Fair Isaac Bundle
How Did Fair Isaac Company Revolutionize Finance?
Ever wondered how your creditworthiness is determined? The answer lies with Fair Isaac Corporation, better known as FICO, a company that has profoundly reshaped the financial landscape. From its humble beginnings, FICO pioneered the Fair Isaac SWOT Analysis to become a global leader in data analytics. Let's delve into the fascinating FICO history and explore its enduring impact on consumer lending and beyond.
The story of Fair Isaac Company, or FICO, is a testament to the power of data and innovation. Founded in 1956, the company's early focus on leveraging mathematics and computers quickly led to the creation of the FICO Score, forever changing the world of credit scoring. This article explores the brief history of FICO, its key milestones, and its evolution from a credit scoring pioneer to a comprehensive decision management solutions provider, highlighting its lasting influence on the history of finance.
What is the Fair Isaac Founding Story?
The story of the Fair Isaac Company, now widely known as FICO, began in 1956. It was founded by William R. 'Bill' Fair, an engineer, and Earl Judson Isaac, a mathematician. Their collaboration marked the beginning of a transformation in how businesses, especially in the financial sector, made critical decisions.
With a modest initial investment of $400 each, Fair and Isaac launched their venture. Their goal was to leverage mathematics and computers to help businesses make better decisions. This pioneering spirit set the stage for the development of the FICO score and its profound impact on the financial industry.
The founders identified a significant problem in the lending industry: the subjective and often biased methods of assessing credit risk. Their solution was groundbreaking: to use algorithms to analyze past customer behavior and predict the credit risk of new applicants. This innovation led to the creation of the FICO score, which revolutionized lending practices.
Fair, Isaac and Company started in a small studio apartment in San Rafael, California.
- The company's initial focus was on providing creditworthiness scoring systems to lenders.
- In 1957, they designed and installed a billing system for Carte Blanche.
- In 1963, they built a credit scoring system for Montgomery Ward.
- The company's early successes were built on the combined expertise of Bill Fair's business acumen and Earl Isaac's computer skills.
The company's early success can be attributed to its innovative approach to credit risk assessment. The FICO score quickly became a standard in the lending industry. This led to more informed lending decisions and a more efficient credit market. The impact of Fair Isaac on the financial landscape cannot be overstated. The company's innovations have shaped how consumers access credit and how lenders evaluate risk. For more details about the company's target market, you can read about the Target Market of Fair Isaac.
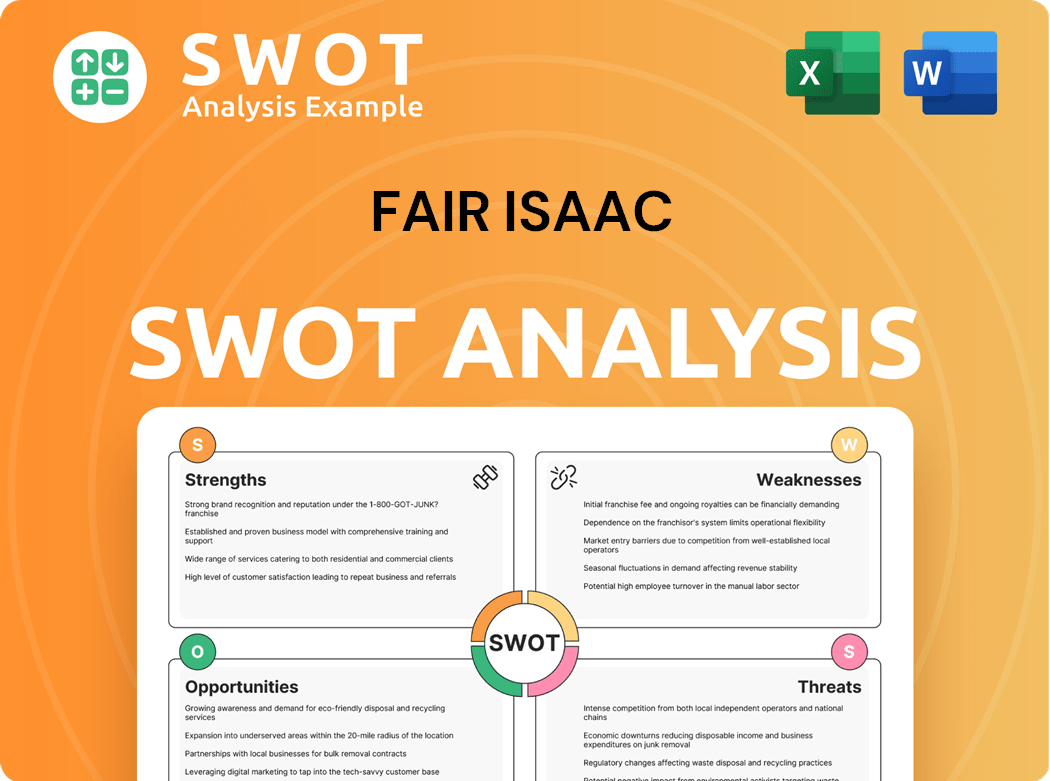
Fair Isaac SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Fair Isaac?
The early growth of the Fair Isaac Company, now known as FICO, centered on popularizing credit scoring and predictive analytics. This challenged traditional lending practices. After establishing its presence, the company expanded, moving its headquarters to San Francisco's Financial District in 1961. Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, FICO continued to innovate, developing automated systems.
FICO created the first fully automated application processing system and the first automated credit account management system, known as FICO Triad Customer Manager. This system manages a significant portion of the world's credit card accounts. These innovations paved the way for the explosive growth in credit card use, fundamentally changing the landscape of finance.
Early clients included major financial institutions such as Connecticut Bank and Trust and Wells Fargo in the 1970s. The company began its international expansion in 1977, implementing its first credit scoring system at a European bank. The first European office opened in Monaco five years later. This global reach expanded further in the early 1980s with offices in Asia, Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East.
A significant milestone occurred in July 1987 when FICO went public on the New York Stock Exchange. In 1989, the company debuted its first general-purpose FICO score, which quickly became synonymous with credit risk scores. By 1991, FICO had made its credit bureau risk scores available at all three major U.S. credit reporting agencies. The company's growth efforts during this period were characterized by a strategic shift towards broader adoption of its scoring systems.
The company's strategic shift towards broader adoption of its scoring systems and a growing international presence solidified its trajectory as a leader in data analytics. This expansion and innovation significantly impacted the financial industry. For more information on the impact of FICO history, you can read this article: 0.
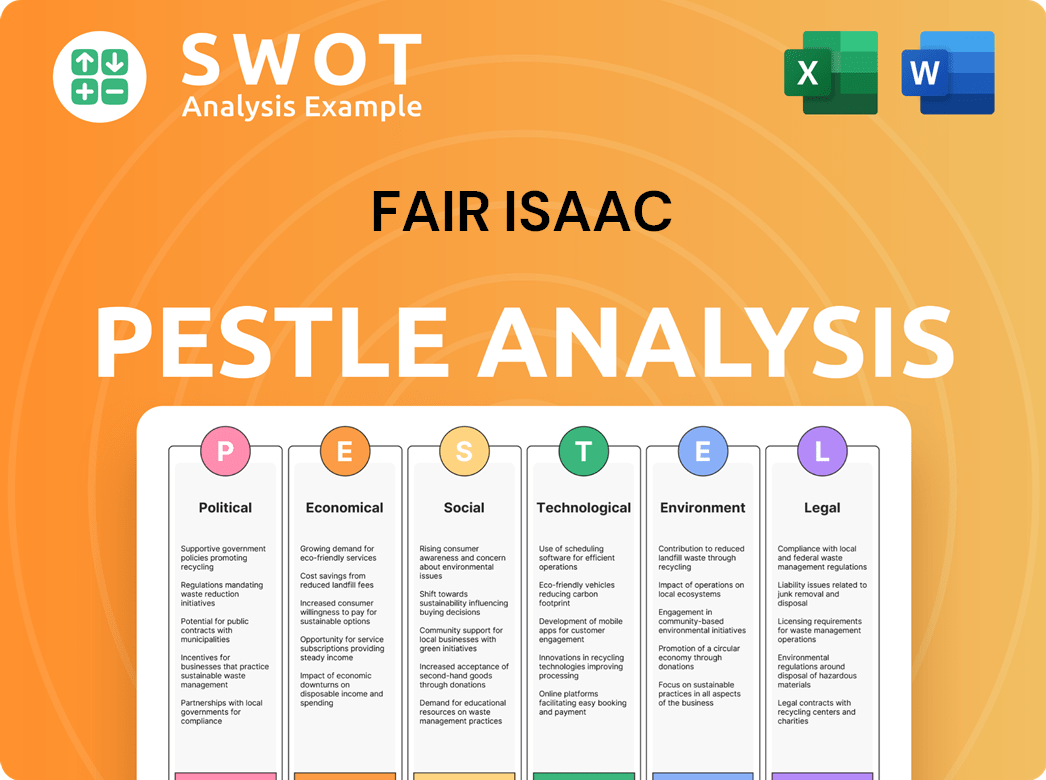
Fair Isaac PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Fair Isaac history?
The Fair Isaac Company, also known as FICO, has a rich history marked by significant milestones in the financial industry, particularly in credit scoring and risk management. This evolution has shaped how credit is assessed and managed globally.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1956 | Fair Isaac Corporation was founded by Bill Fair and Earl Isaac. |
| 1989 | The general-purpose FICO Score was introduced, becoming the standard for U.S. consumer credit risk assessment. |
| 1990s | FICO launched FICO Falcon Fraud Manager, a pioneering system using neural networks for credit card fraud detection. |
| 1998 | Blaze Advisor, a decision rules management system, was launched. |
| 2023 | FICO launched Falcon Fraud Manager 10.1, incorporating advanced AI and ML capabilities. |
| 2025 | FICO established new strategic partnerships, such as with Fujitsu and dacadoo, to enhance digital transformation and precision in underwriting. |
FICO has consistently focused on developing unique intellectual property and technologies, particularly in areas like AI, machine learning, and digital decisioning. As of March 2025, the company's patent portfolio includes 226 active U.S. and international patents, with an additional 75 patent applications pending.
The introduction of the FICO Score in 1989 revolutionized credit scoring, becoming the benchmark for assessing consumer credit risk.
FICO Falcon Fraud Manager, introduced in the 1990s, pioneered the use of neural networks for credit card fraud detection, protecting a significant portion of global transactions.
The development of decision rules management, with products like Blaze Advisor, provided advanced tools for businesses to automate and optimize their decision-making processes.
FICO has continuously invested in AI and machine learning, enhancing its capabilities in fraud detection, credit scoring, and risk management.
Recent patents focus on enhancing data privacy and improving AI model fairness and transparency, aligning with evolving regulatory requirements.
New strategic partnerships, like those with Fujitsu and dacadoo, are aimed at enhancing digital transformation and precision in underwriting, expanding FICO's market reach.
Despite its achievements, FICO has faced various challenges, including market downturns and increased competition. Economic downturns can reduce the demand for credit products, impacting FICO's revenue, and regulatory changes introduce new competitive dynamics.
Economic downturns can decrease demand for credit products, directly affecting FICO's revenue due to fewer credit checks and score inquiries.
Regulatory changes, such as the expansion of allowable credit scores, introduce competition and could potentially dilute FICO's influence in the market.
FICO has experienced a slowdown in software revenue growth and higher-than-expected expenses, leading to conservative guidance in fiscal year 2024.
FICO's dependence on credit scoring revenue presents a concentration risk, making the company vulnerable to shifts in the credit market.
FICO has focused on pricing in scores and platforming its software to increase customer retention and average revenue per customer through integrated solutions.
The company's strong gross profit margins, at 80.83% as of May 2025, demonstrate its operational efficiency and resilience in navigating challenges.
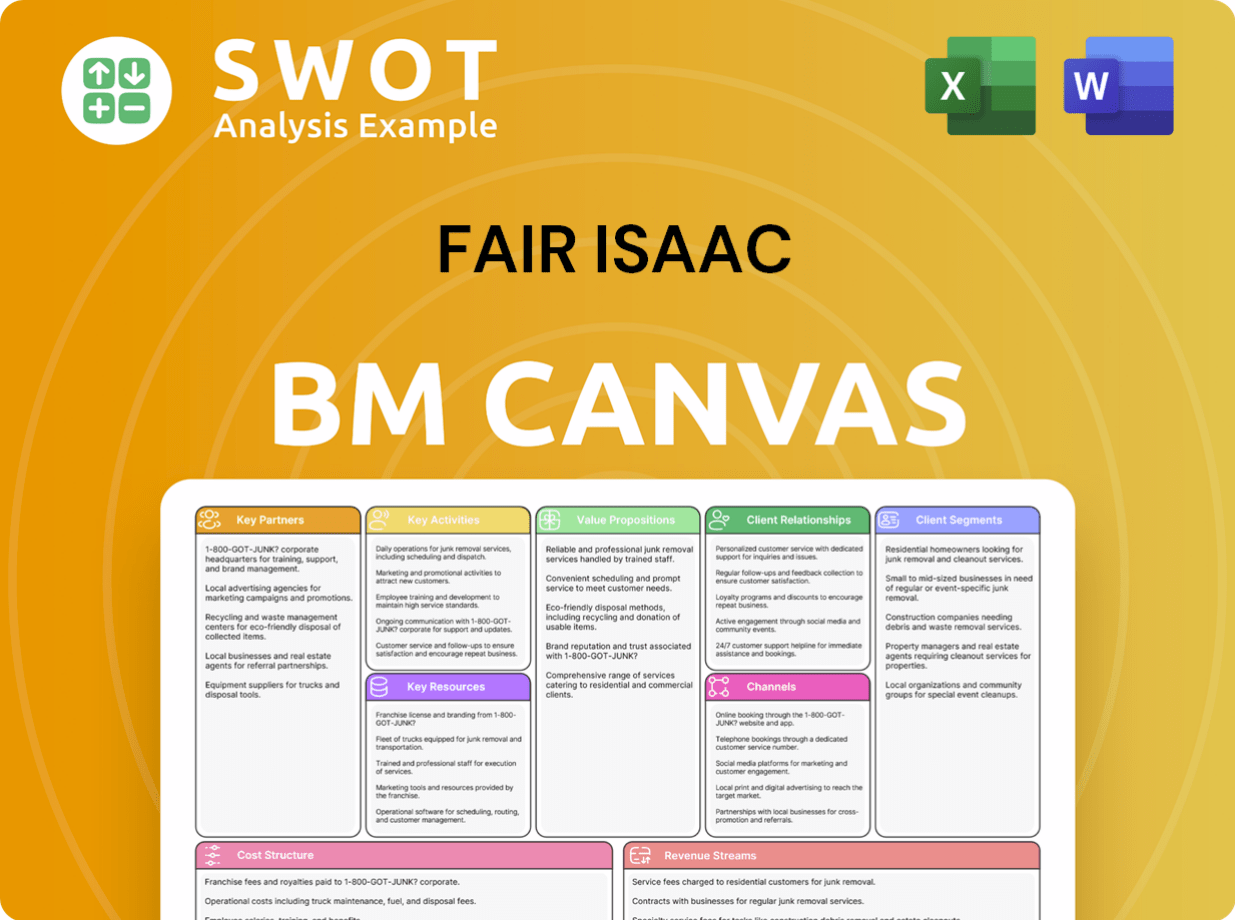
Fair Isaac Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Fair Isaac?
The story of the Fair Isaac Company, now known as FICO, began in 1956 when William R. 'Bill' Fair and Earl Judson Isaac established the company in San Rafael, California. Over the years, the company has been at the forefront of credit scoring and analytics, transforming how financial decisions are made. The Growth Strategy of Fair Isaac shows how the company has adapted and innovated over time, becoming a key player in the financial industry.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1956 | William R. 'Bill' Fair and Earl Judson Isaac found Fair, Isaac and Company in San Rafael, California. |
| 1957 | FICO designs and installs a billing system for Carte Blanche. |
| 1961 | The company moves its headquarters to San Francisco's Financial District. |
| 1963 | FICO builds a credit scoring system for Montgomery Ward. |
| 1977 | The first credit scoring system is implemented at a European bank. |
| 1982 | The first European office opens in Monaco. |
| 1987 | FICO goes public and is traded on the New York Stock Exchange. |
| 1989 | The first general-purpose FICO Score is debuted. |
| 1991 | Credit bureau risk scores are made available at all three major U.S. credit reporting agencies. |
| 1990s | Introduction of FICO Falcon Fraud Manager and Blaze Advisor. |
| 2003 | The company name is legally changed to Fair Isaac Corporation. |
| 2009 | The company rebrands to FICO. |
| 2022 | FHFA announces expansion of allowable credit scores, introducing FICO Score 10 T and VantageScore 4.0 for mortgage processes, with full incorporation targeted for Q4 2025. |
| 2023 | FICO is awarded 12 new patents in AI and ML technology, digital decisioning, and blockchain model governance. |
| 2024 | FICO achieves record annual revenues of $1.72 billion, up 13% year-over-year, and GAAP net income of $513 million, up 21%. |
| 2024 | FICO reports revenues of $454 million, a 16% rise, and earnings per share of $5.44. Scores segment revenue increased by 27%, and Software segment revenue grew by 5%. |
| 2025 | FICO reports significant growth in revenue and EPS, with guidance for fiscal 2025 including projected revenues of $1.98 billion, GAAP net income of $624 million, and GAAP EPS of $25.05. |
| 2025 | FICO announces a $1.5 billion debt offering to capitalize on mortgage market momentum. |
| 2025 | The transition to FICO Score 10 T and VantageScore 4.0 for mortgage processes is expected to be incorporated. |
FICO is focused on expanding its core Scores segment. Mortgage score prices are set to increase to $4.95 in 2025 from $3.50 in 2024. This increase has the potential to generate an additional $200 million in revenue for FY25.
The company's software segment, particularly the FICO Platform, is a significant growth area. Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) growth is anticipated to accelerate back to 30% by the end of fiscal year 2025, indicating strong potential.
FICO is expanding its market footprint and enhancing product offerings through innovation in AI and machine learning. The fraud detection and prevention market, where FICO is a major player, is projected to grow from $24.31 billion in 2024 to $42.62 billion by 2029.
Analysts predict FICO to grow earnings and revenue by 18.4% and 13% per annum, respectively. Despite potential economic headwinds, FICO remains confident in its ability to deliver value to stakeholders, continuing its mission of using data and analytics for smarter business decisions.
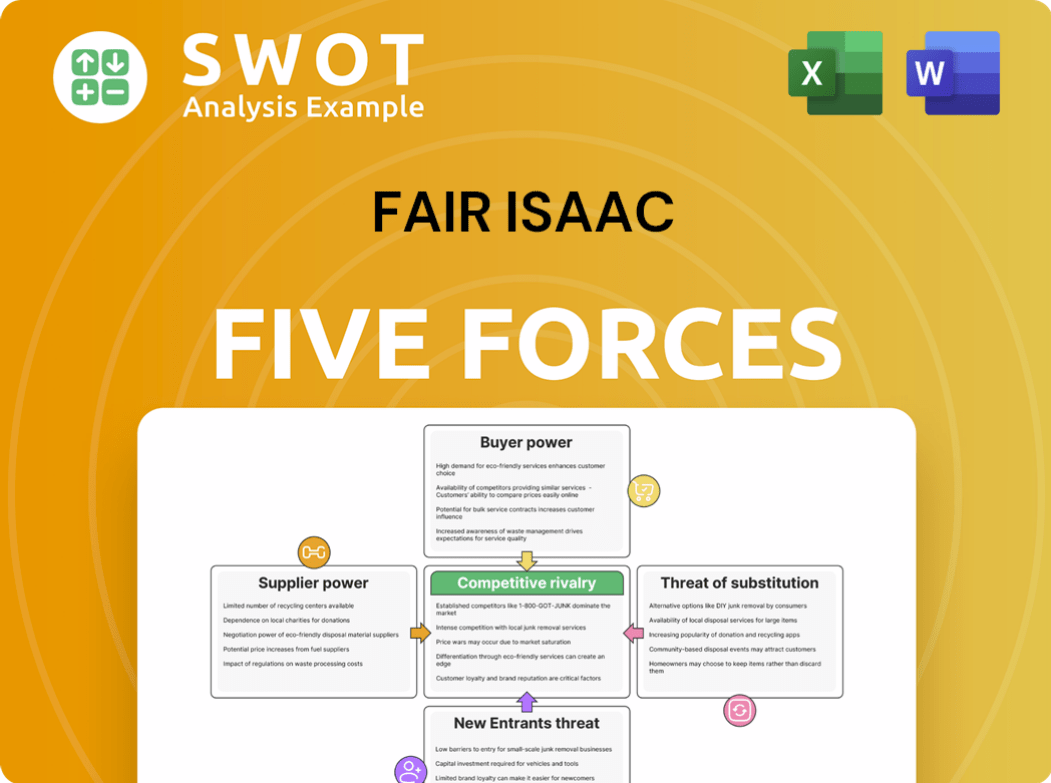
Fair Isaac Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Fair Isaac Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Fair Isaac Company?
- How Does Fair Isaac Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Fair Isaac Company?
- What is Brief History of Fair Isaac Company?
- Who Owns Fair Isaac Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Fair Isaac Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.