Standard Chartered Bundle
Who Truly Controls Standard Chartered?
Understanding the Standard Chartered SWOT Analysis is crucial, but have you ever wondered who pulls the strings behind this global financial giant? The Standard Chartered ownership structure is a complex web of institutional investors, public shareholders, and historical influences, all vying for a piece of the pie. Knowing who owns Standard Chartered is key to understanding its strategic direction and future prospects.
From its humble beginnings as a bank serving expanding trade routes to its current status as a multinational powerhouse, Standard Chartered's history is rich with evolution. This exploration will unravel the Standard Chartered ownership structure, revealing the major players shaping its destiny, including Standard Chartered shareholders. Discovering the Standard Chartered parent company and its influence offers insights into the bank's global presence and strategic decisions. We'll also look at where Standard Chartered headquarters is located.
Who Founded Standard Chartered?
The story of Standard Chartered's ownership begins with the separate foundations of two banks: The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China, and the Standard Bank of British South Africa. These banks, which later merged to form the modern-day entity, each had their unique origins and initial ownership structures.
The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China, established in 1853, was the brainchild of James Wilson, a Scottish businessman. Wilson secured a royal charter from Queen Victoria to establish the bank. The Standard Bank of British South Africa, on the other hand, was founded in 1862 by John Paterson, a Scot from the Cape Colony. Paterson's bank began operations in 1863.
While precise details on the initial equity splits or specific shareholders of these early banks are not readily available in public records, their establishment involved groups of investors and backers. These individuals saw opportunities in the expanding trade between Europe, Asia, and Africa. The banks grew by facilitating trade and financing key industries in their respective regions.
Founded in 1853 by James Wilson. It was granted a royal charter. This bank focused on facilitating trade between Europe, India, and China.
Founded in 1862 by John Paterson. It started operations in Port Elizabeth in 1863. The bank played a key role in financing the diamond and gold industries.
Initial ownership involved groups of investors. These investors aimed to capitalize on trade expansion. The focus was on supporting trade and key industries.
Growth was fueled by facilitating trade and financing industries. The banks supported key sectors in their regions. They expanded their networks to serve growing markets.
The banks' establishment reflected the era's economic opportunities. They responded to the increasing global trade. Their growth mirrored the expansion of colonial economies.
Specific equity splits are not available. Details of initial shareholders are limited. The focus was on establishing banking services.
Understanding the Standard Chartered's target market is crucial to understanding its operations. The early ownership structure of Standard Chartered, therefore, was rooted in the collaborative efforts of investors who recognized the potential of international trade and economic expansion. The bank's history shows a transition from these early ownership groups to its current structure as a publicly traded company with a diverse shareholder base. The company's headquarters are located in London, United Kingdom. As of 2024, the bank continues to operate globally, offering a range of financial services.
Standard Chartered's origins lie in the 19th century with two distinct banks.
- The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China was founded in 1853.
- The Standard Bank of British South Africa was founded in 1862.
- Early ownership involved groups of investors.
- The banks facilitated trade and financed key industries.
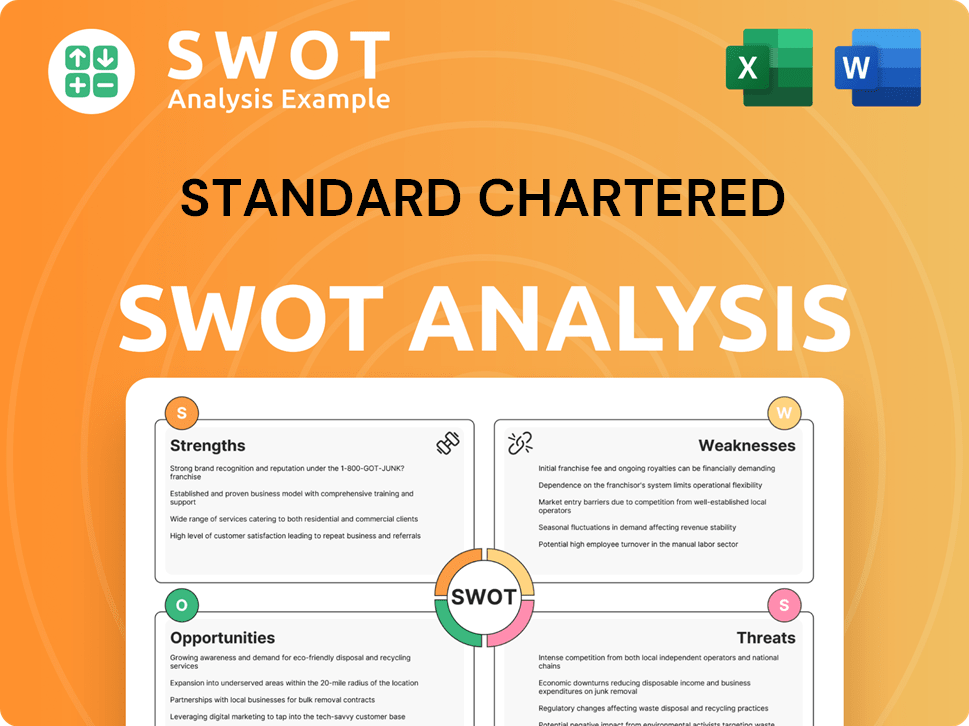
Standard Chartered SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Standard Chartered’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The formation of Standard Chartered Bank in 1969, through the merger of The Chartered Bank and The Standard Bank, was a pivotal moment in its ownership history. This merger, which established the bank with its headquarters in London, set the stage for its future as a global financial institution. The company's evolution continued with its listing on the London Stock Exchange and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 2000, making it a publicly traded entity. As of June 13, 2025, the market capitalization of Standard Chartered is approximately $36.54 billion, reflecting its significant presence in the financial markets.
The ownership structure of Standard Chartered has evolved over time, involving strategic acquisitions and changes in major stakeholders. In 1987, Lloyds Bank acquired Standard Chartered, though the bank continued to operate independently. Later, in 2000, the acquisition of Grindlays Bank further expanded its operations, particularly in India. These strategic moves have played a crucial role in shaping the bank's global presence and its focus on emerging markets. This history is intertwined with the question of Growth Strategy of Standard Chartered, which has been significantly influenced by its ownership and strategic decisions.
| Ownership Category | Percentage of Shares (Approximate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Temasek Holdings | 17% | Government of Singapore-owned sovereign wealth fund. |
| Institutional Investors | 56.54% | Includes BlackRock, Vanguard Group, and various pension funds. (As of June 1, 2025) |
| Individual Insiders | 0.197% | |
| Employee Share Schemes | 1.59% | |
| VC/PE Firms | 17.7% | |
| General Public | 14.2% |
The current ownership structure of Standard Chartered is diversified, with a significant portion held by institutional investors. Temasek Holdings is a major stakeholder, holding a 17% stake. Other key institutional investors include BlackRock and Vanguard Group. As of June 1, 2025, institutional ownership accounts for 56.54% of the shares. Individual insiders hold a smaller portion, approximately 0.197%, while employee share schemes account for about 1.59%. VC/PE firms hold 17.7% and the general public holds 14.2%, reflecting a broad base of shareholders. This structure highlights the bank's status as a publicly traded company with a global investor base.
Understanding the ownership of Standard Chartered is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
- Temasek Holdings is a significant shareholder.
- Institutional investors hold a majority stake.
- The bank is publicly traded on major stock exchanges.
- The ownership structure reflects its global presence.
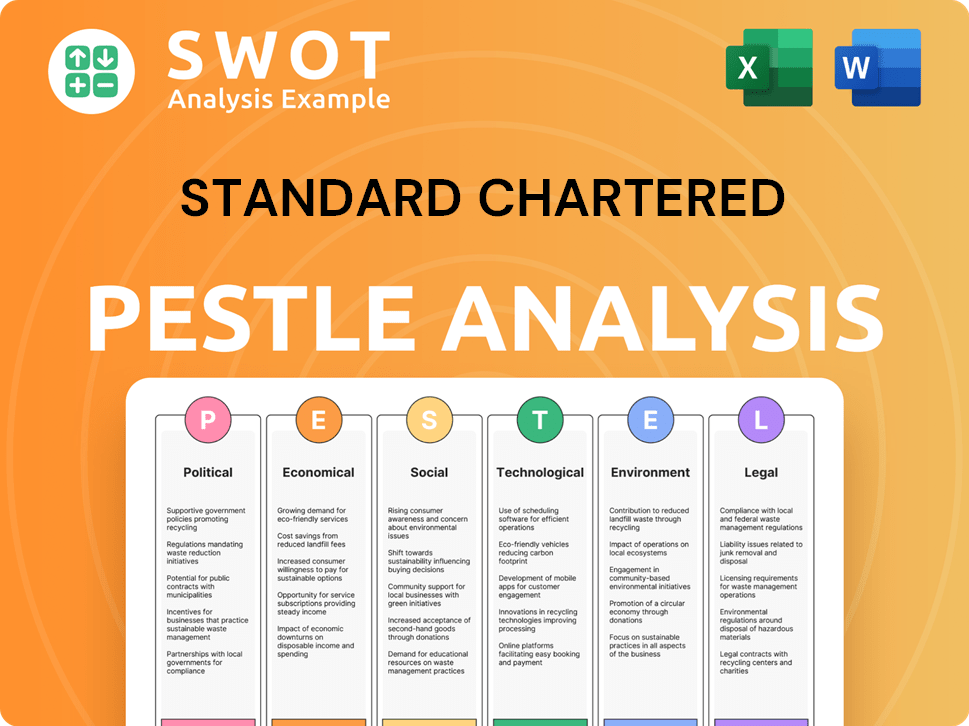
Standard Chartered PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Standard Chartered’s Board?
As of May 2025, the leadership of Standard Chartered includes Maria Ramos as Group Chairman and Bill Winters as Group Chief Executive Officer, a position he has held since June 2015. Diego De Giorgi has served as the Group Chief Financial Officer and a Director since January 2024. The Board of Directors also includes independent non-executive directors, playing a vital role in the company's governance.
Recent changes to the Board and its committees were announced in December 2024. David Conner retired from the Board and its committees on December 30, 2024. Diane Jurgens and Jackie Hunt joined the Board Risk Committee on January 1, 2025, while David Tang stepped down from the same committee on that date. David Tang and Jackie Hunt also joined the Remuneration Committee effective January 1, 2025. Jason Forrester replaced Tracey McDermott on Standard Chartered Bank AG's Supervisory Board, also effective January 1, 2025.
| Position | Name | Since |
|---|---|---|
| Group Chairman | Maria Ramos | May 2025 |
| Group Chief Executive Officer | Bill Winters | June 2015 |
| Group Chief Financial Officer & Director | Diego De Giorgi | January 2024 |
Following the annual general meeting on May 10, 2024, Standard Chartered PLC's share voting structure was updated, granting ordinary shareholders one vote per ordinary share. As of May 31, 2025, the total voting rights comprised 2,347,882,467 ordinary shares, each valued at US$0.50. The free float percentage of voting rights was approximately 75.40% as of March 31, 2025. This structure impacts the Standard Chartered ownership and the influence of Standard Chartered shareholders.
Understanding the Standard Chartered ownership structure is key to grasping the company's direction. The voting rights structure, as well as the role of independent directors, influences decision-making. For a deeper dive into how the company approaches its market strategies, see the Marketing Strategy of Standard Chartered.
- The free float percentage of voting rights was approximately 75.40% as of March 31, 2025.
- The company's leadership includes Maria Ramos as Group Chairman and Bill Winters as Group Chief Executive Officer.
- Independent non-executive directors are critical to the governance structure.
- Shareholders have one vote for every ordinary share they hold.
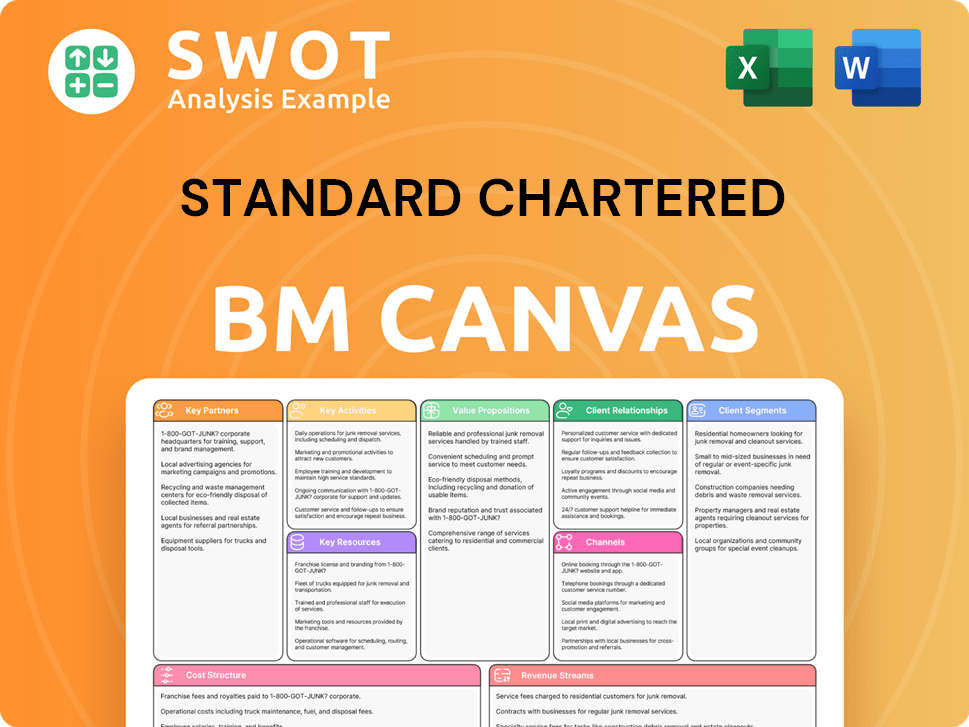
Standard Chartered Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Standard Chartered’s Ownership Landscape?
Recent developments in the ownership structure of Standard Chartered reflect a focus on enhancing shareholder value. The bank has been actively engaged in share buybacks and dividend increases. In February 2025, a new $1.5 billion share buyback program was announced. This is part of a larger plan to return at least $8 billion to shareholders through buybacks and dividends by 2026. As of March 31, 2025, the bank had repurchased 28 million shares, equivalent to 1.17% of outstanding shares, for $431 million. Further repurchases occurred in May 2025, with 1.2 million shares bought for £13.2 million. These actions have reduced the share count significantly.
These share buybacks and dividend payouts signal a commitment to rewarding investors. The bank's Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio, standing at 14.2% as of December 2024, supports this financial flexibility. The CET1 ratio is above its target range of 13-14%. Despite macroeconomic uncertainties, the bank maintains a strong financial position. Institutional ownership is also a key factor, reaching 56.54% as of June 1, 2025, indicating confidence from major investors. The bank's strategic focus on high-growth markets has also contributed to its financial success, with record income in 2024.
| Metric | Details | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Share Buyback Program (February 2025) | New Program Announced | $1.5 billion |
| Total Shareholder Returns by 2026 | Committed Returns | At least $8 billion |
| Shares Repurchased (by March 31, 2025) | Number of Shares | 28 million |
| Shares Repurchased (by March 31, 2025) | Percentage of Outstanding Shares | 1.17% |
| Cost of Shares Repurchased (by March 31, 2025) | Total Cost | $431 million |
| Institutional Ownership (June 1, 2025) | Percentage of Ownership | 56.54% |
| CET1 Ratio (December 2024) | Capital Adequacy | 14.2% |
| Income from High-Growth Markets (2024) | Record Income | $19.7 billion |
| Stock Price Increase (Last Year) | Investor Optimism | 91% |
Leadership changes also mark recent developments. Simon Cooper's departure in March 2024, and the subsequent appointments of Roberto Hoornweg and Sunil Kaushal, reflect strategic adjustments. Zarin Daruwala's retirement as CEO of Standard Chartered in India and South Asia on April 1, 2025, further highlights the ongoing evolution of the bank's management team. These changes, combined with the ownership trends, shape the bank's future. For a deeper understanding of the bank's history and background, consider exploring information about the company's profile.
The ownership of Standard Chartered is characterized by a mix of institutional and individual investors. Institutional investors hold a significant portion of the shares, reflecting confidence in the bank's performance and strategic direction. The bank's focus on shareholder value through buybacks and dividends is also a key factor.
Major investors in Standard Chartered include a variety of institutional shareholders. While specific names and exact holdings can fluctuate, these large investors play a crucial role in the bank's strategic decisions and financial performance. The bank's stock ownership is a dynamic landscape.
To buy Standard Chartered stock, investors typically need to use a brokerage account. The process involves researching the stock, opening an account, and placing a buy order. Investors should consider factors like financial performance and market trends before investing.
Standard Chartered's financial performance is a key indicator of its stability and growth potential. Factors such as revenue, profitability, and asset quality are closely monitored by investors. The bank's recent financial results reflect its strategic focus on high-growth markets.
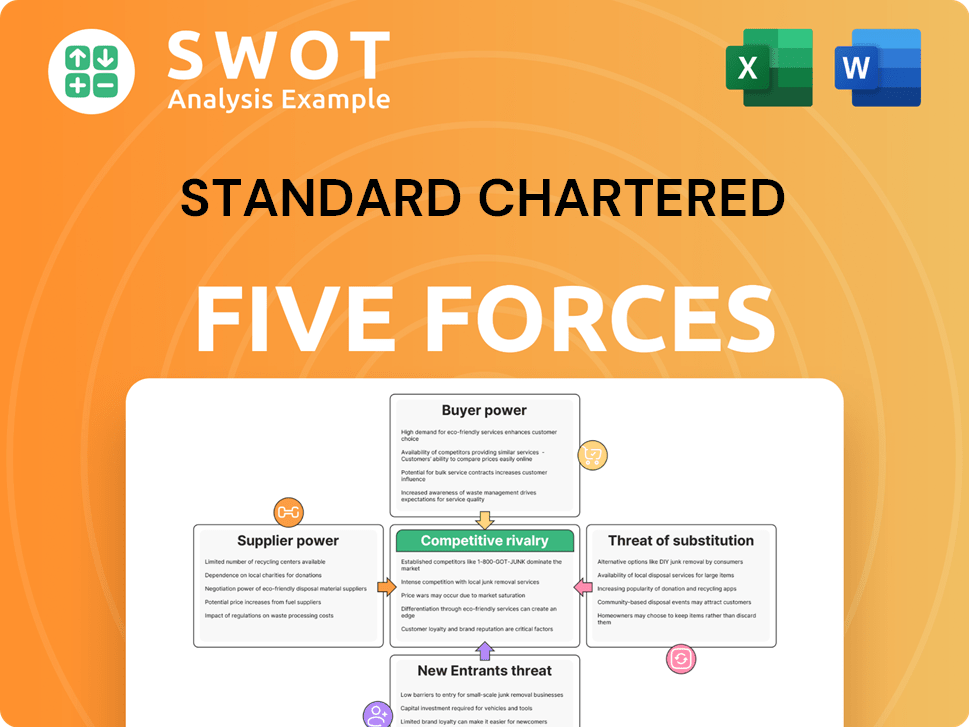
Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Standard Chartered Company?
- How Does Standard Chartered Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Brief History of Standard Chartered Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Standard Chartered Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.