Wells Fargo Bundle
How has Wells Fargo shaped the American financial landscape?
From its roots in the California Gold Rush to its current status as a financial powerhouse, the Wells Fargo SWOT Analysis reveals a fascinating journey. Founded in 1852, the company's early days were marked by innovation in express and banking services, quickly becoming a vital part of the burgeoning American West. This brief history of Wells Fargo bank explores its evolution, highlighting key milestones and pivotal moments.

Exploring the Wells Fargo company timeline unveils a story of remarkable growth and adaptation within the American financial institutions. From its stagecoach era and involvement with the Pony Express to its expansion across America, Wells Fargo's history reflects both triumphs and challenges. This exploration will delve into the early days of Wells Fargo, its impact on the Gold Rush, and its evolution into a leading provider of diverse financial services.
What is the Wells Fargo Founding Story?
The story of the Wells Fargo company began on March 18, 1852. It was founded in New York City by Henry Wells and William G. Fargo. Their vision was to provide essential financial and shipping services to the rapidly growing state of California, fueled by the Gold Rush.
Both founders were already well-known in the express industry, having previously helped establish American Express. Recognizing the need for reliable services in the West, they decided to create their own venture. This marked the beginning of what would become one of America's most significant financial institutions.
The initial business model combined express services with banking. They focused on handling the purchase, sale, and transport of gold dust, bullion, and other goods. They also offered faster and more affordable mail delivery. This dual approach quickly established the company's reputation for trustworthiness and reliability. The iconic stagecoach logo became a symbol of their commitment to service.
Wells Fargo was founded in 1852 to serve the needs of the Gold Rush in California.
- Henry Wells and William G. Fargo, founders, previously helped establish American Express.
- The company offered both express (shipping) and banking services.
- They handled gold, bullion, and other goods, along with mail delivery.
- Wells Fargo quickly gained a reputation for trustworthiness.
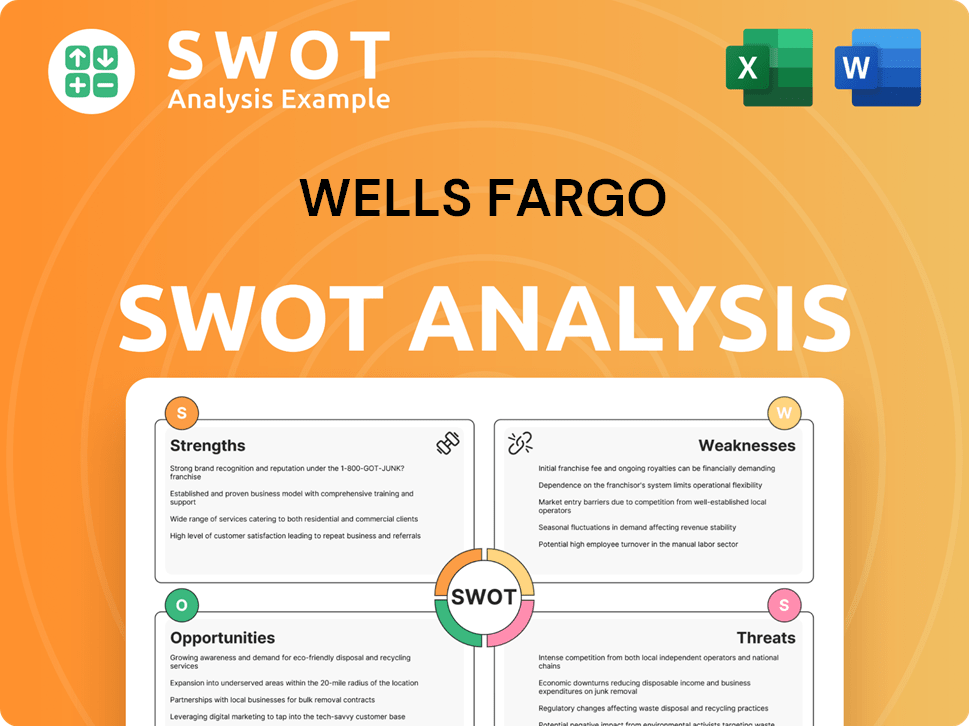
Wells Fargo SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Wells Fargo?
The early growth and expansion of the Wells Fargo company were marked by strategic moves that solidified its presence in the American financial landscape. Starting in 1855, the company aggressively expanded its staging business, establishing crucial routes across the country. A pivotal moment came with the acquisition of the Butterfield Overland Mail Company in 1860, leading to its operation of the western portion of the Pony Express in 1861.
In the decade following 1855, the company significantly expanded its staging operations. This involved establishing overland routes that connected Missouri and the Midwest with the Rockies and the Far West. These routes were essential for transporting goods, people, and mail across the expanding American frontier.
The acquisition of the Butterfield Overland Mail Company in 1860 was a major milestone, leading to the operation of the western portion of the Pony Express in 1861. In 1866, a "grand consolidation" merged Wells Fargo with Holladay and Overland Mail stage lines. This consolidation created the largest stagecoach empire globally, solidifying its dominance during the stagecoach era.
Even with the rise of railroads, the company continued to serve areas without rail access, even into the early 20th century. The 1980s and 1990s saw a series of acquisitions aimed at increasing market share. Notable acquisitions included Crocker National Bank in 1986 and First Interstate Bancorp in 1996, for $11.6 billion.
In 1998, the company was acquired by Norwest Corporation, which then adopted the Wells Fargo name. This merger allowed the company to become a coast-to-coast bank, a status reinforced by the 2008 acquisition of Wachovia for approximately $14.8 billion in stock. The company was an early adopter of technology, becoming the first major U.S. financial services firm to offer internet banking in May 1995.
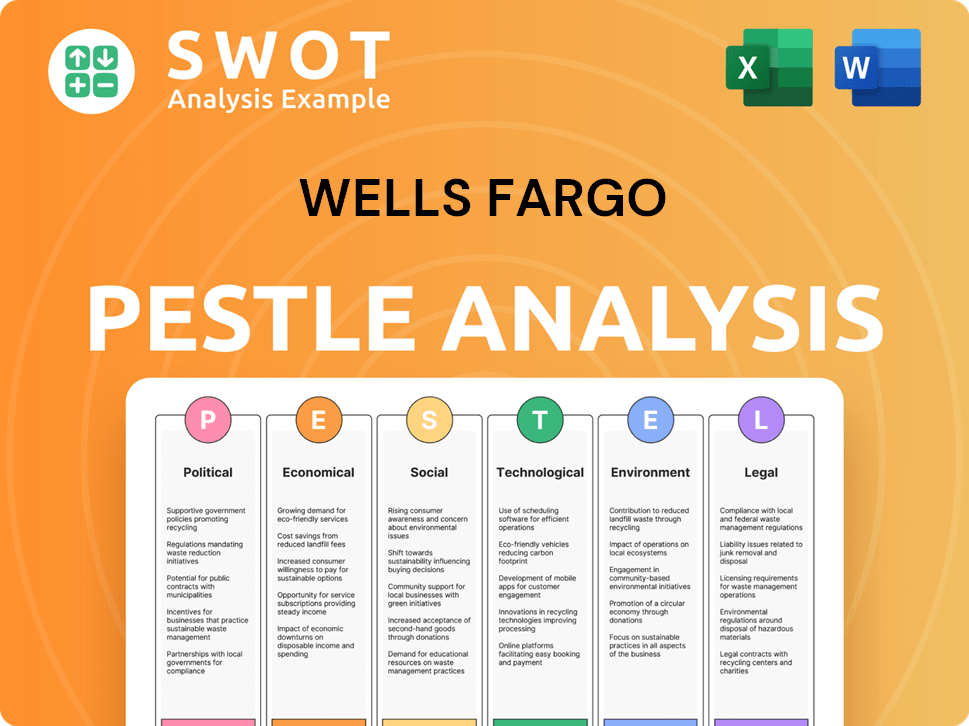
Wells Fargo PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Wells Fargo history?
The Wells Fargo history is marked by significant achievements and strategic adaptations. From its origins to its current status, the Wells Fargo company has navigated numerous economic cycles and regulatory changes, establishing itself as a key player in the American financial landscape. The Wells Fargo timeline reflects a journey of growth, innovation, and resilience, shaping its legacy within the banking history of American financial institutions.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1852 | Founded in New York City by Henry Wells and William G. Fargo. |
| 1852 | Expanded to California, offering banking and express services during the Gold Rush. |
| 1995 | Introduced internet banking, becoming a pioneer in online financial services. |
| 2008 | Acquired Wachovia during the financial crisis, expanding its national presence. |
| 2018 | Placed under an asset cap by the Federal Reserve due to regulatory issues. |
| 2025 | The Federal Reserve lifted the asset cap on June 3, signaling successful remediation. |
Innovations have played a crucial role in Wells Fargo's evolution, particularly in enhancing customer experiences. The company has consistently leveraged technology to provide convenient and efficient banking services, including mobile platforms and digital financial tools. Furthermore, the company has invested in modernizing its branch network and improving digital offerings.
In May 1995, Wells Fargo became the first major U.S. financial services firm to introduce internet banking, revolutionizing customer access to financial services. This early adoption set a precedent for the industry, enhancing customer convenience and operational efficiency.
In 1967, Wells Fargo, along with other banks, introduced the Master Charge Card, now known as Mastercard. This initiative expanded the company's financial services and provided new revenue streams.
The company has consistently invested in technology to enhance customer experiences through digital platforms. This includes offering seamless access to banking services and innovative financial management tools.
In 2024, Wells Fargo completed 730 upgrades to modernize its branch footprint. This initiative aimed to improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
In 2024, Wells Fargo had 1.5 million active mobile app customers, a 5% increase from the prior year. This growth demonstrates the increasing reliance on digital banking solutions.
Customer usage of Zelle increased, with over 1 billion transactions in 2024, up 22% from a year ago. This reflects the growing adoption of digital payment solutions.
Despite these advancements, Wells Fargo has faced significant challenges, including market downturns and regulatory scrutiny. The company has had to navigate internal crises and adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes. These experiences have led to strategic shifts, emphasizing risk management and customer-centric approaches. For further insights into the strategic approaches, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of Wells Fargo.
The 2008 financial crisis led to the acquisition of Wachovia by Wells Fargo. This expansion was a response to market instability and a strategic move to strengthen its market position during a period of crisis.
Since 2018, the company operated under an asset cap imposed by the Federal Reserve. This constraint limited growth to 2020 levels, impacting its operational capacity.
Even after the asset cap was lifted, Wells Fargo still faced lingering regulatory obligations. The company continues to address these issues, with several consent orders remaining.
The company undertook strategic pivots, including a focus on strengthening its risk and control framework. This also involved simplifying its business mix to improve operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Wells Fargo is strategically reconfiguring its capital structure and focusing on fee-based businesses. This includes wealth management and corporate banking to drive sustainable growth and diversify revenue streams.
The company has been actively working to address regulatory issues, closing five consent orders in Q1 2025. Since 2019, a total of eleven consent orders have been closed.
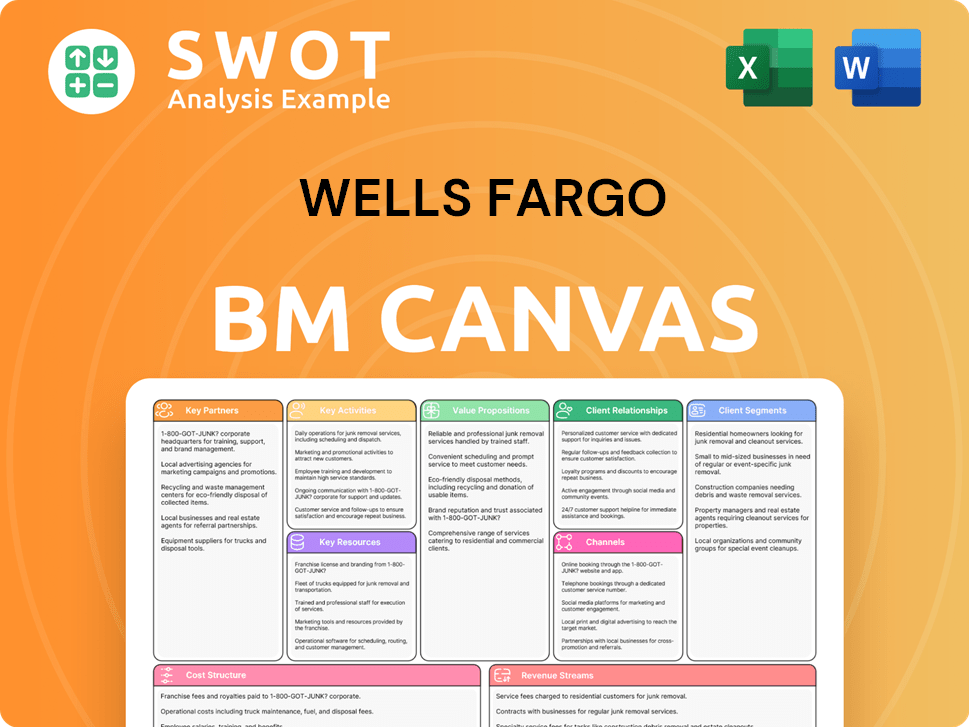
Wells Fargo Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Wells Fargo?
The Wells Fargo history is marked by significant milestones, from its founding in 1852 to its position as a major financial institution today. Initially established to serve the California Gold Rush, the company adapted and expanded, playing a key role in the development of the American West. Its journey includes periods of growth, strategic acquisitions, and regulatory challenges, shaping its evolution in the financial landscape.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| March 18, 1852 | Wells, Fargo & Co. is founded in New York City to provide express and banking services to California. |
| 1860 | Wells Fargo gains control of Butterfield Overland Mail Company, leading to its operation of the western portion of the Pony Express in 1861. |
| 1866 | A 'grand consolidation' unites Wells Fargo, Holladay, and Overland Mail stage lines under the Wells Fargo name. |
| 1905 | Wells Fargo separates its banking and express operations; its bank merges with Nevada National Bank to form Wells Fargo Nevada National Bank. |
| 1918 | Wells Fargo's domestic express business is nationalized by the U.S. government into the US Railway Express Agency (REA). |
| 1967 | Wells Fargo, along with other banks, introduces the Master Charge Card (now Mastercard). |
| May 1995 | Wells Fargo becomes the first major U.S. financial services firm to offer internet banking. |
| 1998 | Wells Fargo Bank is acquired by Norwest Corporation, with the combined company retaining the Wells Fargo name and moving headquarters to San Francisco. |
| 2008 | Wells Fargo acquires Wachovia, significantly expanding its coast-to-coast presence. |
| 2018 | The Federal Reserve imposes an asset cap on Wells Fargo. |
| 2024 | Wells Fargo reports $19.7 billion in net income and $5.37 per diluted share, with a 13.4% return on tangible common equity. |
| Q1 2025 (ended March 31, 2025) | Wells Fargo reports a net income of $4.9 billion, or $1.39 per diluted share, a 6% rise from the same period last year. |
| June 3, 2025 | The Federal Reserve lifts the asset cap imposed on Wells Fargo in 2018. |
With the asset cap lifted, Wells Fargo is focused on growth and increasing returns. CEO Charlie Scharf is leading the company's efforts to expand in consumer, small business, and business banking. The bank is investing in digital banking, payments, and advisory services to improve customer engagement.
Analysts anticipate an EPS of $5.84 for fiscal 2025, a 5.8% increase from fiscal 2024. Further growth is expected in fiscal 2026, with an estimated EPS of $6.83, representing nearly a 17% year-over-year increase. The average analyst price target for the next twelve months is $77.48.
Wells Fargo is investing in technology to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. They are also focusing on sustainable finance and strengthening their risk management framework. The expansion of the Technology Banking team, with additional hires in 2025, is a key component of this strategy.
The Wells Fargo Investment Institute anticipates a modest global growth recovery in 2025, with the U.S. leading the way. The company's leadership is committed to making it 'one of the most well-respected, consistently growing financial institutions in the country,' focusing on innovation and customer success.
Wells Fargo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked

Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Wells Fargo Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Wells Fargo Company?
- How Does Wells Fargo Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Wells Fargo Company?
- What is Brief History of Wells Fargo Company?
- Who Owns Wells Fargo Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Wells Fargo Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.