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Casey's General Stores Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.