EDF Bundle
How did Electricite de France become a global energy leader?
Dive into the fascinating EDF SWOT Analysis and uncover the captivating story of EDF, or Électricité de France, a titan in the electric utility industry. From its humble beginnings in post-war France, EDF has evolved into a multinational powerhouse, shaping the global energy landscape. Discover the pivotal moments and strategic decisions that have defined EDF's remarkable journey.
This brief history of EDF explores the company's origins as a state-owned monopoly, its crucial role in French energy, and its expansion across continents. Learn about EDF's significant impact on the energy market, including its substantial nuclear power France fleet and its involvement in the energy transition. Understanding EDF's past is key to grasping its present and anticipating its future in a rapidly changing world.
What is the EDF Founding Story?
The story of the EDF company, or Électricité de France, begins on April 8, 1946. It emerged from the nationalization of around 1,700 smaller energy producers, transporters, and distributors across France. This significant move was led by Marcel Paul, the Minister of Industrial Production at the time.
The primary goal was to address the fragmented and inefficient state of France's electricity infrastructure after World War II. The vision was to create a unified, state-owned entity. This entity would ensure efficient electricity generation and distribution. It would provide a stable and essential service to the entire nation.
EDF's early years were shaped by its status as a public industrial and commercial establishment (EPIC). It held a monopoly over electricity generation and distribution in France. This model focused on centralized control and public service. The aim was to rebuild and expand the national grid. The name 'Électricité de France' directly reflects its national purpose and ownership. Initial funding came from the French state, reflecting its nationalization rather than a startup seeking external investment. The establishment was influenced by the post-war economic and political context in France. This prioritized national control over key industries for reconstruction and public welfare. The monopoly allowed it to consolidate resources and strategically develop the nation's energy capabilities.
EDF was founded in 1946 through the nationalization of numerous energy companies.
- It was established to create a unified and efficient electricity infrastructure in post-war France.
- The company initially operated as a state-owned monopoly.
- The founding was deeply influenced by the post-war economic and political climate.
- EDF focused on rebuilding and expanding the national grid.
The early focus of EDF was on rebuilding and expanding France's electricity infrastructure. This included a strong emphasis on nuclear power, which became a cornerstone of its energy strategy. The company's role in the French energy market was, and continues to be, significant. EDF played a critical role in ensuring a reliable supply of electricity to the country. This involved the construction and operation of numerous power plants. The company's early decisions shaped its long-term trajectory, influencing its approach to energy generation and distribution for decades to come. For a deeper understanding of its business model, consider exploring the Revenue Streams & Business Model of EDF.
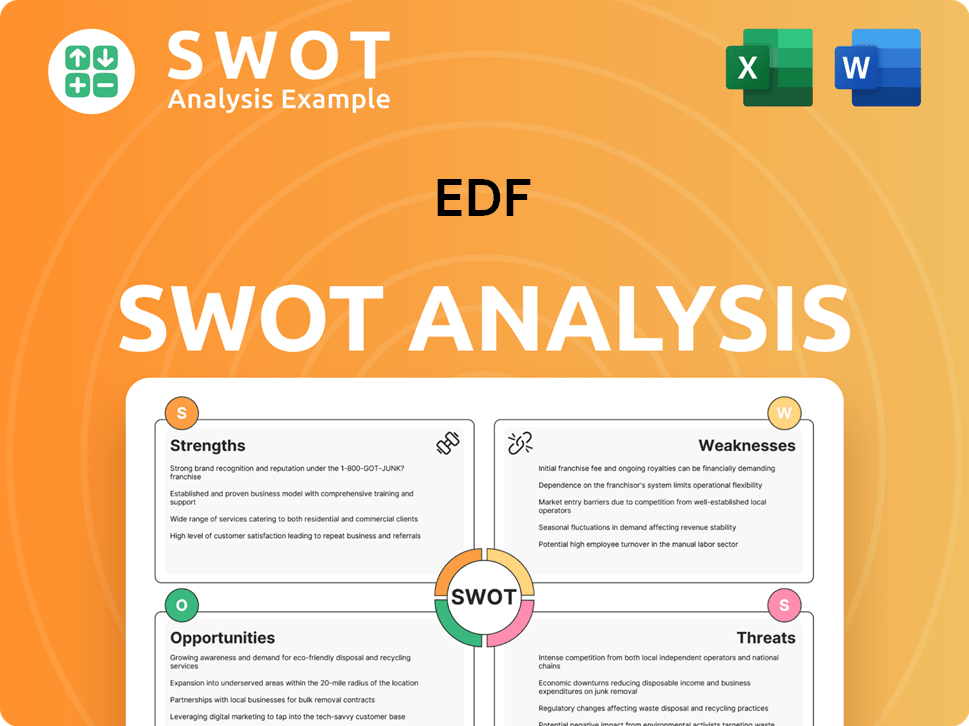
EDF SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of EDF?
The early growth of Electricite de France (EDF) centered on rebuilding and expanding France's electricity infrastructure. This included significant investments in hydroelectric and nuclear power plants, reflecting a strong emphasis on national energy self-sufficiency. The primary service offered was the reliable provision of electricity across the national grid, serving all consumers and industries within France.
EDF's initial focus was on developing France's electricity infrastructure. This included the construction of hydroelectric and nuclear power plants. The company's early growth was marked by a commitment to national energy independence, a key aspect of its strategy during this period.
The primary service offered by EDF was the reliable provision of electricity. Major clients included all consumers and industries within France. The company benefited from its status as a nationalized entity, ensuring widespread access to electricity across the country.
Team expansion was organic and substantial, integrating employees from numerous nationalized entities. Initial office and facility locations were distributed across France, reflecting the consolidation of existing power plants and distribution networks. This expansion supported the growing demand for electricity.
International expansion began later, with initial ventures into South America, followed by entry into European markets. Key acquisitions and mergers included the formation of EDF Energy in the UK in January 2002. By 2005, EDF had expanded its reach significantly.
The company's transformation from a public establishment to a publicly traded entity marked a significant milestone. EDF became a French SA (public limited company) on November 20, 2004, and had its IPO in 2005. Early capital raises were primarily driven by state funding and, later, by its public listing. The Mission, Vision & Core Values of EDF reflect its commitment to public service and sustainable energy.
The market reception in France was largely that of a public service provider. International expansion faced varying competitive landscapes. In 1999, the monopoly in France ended due to European directives. This forced EDF to open up 20% of its business to competitors.
This led to strategic shifts towards a more market-oriented approach while maintaining its core public service mission. In 2019, EDF lost approximately 200,000 customers in the UK to rivals. This highlights the evolving competitive environment in the energy market.
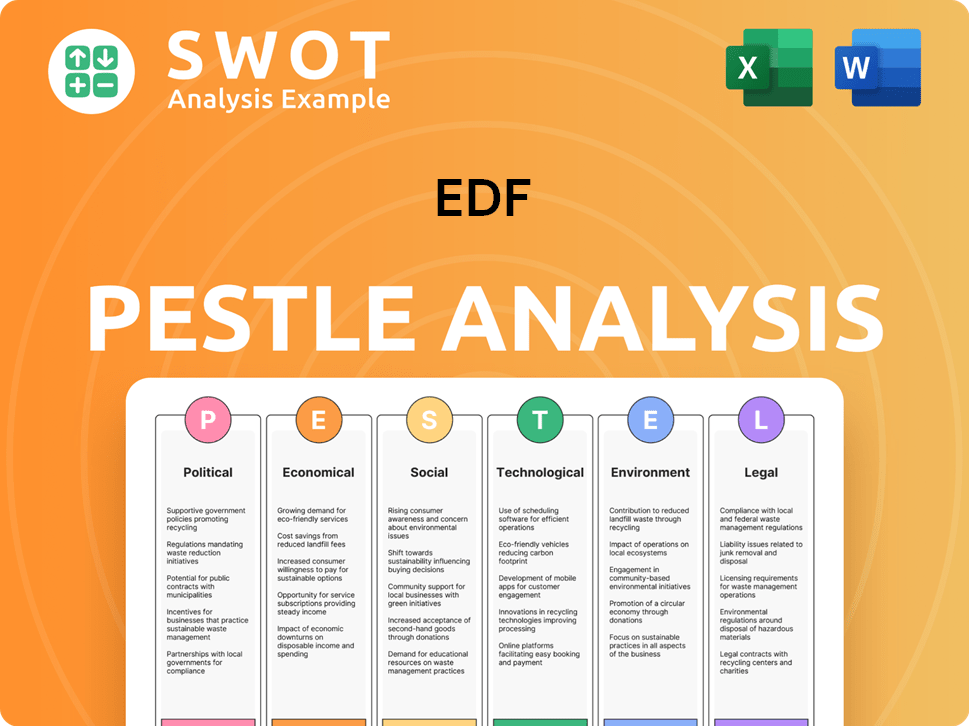
EDF PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in EDF history?
The EDF company history is marked by significant milestones, particularly in the realm of nuclear energy and its role in the French energy market. The company has evolved from a national monopoly to a global player, adapting to the changing dynamics of the energy sector.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1946 | Electricite de France (EDF) was established, nationalizing the electricity sector in France. |
| 1950s-1970s | EDF spearheaded the development of France's nuclear program, becoming a global leader in nuclear power generation. |
| 1999 | The end of EDF's monopoly in France marked a significant shift in the energy market. |
| 2023 | EDF operated 56 active nuclear reactors in France, contributing significantly to the country's electricity supply. |
| 2024 | EDF's nuclear fleet provided around 13% of the UK's total power demand, solidifying its position as Britain's largest generator of zero-carbon electricity. |
Innovations within EDF have been central to its strategy, particularly in nuclear energy and renewable sources. The company has consistently invested in new technologies and strategies to maintain its position in the energy market.
EDF's pioneering work in nuclear power has been a cornerstone of its innovation, establishing France as a leader in the field. This has involved continuous upgrades and safety enhancements to its nuclear fleet.
EDF has significantly expanded into renewables, with EDF Renewables UK aiming to reach 10 GW by 2035. This expansion includes investments in wind, solar, and other renewable energy sources.
EDF Wholesale Market Services received the 'Best Trading and Optimisation Team' award at the Solar Media Limited Energy Storage Awards and the inaugural 'Best Optimiser Award' at the Europe Energy Transition Awards. This highlights its leadership in energy storage and optimization.
Eco Wave Power was awarded the 2024 EDF Pulse Award for its wave energy technology. This demonstrates EDF's commitment to diverse energy solutions.
Despite its successes, EDF has faced several challenges in the energy market. These challenges have tested the company's resilience and required strategic adjustments.
The end of its monopoly in 1999 brought increased competition and market pressures. This has required EDF to adapt its strategies to remain competitive.
EDF has encountered issues with its nuclear fleet, including corrosion problems and maintenance delays. These issues have impacted production and profitability.
In 2022, EDF reported a net loss of €17.9 billion, compounded by the French government's requirement to sell production at reduced rates. Strategic pivots include efforts to divest renewable assets to strengthen its balance sheet.
The construction of the Hinkley Point C nuclear power station has been marked by long delays and cost overruns. This has put a strain on the company's resources.
EDF has shown resilience through restructuring and a focus on operational performance, such as the marked improvement in nuclear and hydroelectric production in the first half of 2024, leading to a net profit of €7 billion. This demonstrates the company's ability to adapt and recover.
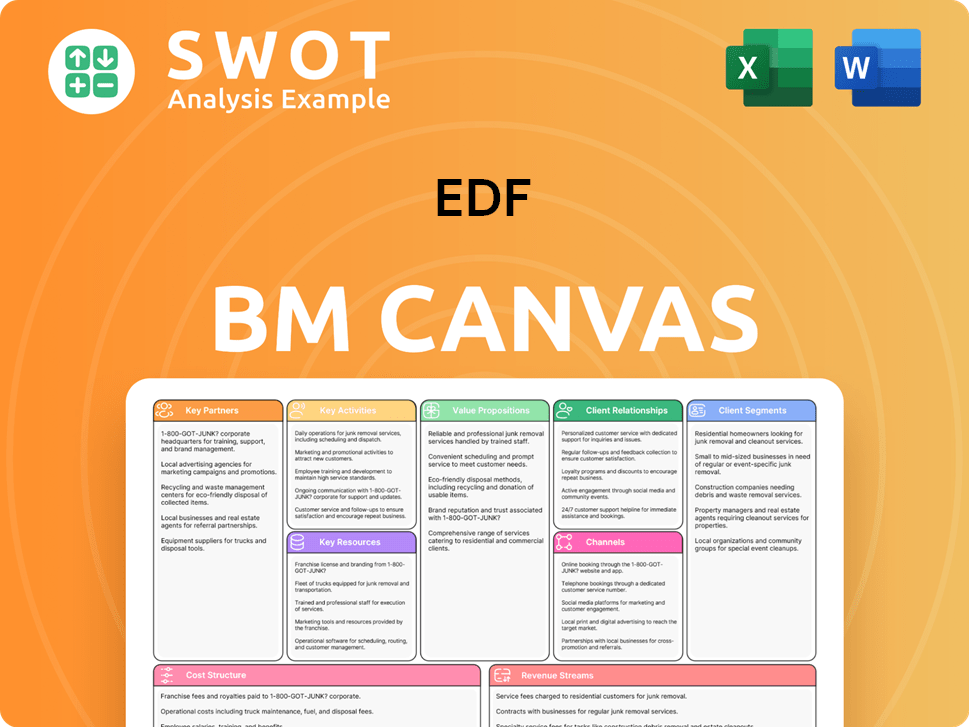
EDF Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for EDF?
The EDF history is marked by significant milestones. Founded in 1946 through the nationalization of French electricity companies, Électricité de France (EDF) has evolved from a national utility to a global energy player. Key developments include the expansion of nuclear and hydroelectric power, international ventures, and navigating market liberalization. The company's journey reflects France's energy policy and the global shift towards sustainable energy sources.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1946 | Founding of Électricité de France (EDF) through the nationalization of French electricity companies. |
| 1963 | Development of the French industrial base, including hydroelectric and nuclear power plants. |
| 1998 | Start of international development, including entry into the UK market. |
| 1999 | End of EDF's monopoly in electricity generation in France. |
| 2002 | Formation of EDF Energy in the UK. |
| 2004 | EDF becomes a French SA (public limited company). |
| 2005 | EDF's Initial Public Offering (IPO). |
| 2010 | Sale of EDF Energy Networks in the UK. |
| 2016 | Signature of final contracts for the Hinkley Point C EPR construction project in the UK. |
| 2020 | EDF awarded at the CDP Europe Awards for sustainable performance against climate change. |
| 2022 | Significant net loss of €17.9 billion due to nuclear reactor issues and government price caps. |
| 2023 | Net income turnaround to €10.0 billion. |
| 2024 | Installation of the first nuclear reactor at Hinkley Point C in December; EDF reports €11.4 billion net profit. |
| 2025 | Expected full operation of the Neart na Gaoithe (NnG) offshore wind project in Scotland. |
EDF is heavily focused on the energy transition, aiming to increase low-carbon electricity production. This includes investments in nuclear power, like the EPR2 reactors, and large-scale solar and wind projects. The Provence Grand Large floating wind pilot project is expected to be commissioned in 2025.
The company anticipates high nuclear output in France for 2025 and 2026, projecting between 315 and 345 TWh. This demonstrates EDF's commitment to nuclear power as a key element of its energy mix. The company is also working to consolidate its nuclear fleet.
EDF plans significant investments in new nuclear projects and the expansion of renewable energy sources. The company aims to recruit over 3,000 roles in 2025, including apprentices and graduates, particularly for the Hinkley Point C project. This investment is essential for future growth.
The company faces challenges from falling electricity prices and evolving energy policies. Luc Rémont, EDF's CEO, is focused on transforming and improving economic performance. The future involves balancing nuclear fleet consolidation with managing foreign investments amid an uncertain energy transition.
EDF Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of EDF Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of EDF Company?
- How Does EDF Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of EDF Company?
- What is Brief History of EDF Company?
- Who Owns EDF Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of EDF Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.