Microchip Technology Bundle
Who Really Controls Microchip Technology?
Ever wondered who steers the ship at a leading Microchip Technology SWOT Analysis? Understanding the ownership structure of a semiconductor giant like Microchip is crucial for anyone looking to understand its future. This knowledge offers a glimpse into the strategic decisions, financial performance, and overall direction of the company.

Microchip Technology, a publicly traded semiconductor company, presents a compelling case study in corporate ownership. From its origins as a spin-off to its current status as a major player in the Nasdaq-100 and S&P 500, the evolution of Microchip's ownership reveals much about its resilience and strategic focus. This analysis will explore the key stakeholders, including institutional investors and insiders, and examine how their influence shapes Microchip's journey in the competitive semiconductor market.
Who Founded Microchip Technology?
The story of Microchip Technology, a prominent semiconductor company, began in 1987. It started as a wholly-owned subsidiary spun off from General Instrument's microelectronics division. This marked the initial step in the company's journey toward becoming a significant player in the tech industry.
The early years were marked by significant shifts and strategic decisions. The company's initial public offering (IPO) plans were derailed by the stock market crash of October 1987. This event altered the course of its early financial strategy. Later, in 1989, the company gained independence through an acquisition by a group of venture capitalists, with Sequoia Capital leading the investment.
During this formative period, Steve Sanghi played a crucial role, becoming president and chief operating officer in 1990. He steered the company away from commodity-based products toward specialized chips, such as RISC technology. This strategic pivot was critical, especially after facing several quarters of losses. This strategic shift helped shape the future direction of Microchip Technology.
The acquisition by venture capitalists in 1989, led by Sequoia Capital, was a pivotal moment. This provided the necessary capital for Microchip's independence and strategic transformation.
Steve Sanghi's leadership in 1990 was instrumental in transitioning the company. This move from commodity products to specialized chips, like RISC technology, was a key strategic decision.
In 1990, Winbond Electronics Corporation of Taiwan offered to acquire Microchip for $15 million. However, the deal was canceled due to the decline in the Taiwanese stock market.
The early ownership events and strategic decisions set the stage for Microchip Technology's eventual public listing. This led to its growth as a prominent semiconductor company.
The venture capital investment provided essential capital for Microchip's initial strategic shift. This was crucial for the company's long-term viability and growth.
Steve Sanghi's role as president and COO was critical in shaping the company's direction. His leadership helped define Microchip's strategic focus.
The early ownership of Microchip Technology was significantly influenced by venture capital investments, particularly the backing from Sequoia Capital in 1989. This funding was crucial for the company's independence and strategic realignment. Although specific equity splits from the very beginning are not publicly detailed, the venture capital infusion was a pivotal moment. For more insights, explore the Brief History of Microchip Technology. This period set the stage for Microchip's future, including its public listing and its rise as a key player in the semiconductor industry. In 2024, the company's net sales reached approximately $8.4 billion, highlighting its continued growth and market presence.
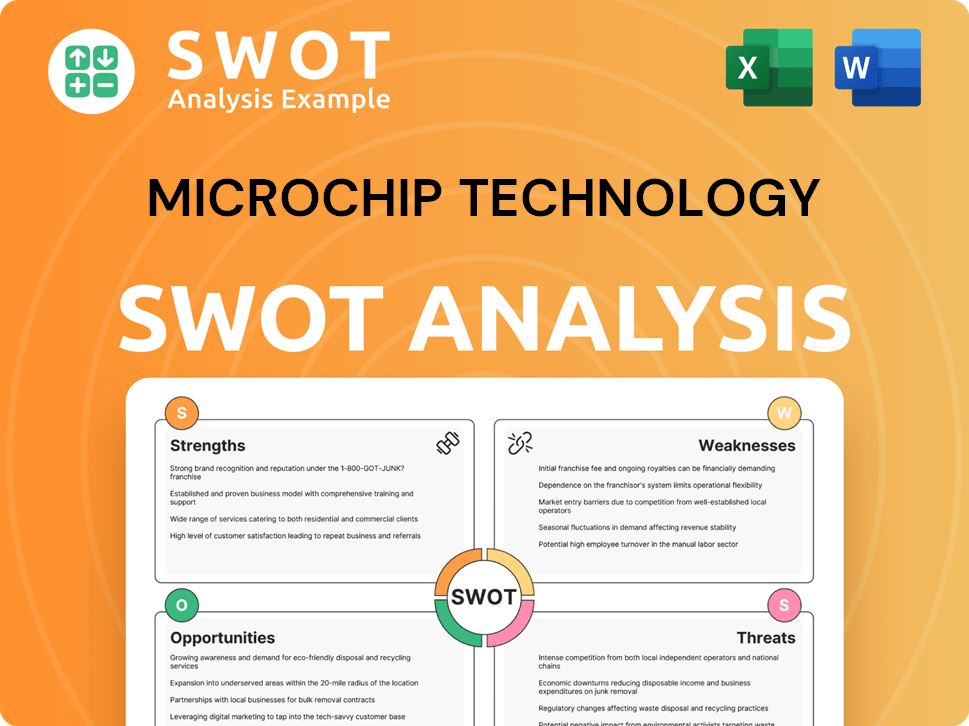
Microchip Technology SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Microchip Technology’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Microchip Technology's ownership structure has been shaped by significant milestones. The company went public on March 19, 1993, with an initial public offering (IPO) at $13.00 per share (pre-split). Fortune magazine hailed it as the best-performing IPO of that year, marking a 500% stock appreciation and exceeding $1 billion in market capitalization. These early successes laid the foundation for the company's future growth and attracted initial investors.
Further shifts in ownership have been driven by strategic acquisitions. The acquisition of Atmel in 2016 for $3.56 billion and Microsemi Corporation in 2018 expanded the company's product portfolio and market reach. These moves have attracted and sustained institutional investment, altering the ownership landscape.
| Ownership Category | Percentage (May 2025) | Notable Shareholders |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Approximately 96.82% | Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock, Inc., State Street Corp, VTSMX - Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund Investor Shares, Invesco Ltd., T. Rowe Price Investment Management, Inc. |
| Insiders | Approximately 0.04% | Steve Sanghi (Former President, CEO, and Chairman) |
| Retail Investors and Public Companies | 14.54% (Combined) | N/A |
As of May 2025, institutional investors primarily dominate the ownership of Microchip Technology. Vanguard Group Inc. holds a significant portion, owning approximately 11.97% of the shares, which equates to 64,376,611 shares, valued at over $3.9 billion. BlackRock, Inc. is another major shareholder. Insiders hold a smaller percentage, with Steve Sanghi, the former President, CEO, and Chairman, being a significant individual shareholder, owning 10,155,770 shares, representing 1.89% of the company, valued at over $617 million. Mutual funds increased their holdings from 76.90% to 77.05% in May 2025. This ownership structure reflects the company's maturity and its position as a key player in the semiconductor industry.
Microchip Technology's ownership is largely institutional, with Vanguard and BlackRock as major holders.
- Institutional investors hold approximately 96.82% of the shares.
- Insiders, including Steve Sanghi, hold a small percentage.
- The IPO in 1993 was a major success, boosting market capitalization.
- Strategic acquisitions have influenced the ownership structure.
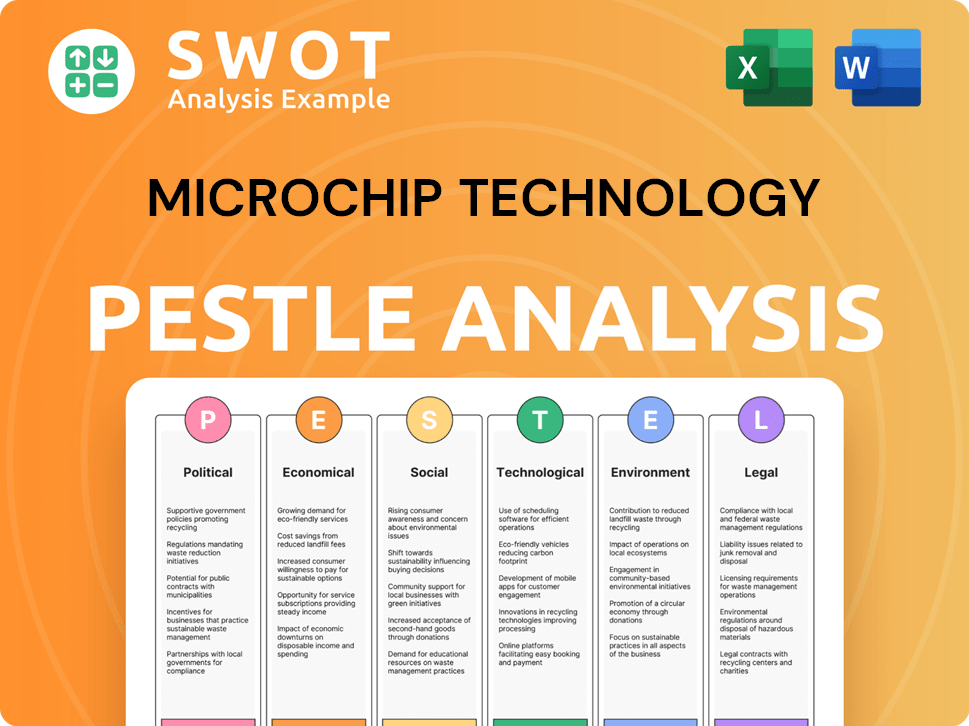
Microchip Technology PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Microchip Technology’s Board?
The current board of directors at Microchip Technology oversees the company's strategic direction and governance. Information on the board members and their affiliations can be found in the company's proxy statement. The board has several committees, including the Audit Committee, the Compensation Committee, and the Nominating, Governance, and Sustainability Committee. The board typically consists of five to seven directors, aiming for diverse perspectives.
Microchip Technology, as a leading semiconductor company, emphasizes responsiveness to its stockholders and proactive engagement with institutional investors. The company's insider trading policy, updated in November 2024, prohibits employees, officers, and directors from speculating in Microchip stock, including short selling, options trading, or hedging.
| Board Committee | Responsibilities | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Audit Committee | Oversees financial reporting and internal controls | Financial statement integrity, risk management |
| Compensation Committee | Determines executive compensation | Performance-based pay, alignment with shareholder interests |
| Nominating, Governance, and Sustainability Committee | Manages board nominations, corporate governance, and sustainability initiatives | Board composition, ethical conduct, environmental and social responsibility |
Microchip Technology operates with a one-share-one-vote structure for its common stock, ensuring that voting power is directly proportional to the number of common shares owned. Holders of depositary shares representing interests in 7.50% Series A Mandatory Convertible Preferred Stock have specific voting rights. If dividends on the Mandatory Convertible Preferred Stock are not declared and paid for a certain period, these holders gain the right to vote for the election of two additional board members. For a deeper dive into how the company generates revenue, consider exploring the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Microchip Technology.
The board of directors at Microchip Technology guides the company's strategic direction and governance, with a focus on diverse perspectives and responsiveness to shareholders.
- The company uses a one-share-one-vote structure for common stock.
- Holders of Mandatory Convertible Preferred Stock have specific voting rights under certain conditions.
- The company's insider trading policy prohibits speculative activities by employees and directors.
- The board has key committees focused on audit, compensation, and governance.
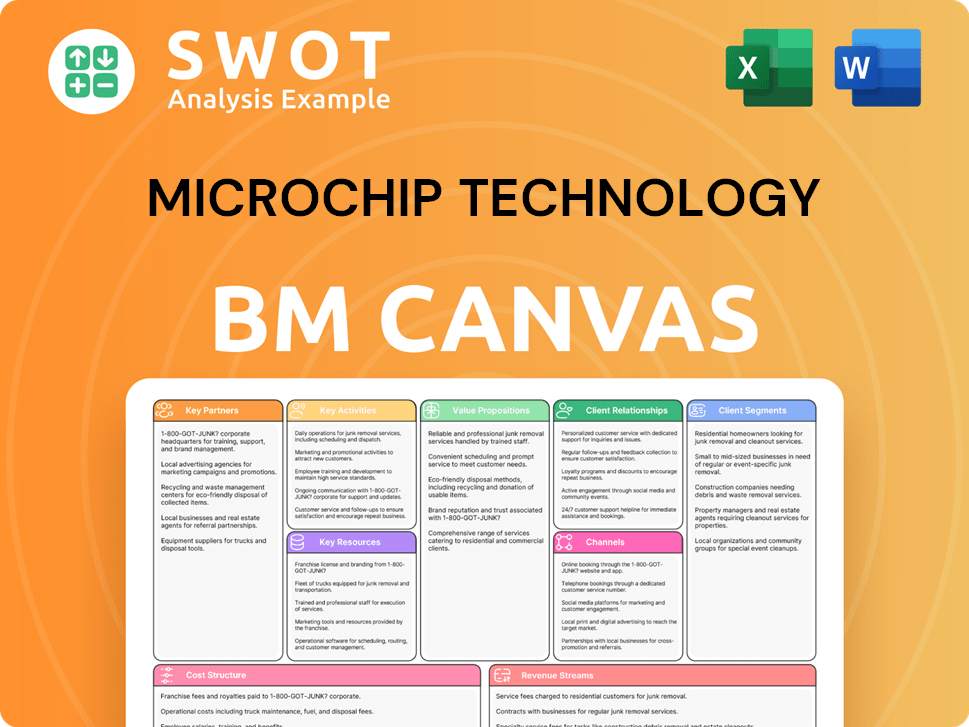
Microchip Technology Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Microchip Technology’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, significant developments have reshaped the ownership and strategic direction of Microchip Technology. A key leadership transition occurred in March 2021 when Ganesh Moorthy took over as CEO from Steve Sanghi. Sanghi later returned as interim CEO in November 2024. The company has actively pursued strategic acquisitions to broaden its product offerings. For instance, in April 2024, Microchip acquired both South Korea-based VSI Co. Ltd. and Neuronix AI Labs. The Neuronix AI Labs acquisition, announced on April 15, 2024, is intended to reduce computer-vision AI cost and power consumption, enabling AI applications on edge devices. More recently, on May 8, 2025, Microchip completed the acquisition of TF Semiconductor Solutions, Inc. (TFSS), issuing shares of its common stock to certain TFSS shareholders as part of the merger.
In terms of financial activities, Microchip returned approximately $315.3 million to stockholders in the June quarter of fiscal year 2025 through dividends ($242.6 million) and share repurchases ($72.7 million). The company bought back 0.8 million shares at an average price of $94.42 per share under its $4.0 billion stock buyback program. Cumulatively, the company repurchased 31.2 million shares over eleven quarters, totaling $2.426 billion. A record quarterly dividend of 45.4 cents per share was declared for the September quarter of 2024, a rise of 10.7% from the previous year. These actions highlight Microchip's commitment to shareholder value and its strategic financial management.
| Metric | Value | Period |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Ownership | Over 96% | May 2025 |
| Share Repurchases | 31.2 million shares | Over eleven quarters |
| Total Value of Share Repurchases | $2.426 billion | Over eleven quarters |
| Quarterly Dividend (Sept 2024) | 45.4 cents per share | September 2024 |
Industry trends in the semiconductor sector, such as increased institutional ownership, are clearly reflected in Microchip's ownership structure, with institutional investors holding over 96% of shares as of May 2025. This demonstrates the confidence institutional investors have in the company. Microchip has also been proactive in managing its manufacturing capacity, including the closure of Fab 2 in December 2024, to right-size operations and build buffer stock for customers. The company is also focusing on megatrends like AI/ML and connectivity/networking, with new market opportunities estimated at $1 billion and $4 billion TAM respectively by 2030, driving future growth initiatives. To learn more about the company's strategic approach, consider exploring the Marketing Strategy of Microchip Technology.
Institutional investors hold over 96% of shares as of May 2025, showcasing strong confidence.
Acquisitions of VSI Co. Ltd., Neuronix AI Labs, and TF Semiconductor Solutions, Inc. expand capabilities.
Returned approximately $315.3 million to stockholders in the June quarter of fiscal year 2025.
Focus on AI/ML and connectivity/networking with significant market opportunities by 2030.
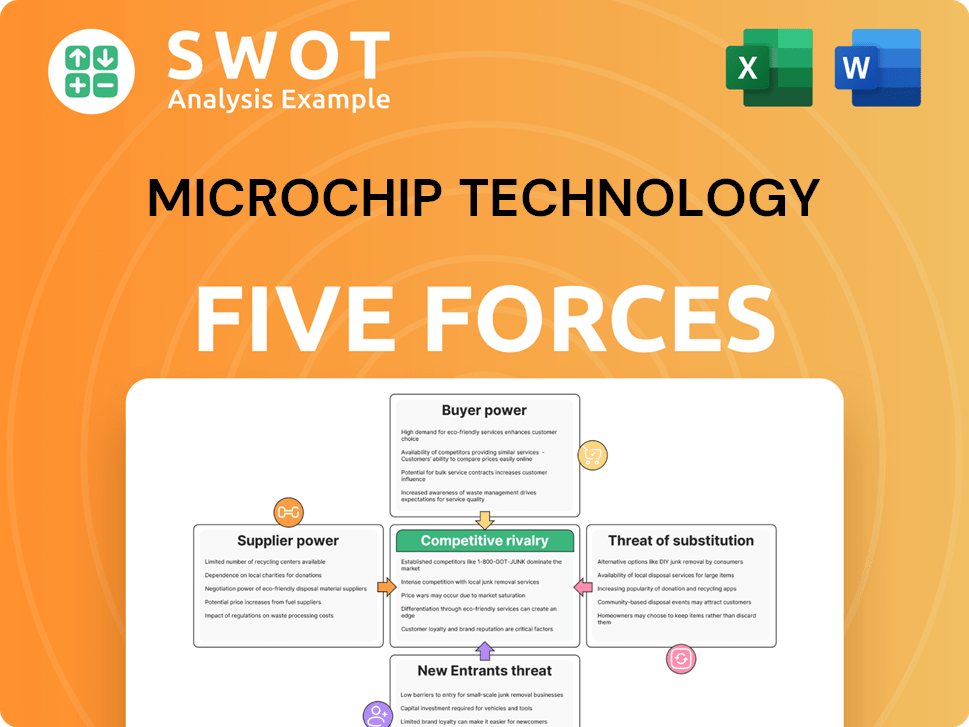
Microchip Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Microchip Technology Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Microchip Technology Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Microchip Technology Company?
- How Does Microchip Technology Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Microchip Technology Company?
- What is Brief History of Microchip Technology Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Microchip Technology Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.