Japan Post Holdings Bundle
Unpacking Japan Post Holdings: How Does It Thrive?
Japan Post Holdings, a cornerstone of Japan's infrastructure, offers a fascinating case study in diversified services and financial influence. Its operations extend far beyond traditional mail delivery, encompassing banking and insurance that touch the lives of millions. With a massive network of post offices, understanding how this conglomerate functions is key to grasping the Japanese market.

With operating revenue of ¥11.05 trillion as of March 31, 2024, Japan Post Holdings SWOT Analysis reveals a company of significant financial scale. This analysis will dissect the Japan Post Group's core operations, exploring its revenue streams and strategic advantages. Whether you're interested in the Japan Post Holdings SWOT Analysis, or simply curious about the Japanese postal service, this exploration of Japan Post's structure will provide valuable insights into its enduring success and the challenges it faces in a changing global landscape, including its financial performance and subsidiaries.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Japan Post Holdings’s Success?
Japan Post Holdings creates value through its three main business areas: postal and logistics, banking (Japan Post Bank), and insurance (Japan Post Insurance). These segments serve a wide range of customers, from individuals and small businesses needing mail services to households seeking savings and life insurance. The company's strength lies in its extensive reach across Japan and the convenience of integrated services available through its vast post office network. Understanding how Japan Post Holdings operates is key to appreciating its impact on the Japanese economy.
The company's value proposition is built on its extensive network and the trust it has cultivated over many years. This allows it to offer a unique combination of services that competitors find difficult to match. The integrated approach, where customers can handle postal, banking, and insurance needs in one place, significantly enhances convenience and accessibility. This extensive physical footprint is a key part of the Japan Post Group's success.
In its postal and logistics segment, Japan Post provides essential mail delivery, parcel services, and international shipping. The banking arm, Japan Post Bank, offers a wide array of financial products. Japan Post Insurance focuses on life insurance products. Its unique distribution network, the post office, is a key differentiator. Its partnerships ensure seamless service integration, offering customers convenience and accessibility unmatched in the Japanese market. For more information, you can explore Owners & Shareholders of Japan Post Holdings.
The postal and logistics segment handles mail delivery, parcel services, and international shipping. This involves a complex logistical network that includes sorting centers, transportation fleets, and a large workforce. In fiscal year 2023, revenue from the postal and logistics business was approximately ¥1.3 trillion.
Japan Post Bank offers a range of financial products, including deposits and remittances. Operations are supported by a robust IT infrastructure and a large branch network within post offices. As of March 2024, the bank held approximately ¥190 trillion in customer deposits.
Japan Post Insurance focuses on life insurance products, using its sales force and post office network. Operations include product development, underwriting, claims processing, and asset management. In fiscal year 2023, the insurance segment generated approximately ¥3.5 trillion in revenue.
The extensive post office network is a key differentiator, allowing Japan Post to reach remote areas. Partnerships within the group ensure seamless service integration. This integrated approach offers convenience and accessibility unmatched in the Japanese market.
The integrated approach and extensive physical footprint translate into significant customer benefits. Customers enjoy convenience and accessibility, with the ability to handle postal, banking, and insurance needs at a single location. This model is a cornerstone of the Japan Post Group's strategy.
- Convenience: One-stop service for various needs.
- Accessibility: Reaching even remote areas.
- Trust: Leveraging long-standing brand recognition.
- Integrated Services: Seamless handling of postal, banking, and insurance needs.
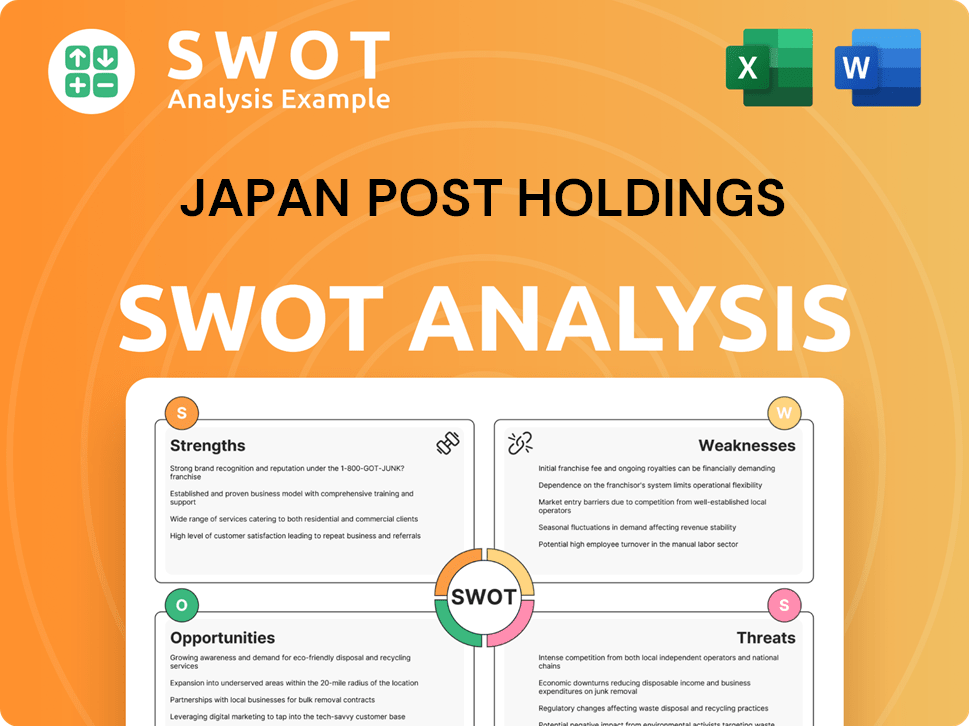
Japan Post Holdings SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Japan Post Holdings Make Money?
Understanding the revenue streams and monetization strategies of Japan Post Holdings is crucial for grasping its financial dynamics. The company, a major player in the Japanese economy, operates through a diversified business model. This approach allows it to generate income from various sectors, including postal services, banking, and life insurance.
Japan Post Holdings, or Japan Post Group, reported operating revenue of ¥11.05 trillion for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024. This substantial revenue reflects the company's significant presence in the Japanese market and its ability to adapt to changing economic conditions. The following sections detail the key revenue streams and monetization strategies employed by the company.
The core revenue streams for Japan Post are divided among its postal and logistics, banking, and life insurance segments. Each segment contributes significantly to the overall financial performance of the company, demonstrating the strength of its diversified business model. The company's ability to generate revenue from multiple sources provides a degree of stability, even as market conditions shift.
The postal and logistics segment generates revenue through mail delivery, parcel services, and international shipping. The banking segment, operated by Japan Post Bank, earns from interest income and fees. Japan Post Insurance, the life insurance arm, generates revenue from premiums and investments.
- Postal and Logistics: This segment generates revenue from mail delivery fees, parcel delivery charges, and international shipping services. While traditional mail volume has declined, the company has focused on expanding its parcel delivery services.
- Banking: Japan Post Bank derives revenue from interest income on loans and investments, as well as fees for banking services. As of March 31, 2024, this segment contributed ¥2.21 trillion to operating revenue.
- Life Insurance: Japan Post Insurance generates revenue from insurance premiums and investment income. For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, this segment reported ¥4.53 trillion in operating revenue.
Japan Post Holdings employs several strategies to monetize its services and maximize revenue. These include leveraging its extensive customer base and integrated service offerings. Tiered pricing and cross-selling are also key components of their monetization approach.
- Cross-selling: The extensive post office network acts as a platform for cross-selling banking and insurance products to customers.
- Tiered Pricing: Postal and logistics services use tiered pricing based on weight, size, and delivery speed.
- Integrated Services: The company benefits from its integrated service offerings, allowing customers to access various financial and postal services in one place.
For a deeper dive into the marketing strategies employed by Japan Post Holdings, consider reading Marketing Strategy of Japan Post Holdings.
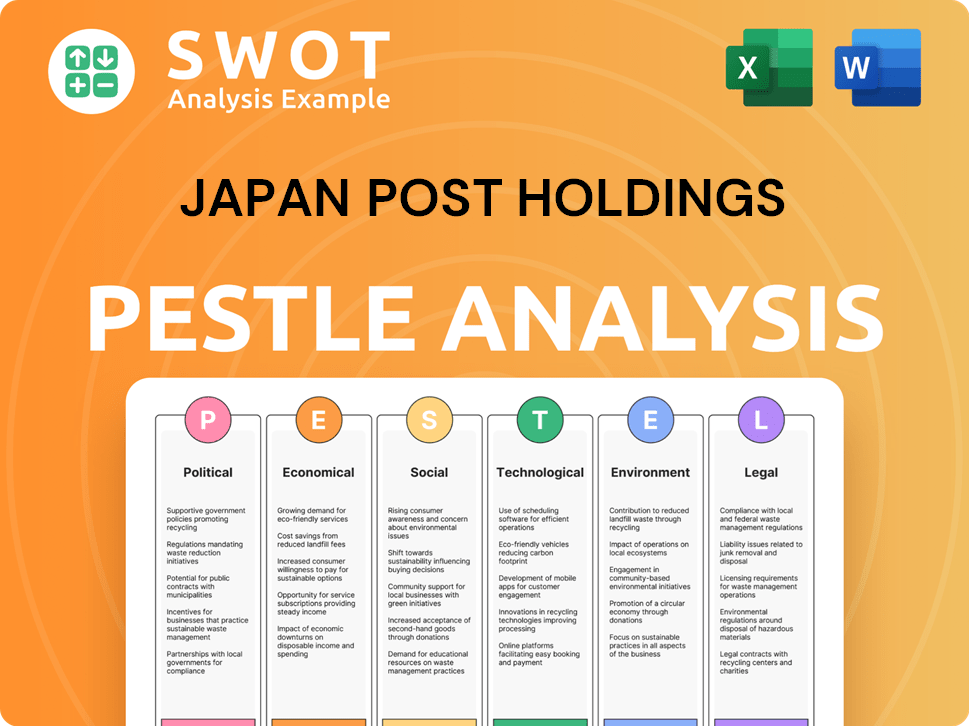
Japan Post Holdings PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Japan Post Holdings’s Business Model?
Japan Post Holdings has undergone significant transformations, with its privatization being a pivotal milestone. The full privatization process, which began in 2007 and continued with share offerings in 2015 and subsequent years, aimed to enhance management efficiency and foster competition. This strategic move allowed the company to operate with greater autonomy and respond more dynamically to market forces.
Another key development was the acquisition of Toll Holdings in 2015, a strategic move to expand its international logistics capabilities. This venture, however, later faced challenges and resulted in impairments. Operational challenges have included declining mail volumes due to digital communication and intense competition in the logistics and financial sectors. In response, Japan Post has focused on enhancing its parcel delivery services, expanding its e-commerce logistics solutions, and diversifying its financial product offerings.
The company has also invested in digital transformation initiatives to improve operational efficiency and customer experience across its segments. Understanding the Competitors Landscape of Japan Post Holdings is crucial for assessing its strategic positioning and future prospects.
The privatization of Japan Post, initiated in 2007, was a landmark event, with subsequent share offerings in 2015. This process aimed to boost management efficiency and competitiveness. The acquisition of Toll Holdings in 2015 expanded international logistics capabilities, though it later faced challenges.
Japan Post has focused on enhancing parcel delivery and e-commerce logistics. Diversifying financial product offerings and investing in digital transformation are also key strategies. These moves are designed to adapt to changing market dynamics and customer needs.
Japan Post's brand strength and extensive physical network provide a significant advantage. Its ubiquitous post offices offer a unique distribution channel, especially in rural areas. Economies of scale and customer trust also contribute to its competitive position.
The company continues to explore new technologies, such as automation and digital platforms. Strategic partnerships are sought to enhance service offerings. Adaptations are driven by market evolution and the need to maintain a competitive edge.
Japan Post Holdings faces challenges like declining mail volumes and competition in logistics and finance. The company is responding by enhancing parcel delivery, expanding e-commerce solutions, and diversifying financial products.
- Focus on digital transformation to boost efficiency and customer experience.
- Investment in automation for sorting facilities.
- Development of digital platforms for banking and insurance services.
- Strategic partnerships to enhance service offerings.
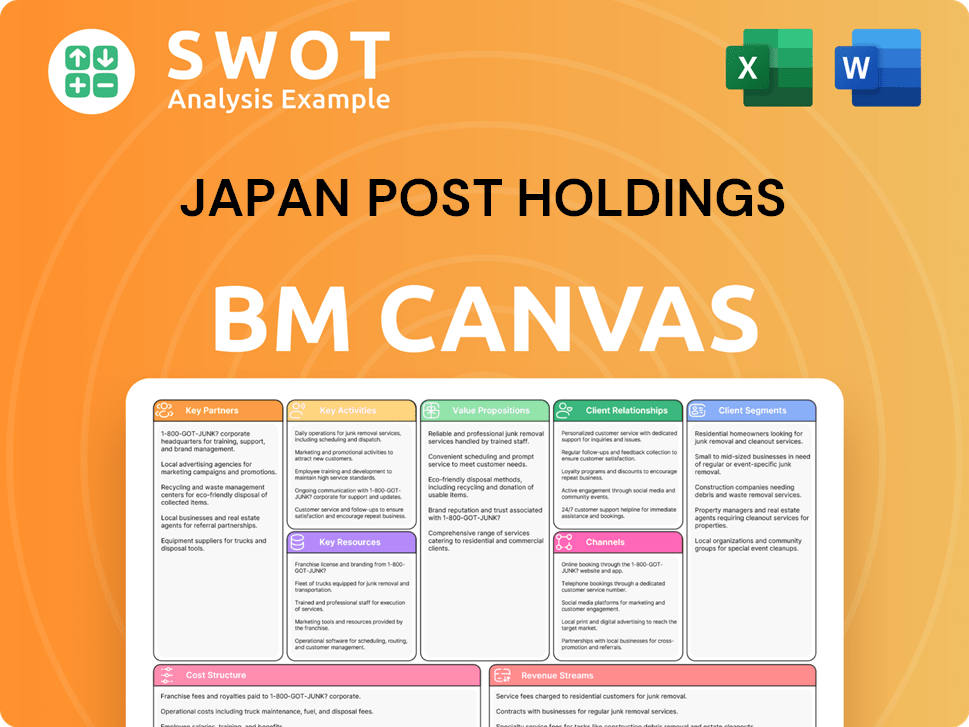
Japan Post Holdings Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Japan Post Holdings Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
Japan Post Holdings (JPH) maintains a strong position in Japan's postal and logistics sector, built on its history as the national postal service. It faces competition from private couriers, but its extensive network, especially in remote areas, gives it a significant advantage. In the financial sector, Japan Post Bank and Japan Post Insurance are major players, holding considerable market share due to their long-standing presence and customer trust.
Despite its strengths, JPH faces risks like regulatory changes concerning its privatization and operations. Competition in all segments, shifting customer preferences towards digital services, and technological disruptions pose challenges. Demographic shifts, including a declining and aging population in Japan, also impact demand and growth. For more information on the target market, you can read about the Target Market of Japan Post Holdings.
Japan Post Group is a dominant force in the Japanese postal and logistics market. Its vast network and historical roots provide a solid foundation. While facing competition, its reach, especially in rural areas, offers a distinct advantage.
JPH faces regulatory uncertainties and intense competition across all segments. Changing customer preferences and technological advancements, such as fintech, require adaptation. Japan's aging population also presents long-term challenges.
JPH is focused on digital transformation and optimizing its logistics network. It aims to develop new financial and insurance products to cater to an aging population. By adapting to market changes, JPH seeks to maintain its crucial role in Japanese society.
The company is investing in digital capabilities across all its sectors. They also plan to optimize the logistics network to meet the needs of e-commerce. JPH will leverage its customer base to offer more integrated and convenient services.
In its financial reports, JPH consistently highlights the importance of adapting to digital transformation and changing customer needs. Recent reports (available up to April 2024) show a focus on optimizing logistics and expanding digital services.
- Japan Post continues to invest in automation and digital solutions to improve efficiency.
- Japan Post Bank is exploring new financial products and services tailored to an aging population.
- Japan Post Insurance is focused on enhancing its digital customer experience and product offerings.
- The company is actively seeking strategic partnerships to enhance its market position and expand its service offerings.
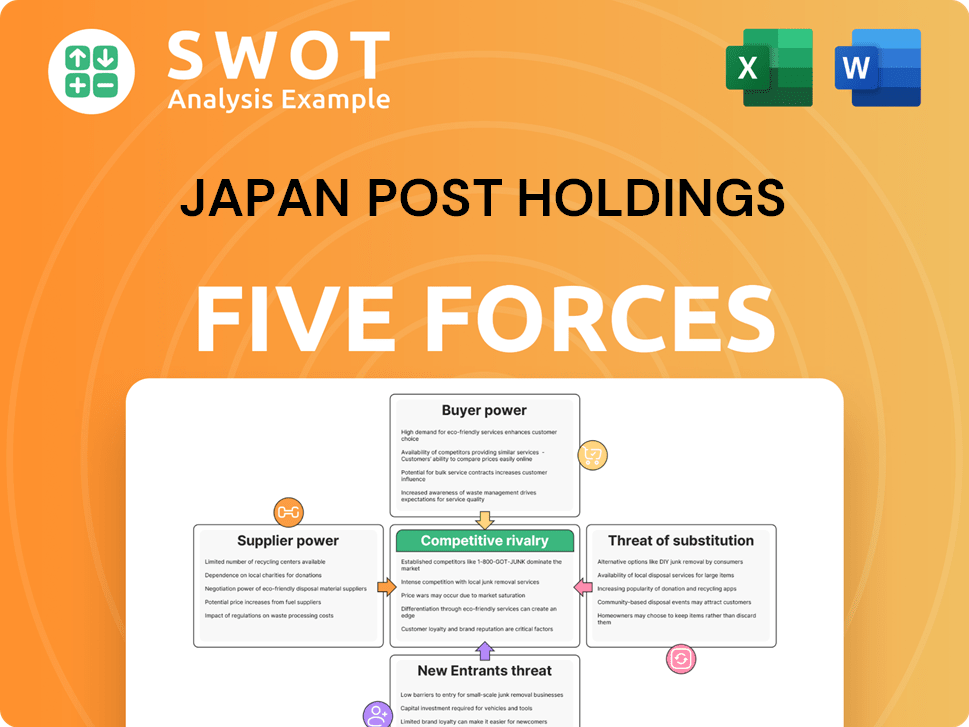
Japan Post Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Japan Post Holdings Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Japan Post Holdings Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Japan Post Holdings Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Japan Post Holdings Company?
- What is Brief History of Japan Post Holdings Company?
- Who Owns Japan Post Holdings Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Japan Post Holdings Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.