Standard Chartered Bundle
How did a bank born in 1853 become a global financial powerhouse?
Journey back in time to 1853, when a visionary Scottish businessman laid the foundation for a banking empire. This marked the beginning of the Standard Chartered SWOT Analysis, a financial institution that would reshape global trade and finance. From its roots in London to its vast presence across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, the story of Standard Chartered is one of remarkable growth and adaptation.
The SCB history is a compelling narrative of strategic foresight and resilience. This article delves into the Standard Chartered Bank's early years, its expansion across continents, and its pivotal role in international trade. Explore the key milestones, mergers, and innovations that have shaped Standard Chartered into a leading global bank, examining its impact on developing countries and its ability to navigate challenges within the ever-evolving landscape of global banking.
What is the Standard Chartered Founding Story?
The story of Standard Chartered Bank, a prominent player in global finance, begins with the convergence of two distinct banking institutions. The present-day entity emerged from the merger of The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China, and Standard Bank of British South Africa in 1969.
This union created a financial powerhouse with a broad reach across Asia and Africa, poised to capitalize on the expanding trade between Europe, Asia, and Africa. The combined entity offered a comprehensive suite of services, from trade finance to wealth management, across diverse markets.
Understanding the Owners & Shareholders of Standard Chartered is crucial to grasping the bank's evolution and influence.
The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China, one of the founding pillars of what is now Standard Chartered Bank, was established on December 29, 1853, in London. The bank's primary objective was to facilitate the growing trade between Europe, India, and China.
- James Wilson, a Scottish businessman and politician, founded The Chartered Bank and received a Royal Charter from Queen Victoria.
- The bank quickly expanded, opening branches in Mumbai (Bombay), Kolkata (Calcutta), and Shanghai in 1858, followed by Hong Kong and Singapore in 1859.
- The Chartered Bank played a vital role in financing traditional trade routes, handling commodities like cotton, indigo, tea, and silk.
- In 1862, it became one of the first banks to issue banknotes in Hong Kong dollars.
Simultaneously, the Standard Bank of British South Africa was founded in London in 1862 by John Paterson. It began operations in Port Elizabeth in 1863.
- Standard Bank was instrumental in financing the development of the diamond fields in Kimberley from the 1870s and later the gold fields in Johannesburg from 1886.
- By 1953, Standard Bank had grown to have over 600 offices across Southern, Central, and Eastern Africa.
- The merger of these two banks in 1969 was a strategic move to combine their extensive networks in Asia and Africa.
Standard Chartered SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Standard Chartered?
Following the 1969 merger, Standard Chartered Bank experienced significant growth, leveraging the combined networks of the Chartered Bank and Standard Bank. This expansion focused on emerging markets across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. This strategic direction has been a defining feature of the bank's operations. The bank's history is closely tied to British banking and its global reach.
Before the merger, in 1957, Chartered Bank acquired the Eastern Bank and established branches in the Gulf region. Post-merger, Standard Chartered Bank solidified its global footprint. A key milestone was entering the Southeast Asian market, becoming the first foreign bank licensed in Malaysia in 1957. In 1986, it was among the first foreign banks to establish a branch in China after economic reforms.
The bank expanded services and geographical reach, emphasizing cross-border capabilities and wealth management. In 2024, Standard Chartered reported a record income of $19.7 billion, with a strong performance in its Wealth Solutions business, which saw a 29% increase. This focus has been a key driver of success. For more details on their strategic approach, you can read about the Target Market of Standard Chartered.
Digital platforms, such as Straight2Bank (S2B), have played a crucial role in Standard Chartered's growth, maintaining high penetration (90%) and utilization (80%). The bank invested $1.5 billion over five years in wealth and digital platforms. In 2024, the bank added 265,000 new affluent clients, boosting its priority and private bank net new money by 61% to $43.6 billion.
Standard Chartered's robust financial performance in 2024, with a 43% increase in pre-tax profit for its Kenyan entity, underscores its continued growth momentum. The bank's focus on emerging markets and digital innovation has allowed it to adapt to changing markets. This global banking approach has helped the bank to maintain a strong presence in various regions.
Standard Chartered PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Standard Chartered history?
The SCB history is marked by significant milestones, reflecting its growth and adaptation in the global banking landscape. From its early days facilitating international trade to its modern digital initiatives, Standard Chartered has consistently evolved to meet the changing needs of its customers and the market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1853 | The company was founded in London by Scottish merchant James MacGregor. |
| 1869 | Played a key role in facilitating trade after the opening of the Suez Canal. |
| 1871 | Extended the telegraph to China, further enhancing its trade capabilities. |
| 1969 | Merged with The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China to form Standard Chartered Bank. |
| 1980s | Navigated a period of change, including divestments and fending off a hostile takeover bid. |
| 2024 | Generated $982 million in income from sustainable finance, a 36% increase from the previous year. |
| 2025 | Launched an AI-powered video column, the 'Standard Chartered Wealth Management FX Intelligent Expert,' providing real-time FX market insights. |
Standard Chartered has been at the forefront of innovation, particularly in leveraging technology. The bank's commitment to digital transformation is evident through its use of AI and content workflow tools like Adobe Experience Manager and Adobe Workfront.
In February 2025, the bank launched an industry-first AI-powered video column, the 'Standard Chartered Wealth Management FX Intelligent Expert,' providing real-time FX market insights to clients.
Standard Chartered is an early adopter of generative AI, using it to enhance customer experience and streamline operations.
The bank utilizes tools like Adobe Experience Manager and Adobe Workfront to accelerate digital transformation and improve personalization and productivity.
Despite its successes,
Standard Chartered has navigated global economic crises, demonstrating its ability to withstand financial instability.
The bank has adapted to evolving regulatory landscapes, ensuring compliance and maintaining its operational integrity.
In the 1980s, the bank successfully defended against a hostile takeover bid, showcasing its resilience.
Standard Chartered Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Standard Chartered?
The SCB history is a story of strategic expansion and adaptation, with key moments shaping its global presence. From its roots in London to its significant operations across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, the bank has navigated various economic climates and regulatory changes. Mergers and acquisitions have played a crucial role in its growth, alongside a commitment to digital innovation and sustainable finance. The following timeline highlights important milestones in the evolution of Standard Chartered Bank.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1853 | James Wilson founded The Chartered Bank of India, Australia, and China in London. |
| 1858 | The Chartered Bank opened its first branches in Mumbai, Kolkata, and Shanghai. |
| 1859 | Branches of The Chartered Bank opened in Hong Kong and Singapore. |
| 1862 | John Paterson established Standard Bank in British South Africa. |
| 1957 | The Chartered Bank became the first foreign bank to receive a banking license in Malaysia. |
| 1969 | Chartered Bank and Standard Bank merged to form Standard Chartered Bank. |
| 1986 | Standard Chartered established its first branch in China after economic reforms. |
| 2000 | Standard Chartered Bank was listed on the London Stock Exchange. |
| 2015 | The bank launched its digital banking platform. |
| 2024 | Standard Chartered reported record income of $19.7 billion, with wealth management income up 29%. The bank mobilized $982 million in sustainable finance income, a 36% increase from 2023. |
Standard Chartered is focusing on sustainable, inclusive growth. The bank is strategically emphasizing its wealth management and cross-border capabilities across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. A significant investment of $1.5 billion is planned over five years for wealth and digital platforms.
The bank aims to mobilize $300 billion in sustainable finance by 2030. In 2025, the bank targets $1 billion in annual sustainable finance income. Standard Chartered is also committed to achieving net-zero emissions from its operations.
The bank expects some moderate decline in profitability in 2025 due to restructuring expenses from its 'fit for growth' cost-saving initiative. However, momentum in its wealth management segment, especially in Hong Kong and Singapore, is expected to provide support.
Standard Chartered projects Islamic Finance assets to reach $7.5 trillion by 2028. This highlights the bank's commitment to expanding its services in key markets and adapting to evolving financial needs. The bank's purpose is to drive commerce and prosperity.
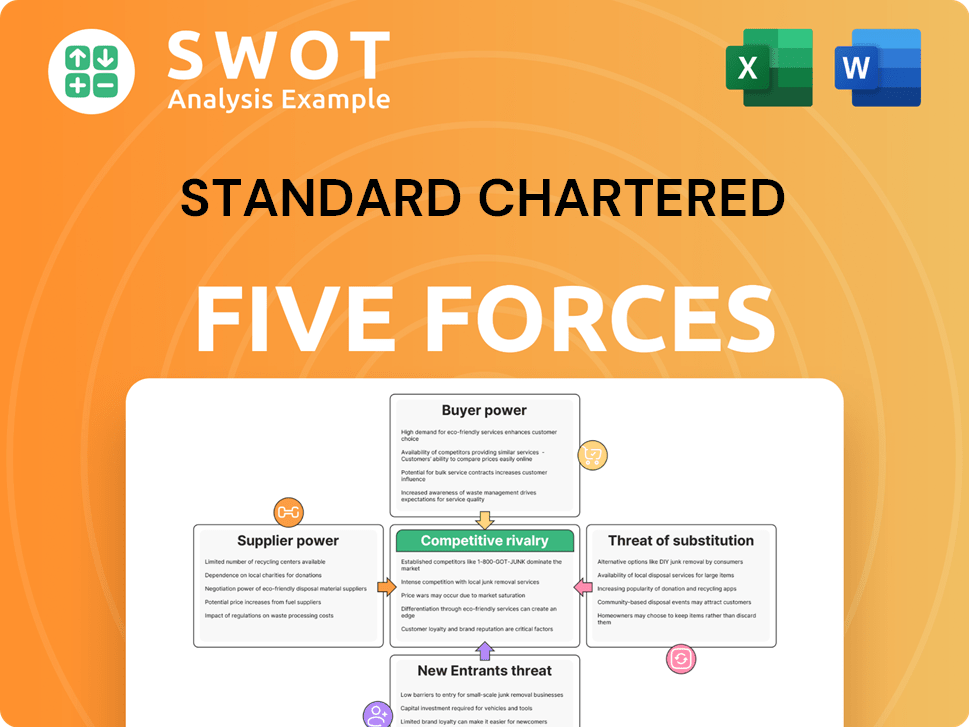
Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Standard Chartered Company?
- How Does Standard Chartered Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Brief History of Standard Chartered Company?
- Who Owns Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Standard Chartered Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.