Rivian Bundle
How Did Rivian Revolutionize the Automotive Industry?
Rivian, an Rivian SWOT Analysis, has quickly become a major player in the electric vehicle (EV) market, but how did it all begin? This EV manufacturer, known for its adventure-focused electric trucks and SUVs, has carved out a unique space in the automotive industry. Its journey from a startup to a publicly traded company is a fascinating story of innovation and strategic pivots.
Founded in 2009 by RJ Scaringe, the Rivian company initially aimed to create sustainable transportation solutions. The company's focus on the electric truck and SUV market, including the R1T and R1S, has set it apart from traditional automakers. This brief history of Rivian explores the key milestones, from its early days in Rockledge, Florida, to its current position as a significant player in the electric vehicle market, examining Rivian's electric vehicles, investment history, and future plans.
What is the Rivian Founding Story?
The story of the Rivian company began on June 22, 2009. Robert 'RJ' Scaringe, armed with a Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from MIT, laid the foundation for what would become a significant player in the automotive industry. His vision was clear: to create sustainable transportation solutions.
Scaringe's initial focus was on developing a versatile 'skateboard' platform. This platform would serve as the foundation for various vehicle types. This innovative approach aimed to address environmental concerns through cutting-edge vehicle technology. The goal was to create electric vehicles (EVs) that could handle diverse terrains.
The company's early days were marked by stealth and strategic planning. The name 'Rivian' itself reflects a connection to nature and exploration. Securing capital for automotive development was a major challenge. The founding team, composed of engineers and designers, was driven by a shared commitment to sustainable innovation.
RJ Scaringe founded Rivian with a vision for sustainable transportation. The company aimed to create versatile electric vehicles. The initial focus was on a 'skateboard' platform.
- The company was founded on June 22, 2009.
- Scaringe's background includes a Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from MIT.
- Rivian's early business model involved vertical integration.
- The initial funding came from Scaringe's personal funds and seed rounds.
The primary problem Scaringe identified was the lack of versatile electric vehicles. Many companies focused on sedans, but Scaringe envisioned EVs that could handle different terrains. The original business model centered on a vertically integrated approach. This meant designing, developing, and manufacturing its vehicles and technology in-house.
Early funding came from Scaringe and undisclosed investors. This allowed the company to operate in stealth mode for several years. The name 'Rivian' is a portmanteau, reflecting a connection to nature. Securing capital was a major challenge. The founding team, composed of engineers and designers, was driven by a shared commitment. To learn more about how Rivian generates revenue, you can read about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Rivian.
Rivian SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Rivian?
The early growth of the Rivian company, from its inception in 2009 to its public unveiling in 2018, focused on developing its core 'skateboard' platform. This platform was designed to support various vehicle types, emphasizing performance, safety, and integrated battery technology. The acquisition of a former Mitsubishi plant in Normal, Illinois, in 2017 for $16 million was a crucial step in establishing a production facility. The company's public debut at the LA Auto Show in November 2018, with the R1T and R1S models, marked a significant milestone for the EV manufacturer.
Rivian's initial years were dedicated to engineering a flexible 'skateboard' architecture, a key element in the company's strategy. This platform was designed to accommodate multiple vehicle types, which was a strategic advantage. The focus was on integrating battery technology, performance, and safety features from the outset. This foundational work was essential for future product offerings, including the electric truck and SUV models.
In 2017, Rivian acquired a former Mitsubishi manufacturing plant in Normal, Illinois, for $16 million. This acquisition was a pivotal move, providing the company with a substantial production facility. The plant was essential for scaling up vehicle manufacturing as the company prepared for its public launch. This strategic investment highlighted Rivian's commitment to becoming a major player in the automotive industry.
Rivian's public debut at the LA Auto Show in November 2018, with the R1T electric pickup truck and R1S electric SUV, was a defining moment. The unveiling garnered significant positive market reception and media attention. This event set Rivian apart from other EV startups, which were primarily focused on sedans or smaller vehicles. The positive response helped establish Rivian's brand identity.
From 2019 onwards, Rivian secured substantial capital through strategic partnerships and investment rounds. Amazon led a $700 million investment round in February 2019, followed by a $500 million investment from Ford in April 2019. Rivian also received a significant order from Amazon for 100,000 electric delivery vans (EDVs) in September 2019. These investments and partnerships were crucial for funding research and development and preparing for production.
Rivian went public through a highly anticipated IPO in late 2021, raising approximately $13.7 billion. This IPO further fueled Rivian's expansion plans and manufacturing ramp-up. The company's initial customer acquisition strategy relied heavily on direct-to-consumer sales and pre-orders. Despite initial production challenges, Rivian began customer deliveries of the R1T in September 2021 and the R1S in December 2021.
The transition from development to commercialization was marked by the start of customer deliveries. The R1T began deliveries in September 2021, and the R1S followed in December 2021. Rivian's focus on direct-to-consumer sales and pre-orders helped build anticipation for its unique product offerings. The company's early production milestones were significant for establishing its presence in the electric truck and SUV market.
Rivian PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Rivian history?
The Rivian company has experienced a dynamic journey characterized by significant milestones, technological advancements, and considerable obstacles. The Rivian history showcases its evolution within the automotive industry, marked by strategic decisions and innovative approaches to electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2009 | Founded by RJ Scaringe, initially focusing on developing an electric sports car. |
| 2011 | Shifted focus to electric trucks and SUVs, recognizing a market opportunity. |
| 2018 | Revealed the R1T electric pickup truck and R1S SUV at the Los Angeles Auto Show. |
| 2021 | Launched the R1T, becoming the first EV manufacturer to market an electric pickup truck in North America; R1S production began shortly after. |
| 2021 | Completed its IPO, raising approximately $13.5 billion, one of the largest in history. |
| 2023 | Produced 57,232 vehicles, exceeding the revised guidance of 54,000. |
| 2024 | Announced a 10% reduction in its salaried workforce to improve profitability. |
Rivian electric vehicles have introduced several innovative features, such as the 'Gear Tunnel' in the R1T, enhancing storage capabilities. The company also developed a modular 'skateboard' platform, which integrates the battery pack, drive units, and suspension, enabling flexible body styles and off-road capabilities.
This platform integrates the battery pack, drive units, suspension, and thermal system, allowing for versatile body styles.
A unique storage compartment in the R1T, enhancing the vehicle's utility.
A proprietary charging network designed to support long-distance travel for Rivian owners.
A comprehensive software system that enhances the user experience and vehicle functionality.
The next-generation platform aimed at a lower price point and broader market appeal, along with the R3 and R3X models.
Despite its advancements, Rivian has faced challenges, particularly in scaling production and managing profitability. Supply chain disruptions, especially for semiconductors, impacted the ability to meet initial production targets, leading to adjustments in manufacturing processes. The company reported a net loss of $5.4 billion in 2023, reflecting ongoing investments and competitive pressures, prompting cost-cutting measures, including workforce reductions.
Rivian struggled to meet initial production targets due to supply chain issues, particularly for semiconductors.
The company reported significant net losses, reflecting investments in manufacturing, technology, and future product development.
Competition from established automakers like Ford and General Motors, as well as Tesla, has increased market pressure.
Rivian has implemented cost-cutting measures, including workforce reductions, to improve profitability and streamline operations.
Global supply chain issues, especially for critical components like semiconductors, have significantly impacted production.
Changes in market conditions and consumer demand have required strategic adjustments to Rivian's business model.
To understand how Rivian is navigating these challenges, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of Rivian.
Rivian Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Rivian?
The Rivian company has a history marked by significant milestones, from its inception to its current position in the automotive industry. Founded in 2009 by RJ Scaringe, the EV manufacturer has navigated various stages of development, including securing substantial investments, launching its initial vehicle models, and facing production challenges. This timeline highlights key events in the company's evolution, illustrating its journey from a startup to a publicly traded entity.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2009 | Rivian is founded by RJ Scaringe. |
| 2017 | Rivian acquires the former Mitsubishi manufacturing plant in Normal, Illinois. |
| 2018 | Rivian publicly unveils the R1T electric pickup truck and R1S electric SUV at the LA Auto Show. |
| 2019 | Amazon leads a $700 million investment round; Ford invests $500 million; Amazon places an order for 100,000 electric delivery vans. |
| 2021 | Rivian goes public with an IPO, raising approximately $13.7 billion; first R1T customer deliveries begin in September, followed by R1S deliveries in December. |
| 2022 | Rivian produces 24,337 vehicles, facing supply chain challenges. |
| 2023 | Rivian produces 57,232 vehicles, exceeding revised guidance; reports a net loss of $5.4 billion. |
| February 2024 | Rivian announces a 10% reduction in its salaried workforce. |
| March 2024 | Rivian unveils its R2, R3, and R3X models, targeting a more affordable price point for future growth. |
Rivian is focused on scaling production of its R1 platform and launching its next-generation R2 platform. The company aims to increase sales volume by expanding into a more accessible price segment. The R2 platform, expected to start at approximately $45,000, is slated for production in 2026 at the Normal, Illinois plant.
Rivian plans to continue fulfilling its order for 100,000 Amazon EDVs, providing a steady commercial revenue stream. The company is also exploring international expansion, although specific timelines are still being determined. These initiatives support Rivian's growth strategy.
The increasing adoption of EVs, advancements in battery technology, and the development of charging infrastructure will influence Rivian's future. The company faces challenges in achieving consistent profitability and scaling. The electric truck market is competitive.
Analyst predictions suggest that Rivian has the potential for growth due to its brand identity, product lineup, and strategic partnerships. The company's long-term vision is to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable transportation. The company's focus is on cost-efficient manufacturing.
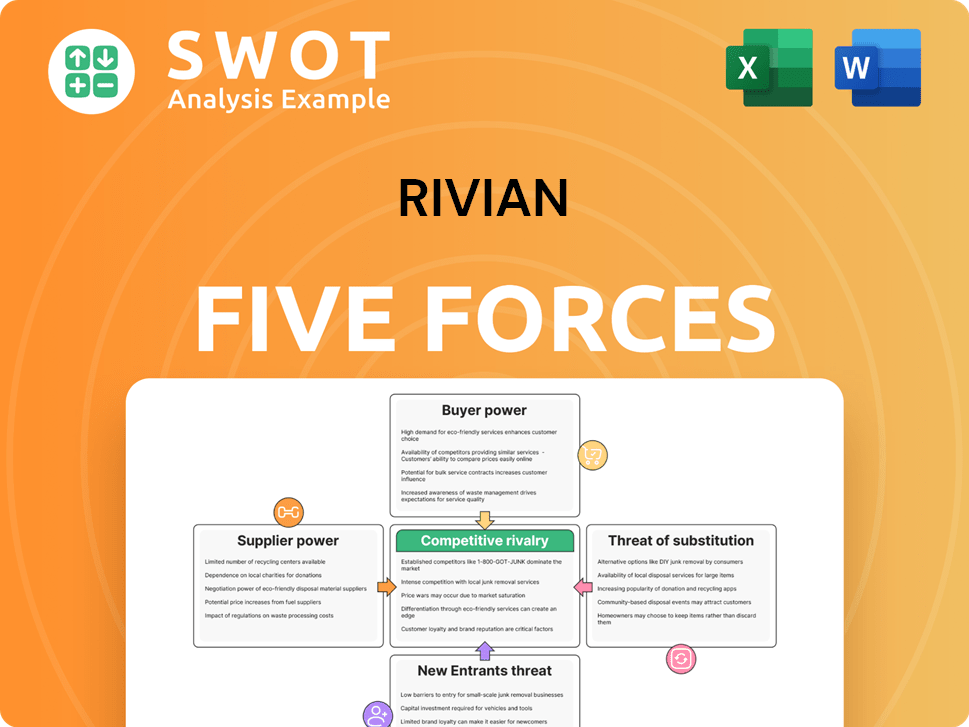
Rivian Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Rivian Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Rivian Company?
- How Does Rivian Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Rivian Company?
- What is Brief History of Rivian Company?
- Who Owns Rivian Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Rivian Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.