Sony Bundle
How did a small Japanese startup become a global icon like Sony?
Sony's story is a testament to innovation and resilience, a journey from post-war Japan to a global entertainment and technology giant. From pioneering the transistor radio to revolutionizing the music industry with the Walkman, Sony has consistently redefined what's possible. Founded by visionary leaders, the Sony SWOT Analysis reveals the company's strategic evolution.
This brief history of Sony company explores its remarkable evolution, tracing its early days from Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo to its current status. Discover who founded Sony and the key milestones that shaped Sony's timeline, including its impact on the consumer electronics market and its expansion into diverse industries. Learn about Sony's first products and innovations, and how it overcame challenges to become a global leader.
What is the Sony Founding Story?
The story of the Sony company, a global giant in consumer electronics and entertainment, began in post-World War II Japan. The company's journey from a small repair shop to a multinational corporation is a testament to innovation, strategic vision, and adaptability. Understanding the Sony history provides valuable insights into the evolution of the consumer electronics market and the impact of technological advancements.
The Sony company's roots are firmly planted in the aftermath of World War II, a time of rebuilding and innovation in Japan. This period set the stage for the company's founding and early development. The founders saw opportunities in the demand for radio repairs and the potential for new electronic products.
The Sony timeline is marked by several key milestones, starting with the company's founding and progressing through significant product launches and market expansions. These milestones reflect the company's commitment to innovation and its ability to adapt to changing market dynamics. The company's story is a compelling example of how vision and innovation can transform a small startup into a global leader.
The journey of Sony began on May 7, 1946, when Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita established Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo K.K. (Tokyo Telecommunications Engineering Corporation). Ibuka, an electronics engineer, and Morita, a physicist, had previously collaborated during wartime research. The company's initial capital was ¥190,000, and it started with eight employees.
- The initial business focused on radio repairs and manufacturing simple consumer electronics.
- The first product was an electric rice cooker, which had limited success.
- The company's first significant product was the Type-G magnetic tape recorder, launched in 1950.
- The company's vision was to create an 'ideal factory' that embraced freedom, open-mindedness, and technological contributions to Japanese culture.
The name 'Sony' was adopted in 1958, a combination of 'sonus' (Latin for sound) and 'sonny,' representing a group of young innovators. This name change was driven by global ambitions as the original name was difficult for non-Japanese speakers to pronounce. The company went public in August 1955 and was listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange in December 1958. The company's early focus on innovation and product development laid the foundation for its future success. For more insights into how Sony has maintained its market position, consider exploring the Marketing Strategy of Sony.
Sony SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Sony?
The early growth of the company, now known as the Sony Corporation, was characterized by its strategic entry into new product categories and ambitious global expansion. This period saw the company establish itself as a leader in consumer electronics through innovative products and aggressive market strategies. From its initial focus on transistor radios, the company rapidly expanded its product line and geographic reach, setting the stage for its future success and influence in the global market. This Sony history is a testament to its innovative spirit.
A pivotal moment in the Sony company's early development was the acquisition of transistor technology from Bell Laboratories in the early 1950s. Instead of focusing on military applications, the company aimed to apply transistors to consumer products. This led to the release of Japan's first commercially produced transistor radio, the Sony TR-55, in August 1955. The TR-63, released in 1957, further solidified the company's reputation. By the end of 1968, annual sales of portable transistor radios reached 5 million units, showcasing the impact of these early products.
In 1960, the company established its first U.S. subsidiary, Sony Corporation of America, and became the first Japanese company listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 1970. That same year, the company released the world's first non-projection type all-transistor and portable television, the Sony TV8-301. The company continued its expansion with the launch of the world's first compact transistor VTR, the PV-100, in 1961. These moves marked the beginning of the Sony evolution.
A significant innovation in television technology came in 1968 with the introduction of the Trinitron color television, which earned the company an Emmy in 1973, the first such award for an electronics company. During the 1970s and 1980s, the company experienced rapid revenue and profit growth. Key product launches during this period included the Betamax VCR in 1975 and the revolutionary Walkman portable audio player in 1979, which sold millions of units globally. For more information on the company's core values, check out Mission, Vision & Core Values of Sony.
In 1982, in collaboration with Philips, the company launched the world's first Compact Disc (CD) player, the CDP-101, which became an industry standard for digital audio. The company also introduced the 3.5-inch floppy disk structure in 1981, which quickly became a de facto standard. This period saw the company diversifying beyond electronics, notably acquiring CBS Records in 1988 and Columbia Pictures in 1989, entering the entertainment industry. The Sony timeline is filled with these milestones.
Sony PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Sony history?
The Sony history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped the consumer electronics industry. From its humble beginnings to its global presence, the Sony company has consistently pushed boundaries. The Sony timeline showcases a journey of innovation, resilience, and strategic adaptation, reflecting its evolution over several decades.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1955 | Launched the TR-55 transistor radio, marking an early success in portable electronics. |
| 1968 | Introduced the Trinitron color television, which set new standards for picture quality. |
| 1979 | Released the Walkman, revolutionizing personal audio and becoming a global phenomenon. |
| 1982 | Co-developed the Compact Disc (CD) with Philips, transforming the music industry. |
| 1994 | Entered the home video game console market with the launch of the PlayStation. |
Sony products have consistently demonstrated technological prowess. The company's innovations, from the Walkman to the PlayStation, have significantly impacted how people consume media and entertainment. Sony's evolution has been defined by its ability to anticipate and adapt to changing market demands.
The TR-55 transistor radio was one of Sony's first products and innovations, establishing its reputation for miniaturization and quality. This portable device was a key step in Sony's origins and development.
The Trinitron color television set a new benchmark for picture quality, earning an Emmy award in 1973. This innovation showcased Sony's commitment to superior visual technology.
The Walkman revolutionized personal audio, allowing people to enjoy music on the go. The story behind the Sony Walkman is one of cultural impact and technological advancement.
Co-developing the CD with Philips transformed the music industry. The CD provided superior audio quality and durability compared to vinyl records, changing how Sony changed the music industry.
The PlayStation marked Sony's contribution to gaming history, becoming a major player in the video game console market. PlayStation 2 is the best-selling console in history, with over 155 million units sold.
Sony played a leading role in the development of the Blu-ray optical disc format. Blu-ray became the standard for HD media after winning the format war against HD DVD.
Despite its successes, Sony has faced numerous challenges. The 'Betamax vs. VHS' format war was a setback, and the company experienced financial difficulties in the early 1990s. The company has had to adapt to shifting market dynamics and intense competition. For an in-depth look at how Sony has navigated these challenges, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Sony.
The format war with VHS was a significant challenge, with Betamax losing market share despite its technological advantages. This highlighted the importance of market adoption and strategic partnerships.
The early 1990s saw Sony facing economic challenges, including the Japanese recession. The company declared its first loss of over $200 million in 1993, impacting its financial performance.
From the mid-1990s, Sony experienced a decline in market share in some areas, partly due to internal changes. This decline underscored the need for continuous innovation and adaptation.
Sony has undertaken strategic restructuring efforts, such as the 2021 renaming to Sony Group Corporation. These changes aimed to streamline operations and adapt to evolving market conditions.
The consumer electronics market is highly competitive, requiring Sony to continually innovate. Competition from other major players has put pressure on Sony to maintain its market position.
Sony has had to adapt to digital trends, including streaming and cloud services, to stay relevant. The company has invested heavily in these areas to meet changing consumer preferences.
Sony Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Sony?
The Sony timeline is a story of innovation and adaptation, from its humble beginnings to its global presence. Founded in 1946 as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo K.K., the company, led by Sony founder Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita, quickly established itself as a pioneer in consumer electronics. Over the decades, Sony's evolution has seen it introduce groundbreaking products, expand into diverse industries, and navigate significant market shifts. This journey reflects a commitment to technological advancement and a deep understanding of consumer needs, solidifying its place as a cultural and technological icon.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1946 | Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita establish Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo K.K. in Tokyo, Japan. |
| 1950 | Japan's first magnetic tape recorder, the Type-G, is launched. |
| 1955 | Japan's first transistor radio, the TR-55, is released, showcasing early Sony products. |
| 1958 | The company officially changes its name to Sony Corporation. |
| 1960 | Sony Corporation of America (SCA) is established in the U.S., and the world's first portable transistor TV, the TV8-301, is launched. |
| 1968 | The 'Trinitron' color TV, the KV-1310, is launched. |
| 1970 | Sony becomes the first Japanese company to be listed on the New York Stock Exchange. |
| 1979 | The iconic Walkman portable stereo cassette player (TPS-L2) is launched. |
| 1982 | The world's first CD player, the CDP-101, is launched in collaboration with Philips. |
| 1988 | Sony acquires CBS Records, later renamed Sony Music Entertainment. |
| 1989 | Sony expands into the film industry by purchasing Columbia Pictures. |
| 1994 | Sony Computer Entertainment (now Sony Interactive Entertainment) launches the PlayStation home video game console in Japan, a pivotal moment in Sony's gaming history. |
| 2006 | The first Blu-ray players become commercially available, with Sony being a leading developer of the format. |
| 2021 | The company is renamed Sony Group Corporation, transitioning to a holding company structure. |
| Fiscal Year 2024 (ending March 2025) | Sony reports a net profit of 1.14 trillion yen ($7.7 billion), an 18% increase year-over-year; the Game & Network Services division's operating income jumped 43% to ¥414.8 billion ($2.8 billion). |
| Fiscal Year 2025 (ending March 2026) | Sony forecasts a nearly 13% decline in net profit to 930 billion yen ($6.3 billion) and an 8% decline in sales for its Game & Network Services division to ¥4.3 trillion (€26.36 billion), mainly due to expected declines in console sales. |
Sony is focused on creating seamless digital entertainment experiences by integrating its products with content and services. This strategy aims to enhance user engagement and provide a comprehensive entertainment ecosystem. This approach is central to Sony's future growth plans, ensuring it remains competitive in the evolving digital landscape.
The company is emphasizing the strengthening of its core business segments, including digital imaging, televisions, and gaming. In gaming, Sony anticipates stable growth in revenue and profit from network businesses due to an increase in monthly active users and higher revenue from PlayStation Plus. They are also focusing on profitable peripherals like the PlayStation Portal.
Sony is committed to ongoing investments in research and development, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, 5G, and next-generation imaging. These investments are critical for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly changing technology landscape. The company's focus on technology is consistent with its founding vision.
Sony expects further growth in its studio business, driven by new titles like 'Ghost of Yōtei' and 'Marathon,' as well as ongoing titles like 'HELLDIVERS 2'. Despite a projected decline in overall sales for the Game & Network Services division, operating profit for the gaming business is expected to rise by almost 16% due to increased sales of first-party game software titles.
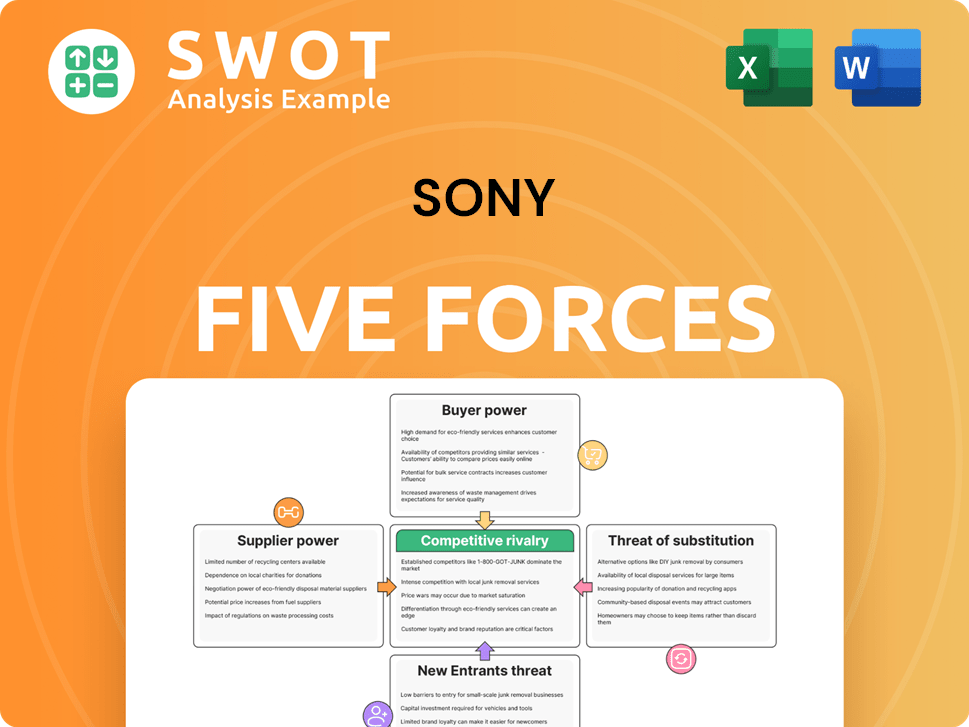
Sony Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Sony Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Sony Company?
- How Does Sony Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sony Company?
- What is Brief History of Sony Company?
- Who Owns Sony Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sony Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.