Vroom Bundle
How Did Vroom Revolutionize Car Buying?
The automotive landscape has been dramatically reshaped by digital platforms, and Vroom's story is one of significant innovation. Founded in 2013, the Vroom SWOT Analysis reveals a fascinating journey from a New York City startup to a key player in online car sales. This brief history of Vroom explores how this company transformed the traditional car buying experience.
Vroom's commitment to Vroom online car sales was a pivotal move, aiming to offer a seamless experience for buying and selling Vroom used cars. The company's early focus on transparent pricing and home delivery challenged the status quo of physical dealerships. Understanding the Vroom company timeline helps to see how it navigated challenges and capitalized on opportunities in the competitive market.
What is the Vroom Founding Story?
The story of the company, now known as Vroom, began in 2013. It was the brainchild of Kevin Westfall, Paul Walborsky, and Allon Bloch, who initially launched their venture under the name Honk Honk. Their goal was to revolutionize the used car market.
The founders recognized the inefficiencies and lack of transparency in the traditional used car market. They envisioned an online platform that would streamline the buying and selling process. This platform aimed to provide a better customer experience through technology.
Vroom's initial strategy involved acquiring used vehicles and reselling them directly to consumers online. This direct-to-consumer approach was designed to eliminate intermediaries and offer competitive pricing. Early funding, secured through seed rounds, helped the company establish logistics for vehicle acquisition, reconditioning, and delivery. The founders' combined expertise in e-commerce and logistics was key to building Vroom's operational foundation.
Vroom's early business model focused on direct online sales of used cars.
- The company aimed to cut out intermediaries.
- They offered home delivery to customers.
- Early funding was crucial for setting up logistics.
- The founders' experience in e-commerce was key.
The company's early success was driven by its innovative approach to Growth Strategy of Vroom. By 2020, Vroom had expanded its operations significantly. In 2020, Vroom's revenue was approximately $1.35 billion. The company's online platform allowed customers to browse, purchase, and arrange delivery of used cars, which was a major shift from traditional dealerships. Despite initial growth, Vroom faced challenges, including operational complexities and market competition.
Vroom's journey from its founding to its current standing highlights the evolution of online car sales. The company's ability to adapt to market demands and technological advancements has been crucial. The direct-to-consumer model, while innovative, presented challenges in terms of logistics and scaling operations. In 2024, the used car market continues to evolve, with companies like Vroom navigating changing consumer preferences and economic conditions.
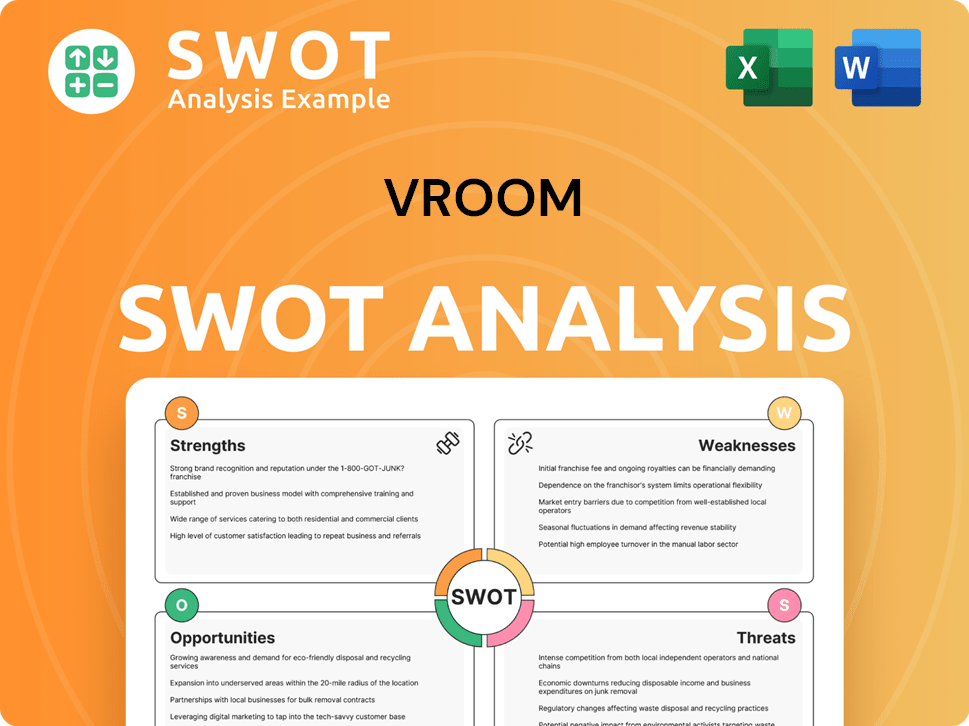
Vroom SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Vroom?
The early growth of the Vroom company, a prominent player in the Vroom car sales sector, was characterized by expanding its vehicle inventory and refining its online platform. Founded in 2013, Vroom focused on creating a digital marketplace for customers to browse, finance, and purchase vehicles entirely online. This innovative approach set the stage for its future growth, making it a key part of the brief history of Vroom.
A significant milestone in the Vroom company timeline was the 2015 acquisition of Texas Direct Auto. This provided Vroom with established reconditioning facilities and a strong logistical network, particularly in the southern United States. This acquisition was pivotal in scaling operations and enhancing vehicle sourcing and preparation capabilities, contributing to Vroom's online car marketplace growth.
Vroom rapidly expanded its vehicle selection and geographical reach, aiming for nationwide home delivery, a key feature of its Vroom car delivery service. The company focused on developing its proprietary technology to streamline the online car buying experience. This included features for virtual vehicle tours and simplified financing applications, setting it apart in the Vroom used cars market.
Early customer acquisition strategies centered on digital marketing, emphasizing the convenience and transparency of its service compared to traditional dealerships. By 2020, Vroom went public, marking a major leap in its growth and capital-raising efforts. The Vroom IPO date was a significant moment in the company's history, fueling further expansion.
The company continued to face a competitive landscape with other online and traditional dealerships, necessitating continuous innovation in its service offerings and operational efficiency. Understanding the Vroom business model is crucial to evaluating its position in the market. For more details on how Vroom operates, explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Vroom.
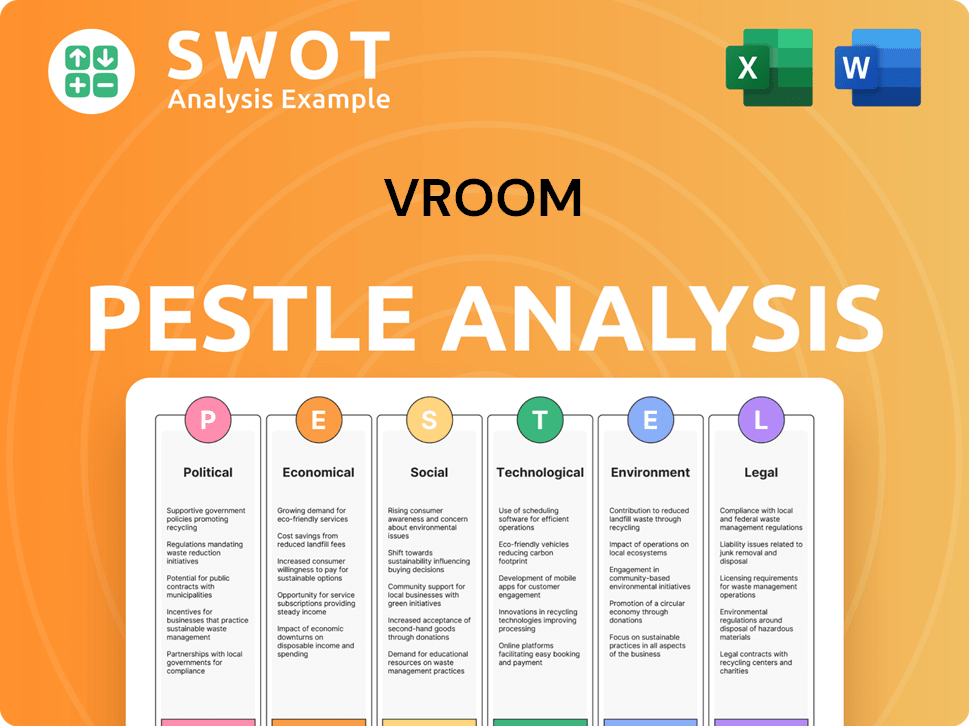
Vroom PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Vroom history?
The Vroom company has experienced several significant milestones since its inception, marking its journey in the online automotive retail sector. These achievements reflect the company's growth, strategic decisions, and its ability to adapt to market dynamics.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2015 | Acquired Texas Direct Auto, expanding reconditioning capacity and logistics. |
| June 2020 | Went public with an initial public offering (IPO), raising approximately $467 million. |
| January 2024 | Announced the decision to wind down its used vehicle dealership business and transition to a B2B marketplace model. |
Vroom's early adoption of a fully online transaction model, including financing and home delivery, was a key innovation in the used car market. This approach streamlined the car-buying experience and set it apart from traditional dealerships.
Vroom pioneered a fully online car-buying experience, offering financing and home delivery, which was a significant innovation in the used car market. This model streamlined the process, making it more convenient for customers.
The company invested heavily in logistics to offer nationwide home delivery, which was a key differentiator. This service enhanced the customer experience by removing the need to visit a physical dealership.
Despite its innovations, Vroom faced challenges, including intense competition and difficulties in managing a nationwide logistics network. Market downturns and supply chain disruptions also impacted its operations, leading to strategic shifts.
The used car market is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. This competition put pressure on pricing and profitability, impacting Vroom's ability to sustain growth.
Managing a nationwide logistics network for vehicle delivery and reconditioning proved complex and costly. These operational challenges affected Vroom's ability to scale efficiently and maintain profitability.
External factors, such as market downturns and supply chain issues, further complicated Vroom's operations. These disruptions led to strategic pivots, including workforce reductions and changes in business model.
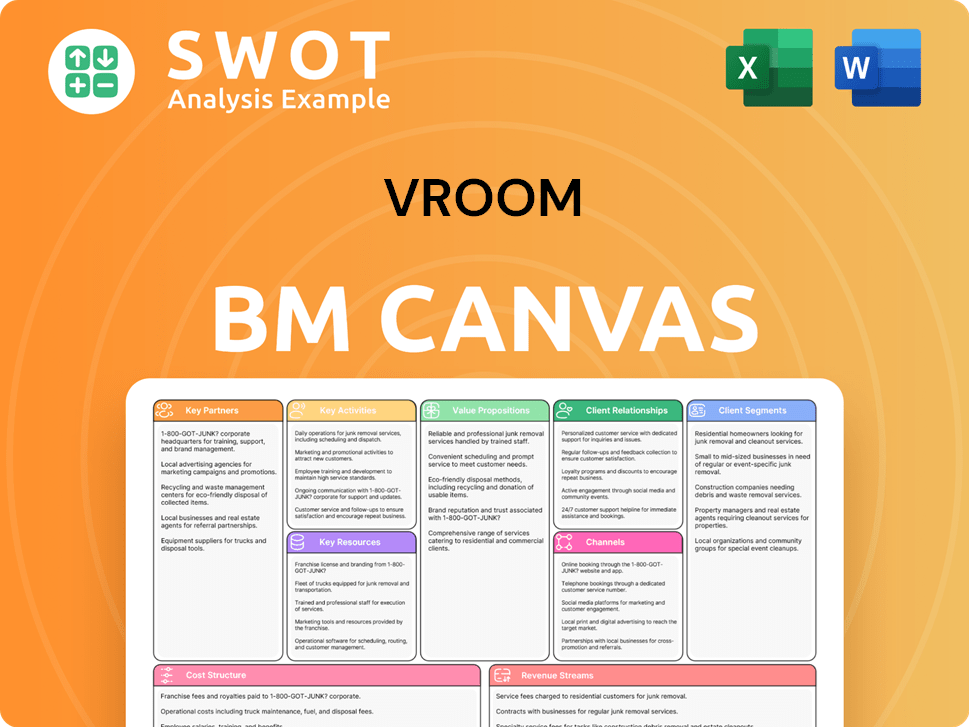
Vroom Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Vroom?
The Vroom history is marked by significant shifts and strategic decisions. Initially founded as Honk Honk, the
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2013 | Founded as Honk Honk in New York City, marking the beginning of Vroom's journey. |
| 2015 | Acquired Texas Direct Auto, enhancing its reconditioning and logistics capabilities. |
| June 2020 | Completed its Initial Public Offering (IPO), raising $467 million, a pivotal moment for Vroom. |
| Q4 2023 | Reported a significant decrease in vehicle sales and a net loss, indicating operational challenges. |
| January 2024 | Announced the winding down of its online used vehicle dealership business to focus on its B2B marketplace. |
| January 2024 | Implemented a workforce reduction of approximately 800 employees as part of its strategic shift. |
Vroom's future outlook centers on its transition to a B2B automotive marketplace. This move, announced in January 2024, represents a strategic pivot away from direct-to-consumer
The B2B model is intended to reduce operational complexities and improve financial performance. By focusing on a less capital-intensive segment, Vroom aims to achieve profitability and sustainable growth. Analyst predictions suggest a focus on efficiency within this refined business model.
The company must effectively execute this transition to establish its position in the competitive B2B automotive space. Success depends on its ability to attract and serve dealers effectively. This strategic shift is key for the long-term viability of Vroom.
The workforce reduction of approximately 800 employees reflects the significant changes underway. These adjustments are part of a broader strategy. The company is streamlining operations to align with its new B2B focus, moving away from
Vroom Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Vroom Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Vroom Company?
- How Does Vroom Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Vroom Company?
- What is Brief History of Vroom Company?
- Who Owns Vroom Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Vroom Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.