Standard Chartered Bundle
How Does Standard Chartered Bank Thrive in Global Markets?
Standard Chartered, a titan in the international banking arena, offers a fascinating case study in financial services. With a strong foothold in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, this multinational banking and financial services company has built a diverse client base. Understanding the inner workings of Standard Chartered, from its Standard Chartered SWOT Analysis to its revenue streams, is key for anyone interested in global finance.
Delving into Standard Chartered's operations reveals a complex yet strategic approach to international banking. Its 2023 financial performance, marked by a significant profit increase, highlights its robust growth. This analysis will dissect the core of Standard Chartered's business model, examining its banking operations, revenue generation, and competitive advantages to provide a comprehensive understanding of its success in the financial services industry.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Standard Chartered’s Success?
Standard Chartered Bank (SCB) generates value through a comprehensive suite of financial services, primarily targeting corporate, institutional, and individual clients across its strategic markets in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Its core offerings span retail banking, wealth management, corporate and institutional banking, and private banking, providing a diverse range of products to meet varied financial needs. This approach allows SCB to cater to a broad client base, leveraging its global presence and localized expertise to offer tailored solutions.
The bank's operations are underpinned by extensive technological infrastructure, including digital platforms like the SC Mobile app and online banking portals. These platforms facilitate seamless customer interactions and transactions, enhancing efficiency and reducing reliance on physical branches. SCB also utilizes advanced analytics and AI to improve risk management, personalize customer offerings, and streamline back-office functions. This commitment to technological innovation is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving financial landscape.
SCB's global network, encompassing over 1,000 branches and offices in 53 markets, supports cross-border transactions and trade finance, a key area of its expertise. This robust distribution network, combined with partnerships and correspondent banking relationships, enables SCB to provide efficient services to its clients worldwide. This global reach allows SCB to offer enhanced access to international trade finance, sophisticated wealth management solutions, and efficient cross-border payment services, differentiating it from competitors with less established footprints in these regions. For more insights, see the Growth Strategy of Standard Chartered.
SCB's retail banking offers a range of services, including current and savings accounts, credit cards, mortgages, and personal loans. These services cater to the everyday financial needs of individual customers, providing convenient and accessible banking solutions. The bank's focus on digital platforms enhances the customer experience, making it easier to manage finances and access services.
The wealth management arm provides investment products, insurance, and financial planning advice. This segment focuses on helping clients grow and protect their wealth through tailored financial solutions. SCB's wealth management services are designed to meet the diverse needs of high-net-worth individuals and families.
This segment focuses on transaction banking (cash management, trade finance), financial markets (foreign exchange, interest rates, credit), and corporate finance (lending, advisory). SCB supports businesses with a wide range of financial services, facilitating their operations and growth. The bank's expertise in trade finance is particularly significant in its core markets.
SCB caters to high-net-worth individuals with tailored financial solutions. This includes personalized banking services, investment management, and wealth planning. Private banking clients receive specialized attention and access to exclusive financial products and services.
SCB's operational success is closely tied to its ability to navigate the complexities of international banking and financial services. The bank's strategic focus on emerging markets and its commitment to technological advancements drive its operations. SCB's ability to offer a wide range of financial products and services, combined with its global reach and localized expertise, is central to its value proposition.
- Digital Transformation: SCB has invested heavily in digital platforms, with SC Mobile and online banking portals enhancing customer experience. In 2024, the bank continued to expand its digital capabilities, with a focus on mobile banking and online services.
- Global Network: The bank's extensive network of branches and offices across 53 markets supports its international operations. This global presence is crucial for facilitating cross-border transactions and trade finance.
- Risk Management: SCB utilizes advanced analytics and AI to enhance risk management and ensure regulatory compliance. This focus on risk management is critical for maintaining financial stability and protecting client assets.
- Sustainability: SCB is committed to sustainable finance and corporate social responsibility. The bank integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into its business strategy.
Standard Chartered SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Standard Chartered Make Money?
Standard Chartered Bank (SCB) generates revenue through a diverse range of streams. Its financial success is primarily driven by two key categories: Net Interest Income (NII) and Non-Interest Income. These revenue streams are crucial in understanding how Standard Chartered operates and maintains its financial health.
Net Interest Income (NII) is a significant contributor to the bank's overall revenue. This income represents the difference between the interest earned on assets, such as loans, and the interest paid on liabilities, like customer deposits. Non-Interest Income encompasses various sources, including fees, commissions, trading activities, and other operational revenues.
In 2023, the Group's net interest income increased by 23% to $9.9 billion, driven by higher interest rates across its key markets. Total underlying operating income for Standard Chartered increased by 10% to $17.4 billion in the same year. This performance highlights the bank's robust revenue generation capabilities.
This is the difference between interest earned on assets (loans) and interest paid on liabilities (deposits).
This includes fees, commissions, trading income, and other operational revenues.
Derived from wealth management, trade finance, cash management, and credit card services.
Generated from activities in financial markets, including foreign exchange and fixed income.
Includes gains from investments and other miscellaneous income sources.
Increased by 30% to $2.2 billion in 2023, reflecting strong client demand.
SCB employs several monetization strategies to optimize its revenue streams. These include leveraging digital platforms for bundled services, applying tiered pricing models for corporate clients, and focusing on sustainable finance. These strategies help diversify its revenue base and enhance its financial resilience. For a deeper understanding of its origins, consider exploring the Brief History of Standard Chartered.
Standard Chartered employs various strategies to boost revenue and customer engagement.
- Bundled Services: Offering integrated banking and wealth management solutions via digital platforms.
- Tiered Pricing: Structuring service fees for corporate clients based on transaction volume and complexity.
- Sustainable Finance: Focusing on green bonds and ESG trends to attract environmentally conscious investors.
- Affluent Client Segment: Targeting affluent clients, particularly in Asia, to increase wealth management fees.
Standard Chartered PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Standard Chartered’s Business Model?
The trajectory of Standard Chartered Bank (SCB) has been marked by significant milestones and strategic decisions that have shaped its operations and financial performance. A key strategic move has been its sustained focus on and investment in its network across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, recognizing the substantial growth potential within these regions. The bank has consistently expanded its digital capabilities in these markets, launching innovative mobile banking platforms and digital payment solutions tailored to local customer needs.
SCB has also navigated operational and market challenges, including complex regulatory environments and global economic downturns. For instance, the bank has adapted its compliance frameworks to meet evolving anti-money laundering (AML) and sanctions regulations, investing heavily in technology and personnel. During periods of market volatility, Standard Chartered has demonstrated resilience through its diversified revenue streams and robust risk management frameworks. The bank's ability to adapt and innovate has been crucial for its sustained success in a dynamic global landscape.
Standard Chartered's competitive advantages are multifaceted, stemming from its strong brand presence and deep-rooted relationships in its core markets, some spanning over a century. Its leadership in technology, particularly in digital banking and transaction banking solutions, enables it to offer efficient and innovative services. Furthermore, its extensive network and expertise in facilitating cross-border trade and investment, especially along the Belt and Road Initiative corridors, give it a unique competitive edge. The bank's commitment to sustainability and its leadership in green finance also position it favorably with increasingly ESG-conscious clients and investors.
SCB's history includes significant mergers and acquisitions that expanded its global footprint. The bank's entry into new markets and the evolution of its service offerings have been key to its growth. Strategic partnerships have also played a vital role in enhancing its capabilities and market reach.
The bank has strategically invested in digital transformation to improve customer experience. Expansion into high-growth markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, has been a consistent focus. SCB has also emphasized sustainable finance and ESG initiatives to align with evolving market demands.
SCB leverages its established brand and long-standing relationships in key markets. Its technology leadership in digital banking and transaction services provides a competitive advantage. Expertise in cross-border trade and investment, including along the Belt and Road Initiative, is also a key strength.
In recent financial reports, such as the 2024 annual report, SCB has highlighted its strong performance in key markets. The bank's revenue streams are diversified across various business segments, including corporate and institutional banking, consumer, private banking, and wealth management. SCB's commitment to cost efficiency and risk management has helped maintain profitability. The bank's Return on Tangible Equity (RoTE) is a key metric that reflects its financial performance.
SCB continues to adapt to new trends, such as the rise of fintech and increasing demand for sustainable financial products, by forming strategic partnerships and investing in new technologies. The bank is focused on expanding its digital banking services and enhancing its customer experience through innovative solutions. SCB's commitment to sustainability and ESG principles is expected to drive future growth and attract environmentally conscious investors.
- Expansion of digital banking platforms and services.
- Strategic partnerships to enhance technological capabilities.
- Focus on sustainable finance and ESG initiatives.
- Continued investment in risk management and compliance.
For a deeper understanding of how SCB competes in the financial landscape, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Standard Chartered.
Standard Chartered Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Standard Chartered Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
Standard Chartered Bank (SCB) holds a distinctive position in the global banking industry, particularly due to its strong presence in high-growth emerging markets. Although it may not have the same global market share as some of the largest universal banks, its focus on Asia, Africa, and the Middle East gives it significant market share and customer loyalty in these regions. Its extensive network and long-standing relationships offer a strong competitive advantage against both local and international rivals. For instance, in trade finance, SCB is consistently recognized as a leading provider, leveraging its network to facilitate global trade flows.
However, Standard Chartered faces several key risks that could impact its operations and revenue. These include geopolitical risks and economic instability in its core markets, regulatory changes and compliance burdens, and the intensifying competition from fintech companies and digital challengers. Fluctuations in commodity prices can also affect its clients and, consequently, the bank's loan book quality, given its exposure to resource-rich economies. Furthermore, the ongoing global push for de-dollarization and the rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) present both opportunities and potential disruptions to its traditional business model.
SCB's specialized focus on Asia, Africa, and the Middle East provides a competitive advantage. It has a strong presence in trade finance, facilitating global trade flows. The bank's long-standing relationships and extensive network are key strengths in these markets.
Geopolitical risks and economic instability in core markets pose significant challenges. Regulatory changes and competition from fintech companies are also major concerns. Fluctuations in commodity prices and the shift towards de-dollarization present additional risks.
The bank is investing heavily in digital transformation to enhance customer experience and improve efficiency. It aims to grow its wealth management business, especially in Asia. SCB plans to leverage its footprint to facilitate trade and investment, sustaining profitability.
Focus on digital transformation and enhancing customer experience. Expansion of wealth management services, particularly in Asia. Capitalizing on trade and investment corridors within core markets. Disciplined capital allocation and prudent risk management.
Standard Chartered is focused on driving shareholder value through disciplined capital allocation and prudent risk management. The bank is investing in digital transformation to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. SCB aims to capitalize on the increasing demand for sustainable finance solutions and drive further growth in its wealth management business, particularly in Asia.
- Digital transformation initiatives to improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Expansion of wealth management services, especially in Asia.
- Focus on sustainable finance solutions to meet growing demand.
- Disciplined capital allocation and prudent risk management to drive shareholder value.
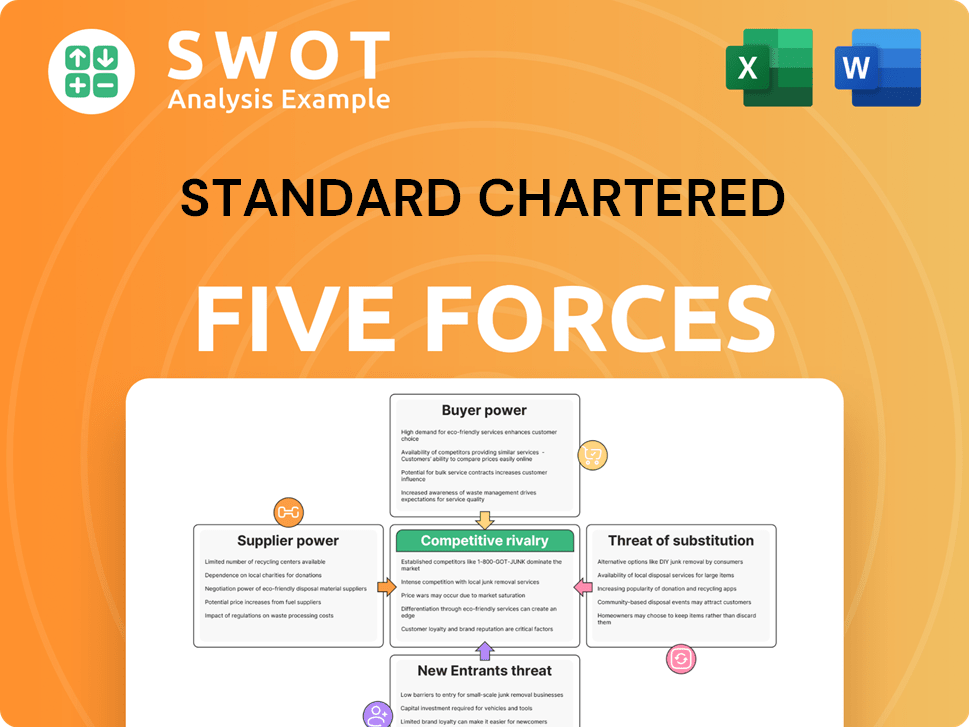
Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Brief History of Standard Chartered Company?
- Who Owns Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Standard Chartered Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.