Paytm Bundle
How Did Paytm Conquer India's Digital Realm?
Paytm, a name synonymous with digital payments in India, started its journey with a simple vision: to make mobile recharging easier. Founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, this Paytm SWOT Analysis reveals the company's strategic moves. From its humble beginnings in Noida, the company has become a cornerstone of the Indian fintech revolution.
This exploration into the Paytm history will uncover how a mobile wallet transformed into a comprehensive financial services provider. Discover the Paytm company's remarkable growth trajectory, key innovations, and the challenges it overcame to become a leader in digital payments and a significant player in the Indian fintech landscape. Learn about its Paytm origin and its impact on the Indian economy.
What is the Paytm Founding Story?
The story behind the Paytm company began on August 10, 2010, with Vijay Shekhar Sharma at the helm. He launched the company under the parent organization, One97 Communications. Sharma, a Delhi College of Engineering graduate, saw a chance to capitalize on India's growing mobile use and the early days of digital payments. His goal was to create a platform that would make everyday transactions easier, starting with mobile recharges.
The initial focus was on online mobile recharge services, a crucial need in a country with a rapidly expanding mobile subscriber base. Paytm started as a self-funded venture, with Sharma investing $2 million from his own resources. Sharma's strong belief in the potential of the mobile internet, even when others were doubtful, drove him to pursue the venture despite initial financial challenges and the task of convincing early users of the security and convenience of online transactions.
Paytm's name was chosen to be simple and memorable, reflecting its core function: 'Pay Through Mobile.' The founding team's expertise in telecommunications and technology was key in building the initial platform and navigating the complexities of the digital payments infrastructure.
- When was Paytm founded? August 10, 2010.
- Paytm founder and CEO: Vijay Shekhar Sharma.
- Paytm's initial services: Online mobile recharge.
- Paytm's funding history: Initially bootstrapped with $2 million from Vijay Shekhar Sharma.
Paytm SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Paytm?
The early growth of the company, starting with its origin in 2010, saw a strategic expansion beyond mobile recharge services. The company quickly diversified into utility bill payments by 2012, broadening its user base. A pivotal moment came in 2014 with the launch of its mobile wallet, coinciding with the rapid adoption of smartphones in India, enhancing convenience for users. This expansion marked a significant step in the company's history.
The demonetization event in late 2016 acted as a catalyst for the company's growth, leading to a surge in user adoption and transaction volumes. The company reported a 700% increase in overall transactions and a 1000% increase in money added to wallets shortly after the announcement. This period also saw an aggressive expansion of its merchant network, extending digital payment acceptance across the economy. This growth trajectory showcased the company's impact on the Indian economy.
In 2017, the company launched Paytm Payments Bank, venturing into financial services by offering savings accounts and debit cards, a significant strategic shift. It also entered the e-commerce space with Paytm Mall, aiming to compete with established players. Early customer acquisition strategies focused on cashback offers and a seamless user experience. You can read more about the Owners & Shareholders of Paytm.
By early 2024, the company's average monthly transacting users (MTU) stood at approximately 90 million, reflecting continued user engagement despite market fluctuations. The company's evolution from recharge to payments has been significant. The company's history is marked by strategic moves and expansions that solidified its position in the Indian fintech landscape, revolutionizing digital payments.
The company's early growth demonstrates its ability to adapt and capitalize on market opportunities. The company's expansion into various financial services and e-commerce reflects its ambition to become a comprehensive platform. The company's impact on digital payments is undeniable, with its mobile wallet and merchant network playing a crucial role in India's digital transformation, influencing the Indian fintech sector.
Paytm PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Paytm history?
The story of the Paytm company is a compelling narrative of growth, innovation, and resilience in the rapidly evolving digital payments landscape. From its origin as a mobile recharge platform, Paytm has transformed into a comprehensive financial services provider, significantly impacting the Indian fintech sector.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2010 | Paytm was founded by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, initially focusing on mobile and DTH recharges. |
| 2014 | Paytm launched its mobile wallet, marking a significant shift towards digital payments. |
| 2017 | Paytm Payments Bank was launched, expanding its services to include banking operations. |
| 2017 | Paytm Money was introduced, offering wealth management services like mutual funds and stockbroking. |
| 2021 | Paytm conducted its Initial Public Offering (IPO), raising approximately $2.5 billion, one of the largest IPOs in India's history. |
| 2024 | The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) imposed restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank, impacting its operations. |
Paytm's innovations have been central to its success in the Indian fintech market. A key innovation was the introduction of its QR code-based payment system, which enabled small merchants across India to accept digital payments easily. This initiative played a crucial role in expanding the reach of digital payments, especially in areas with limited access to traditional banking services.
Paytm's QR code system enabled millions of small merchants to accept digital payments, driving the adoption of digital payments across India.
The launch of Paytm Payments Bank in 2017 allowed the company to offer banking services, expanding its financial service offerings.
Paytm Money provided wealth management services, including mutual funds and stockbroking, broadening its financial service offerings.
Paytm's seamless integration with the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) further simplified digital transactions, making it user-friendly.
Paytm expanded its services to include bill payments, travel bookings, and e-commerce, creating a comprehensive ecosystem.
Paytm provided various services for merchants, including payment processing, marketing tools, and business loans, supporting their growth.
Despite its successes, Paytm has faced several challenges. Intense competition from both domestic and global players in the Indian fintech market has continuously pressured its market share and profitability. Regulatory hurdles, particularly the restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank by the RBI in early 2024, have also presented significant challenges, leading to operational adjustments and impacting the company's stock performance.
The Indian fintech market is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share, including global giants and domestic rivals.
Regulatory actions, such as restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank by the RBI, have disrupted operations and impacted investor confidence.
Achieving and maintaining profitability in a competitive market with high operational costs remains a significant challenge for Paytm.
Some of Paytm's ventures, such as Paytm Mall, have not achieved the desired success, highlighting the challenges of diversification.
Ensuring robust compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining high standards of data security are ongoing challenges.
Market fluctuations and shifts in consumer behavior can impact Paytm's performance and require strategic adaptation.
Paytm Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Paytm?
The Paytm history is a story of rapid evolution in the Indian fintech landscape. Founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, the company started with mobile recharge services and expanded into digital payments and financial services. This journey, marked by strategic expansions and significant growth, has positioned it as a major player in India's digital economy. The company's ability to adapt to market changes and regulatory environments has been crucial to its trajectory.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2010 | Founded by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, initially offering mobile recharge services. |
| 2012 | Expanded services to include utility bill payments. |
| 2014 | Launched the Paytm Wallet, enabling digital payments for various services. |
| 2016 | Witnessed significant growth due to India's demonetization policy. |
| 2017 | Launched Paytm Payments Bank, venturing into banking services. |
| 2017 | Introduced Paytm Mall for e-commerce. |
| 2018 | Launched Paytm Money for wealth management services. |
| 2021 | Successfully completed its Initial Public Offering (IPO). |
| 2024 | Faced regulatory restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank by the RBI. |
Paytm is concentrating on strengthening its primary payments and financial services. This includes improving its lending portfolio and expanding its merchant acquisition efforts, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The company aims to enhance its existing services and explore new avenues for revenue growth within the digital payments sector.
Strategic initiatives involve using AI and data analytics to personalize financial products and improve risk assessment. This approach allows for more tailored services and more efficient risk management, which is crucial for sustainable growth. Leveraging technology helps in enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
Paytm plans to focus on high-ticket transactions to drive revenue growth, aiming to increase the value of transactions processed. This strategy is designed to boost profitability and enhance the company's financial performance. Prioritizing larger transactions is a key element of their growth plan.
The company is committed to compliance and sustainable growth, focusing on operating within the regulatory framework. The ability to navigate regulatory scrutiny and adapt to changes is critical for long-term success. Maintaining trust among its user base is essential.
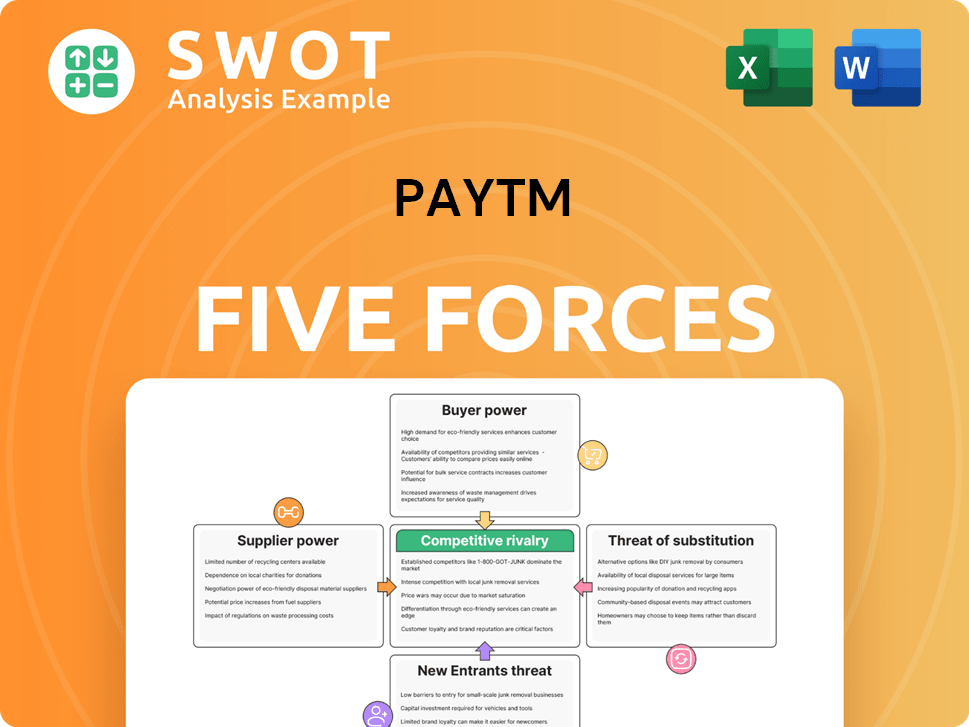
Paytm Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Paytm Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Paytm Company?
- How Does Paytm Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Paytm Company?
- What is Brief History of Paytm Company?
- Who Owns Paytm Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Paytm Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.