Snam Bundle
Who Really Controls Snam?
Unraveling the Snam SWOT Analysis reveals more than just strengths and weaknesses; it demands an understanding of its ownership. The Snam company, a cornerstone of Italy's energy infrastructure, operates within a complex web of stakeholders. Knowing who owns Snam is crucial for any investor or industry watcher.

Understanding the Snam ownership structure is key to grasping its strategic direction and market responsiveness. From its roots as a state-owned entity to its current status, the evolution of Snam Italy reflects broader trends in privatization and energy market liberalization. This exploration will examine the key Snam shareholders and their influence, providing insights into the company's future.
Who Founded Snam?
The story of Snam's beginnings is deeply rooted in Italy's post-World War II industrial growth and strategic energy policies. Unlike companies with private founders, Snam's initial ownership was entirely held by the Italian state through Eni. This structure meant there were no individual founders with personal equity or shareholdings when the company was first established.
Early capital for Snam was essentially a public investment, designed to build essential national infrastructure. The company's primary mission was to serve as a public utility, focusing on the development and maintenance of a natural gas pipeline network across Italy. This reflected the state's control and its long-term goals for energy security.
Therefore, there were no angel investors or family members acquiring stakes during its early stages. Agreements like vesting schedules or buy-sell clauses were not relevant, given that it was fully owned by the state. Any changes in control or strategic direction were determined by government policy and Eni's broader strategy.
The Italian state, through Eni, held complete ownership of Snam at its inception.
Snam did not have traditional founders with equity stakes; it was a state-owned entity.
Early capital was a public investment to develop critical national infrastructure.
Snam's mandate was to serve as a public utility, focusing on the natural gas pipeline network.
The founding team's vision was to build a robust gas pipeline network, reflecting the state's control and long-term energy security goals.
Changes in control were dictated by governmental policy and Eni's strategy.
The initial Snam ownership structure was straightforward: the Italian government, through Eni, held complete control. The company's primary function was to develop and maintain natural gas infrastructure, aligning with Italy's strategic energy objectives. Over time, the Snam company has evolved, with changes in its Snam shareholders and operational focus. For those interested in the broader competitive landscape, further insights can be found in the Competitors Landscape of Snam. As of 2024, Snam's financial performance shows its continued importance in the Italian energy market, with a focus on expanding its Snam infrastructure to meet evolving energy demands. The Snam Italy operations remain central to the nation's energy security.
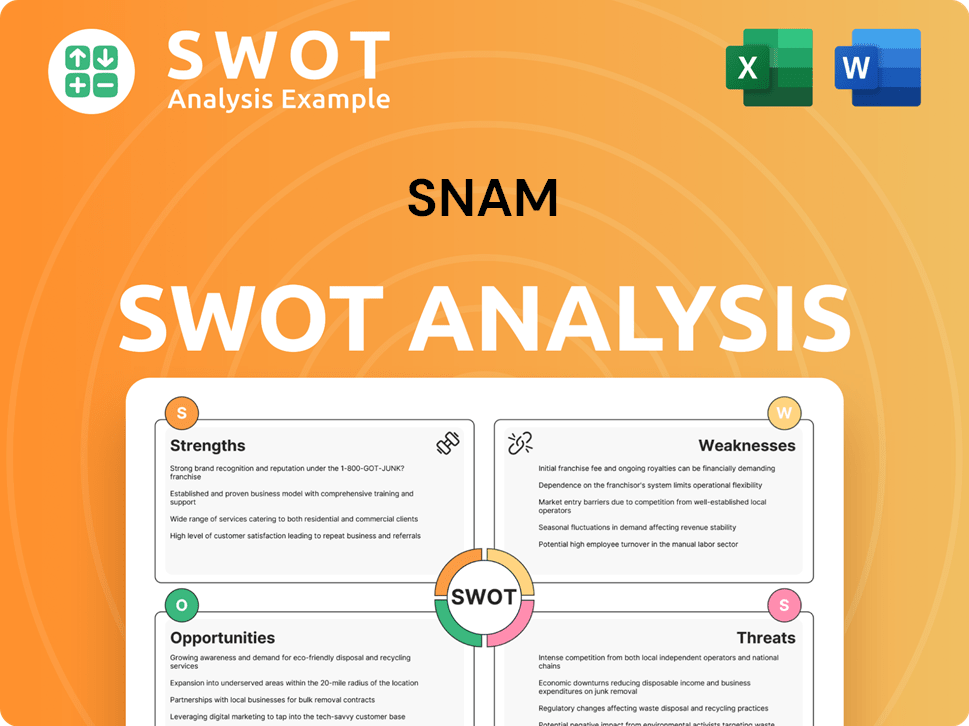
Snam SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Snam’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Who Owns Snam has been marked by a shift from complete state control to a publicly traded model. A pivotal moment in the Snam company's history was its separation from Eni and subsequent listing on the Milan Stock Exchange. This transition initiated its journey as a publicly listed entity, opening it up to a diverse range of investors, while still retaining significant state influence.
The Italian state's influence on Snam infrastructure has been maintained through various entities, ensuring its strategic importance in the national energy sector. The initial public offering (IPO) marked the beginning of its public ownership, setting the stage for the current Snam ownership structure.
| Event | Details | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Spin-off from Eni | Separation from the parent company. | Transition from state-owned to publicly traded. |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Listing on the Milan Stock Exchange. | Opened up ownership to public investors. |
| CDP Reti S.p.A. Acquisition | Acquisition of a significant stake. | Reinforced state influence through Cassa Depositi e Prestiti (CDP). |
As of April 2025, the major shareholder in Snam Italy is CDP Reti S.p.A., which is controlled by Cassa Depositi e Prestiti (CDP). CDP is largely owned by the Italian Ministry of Economy and Finance, ensuring the Italian state maintains a strategic interest. Other significant Snam shareholders include institutional investors like BlackRock, Inc., and The Vanguard Group. Their holdings fluctuate based on market conditions. For example, in 2024, institutional investors held varying percentages, often in the single digits. These major stakeholders influence Snam's strategy by demanding strong governance, sustainable practices, and consistent financial performance. For more information on the company, you can read this article about the company's operations.
Snam's ownership structure has evolved significantly, from state control to a publicly traded company.
- CDP Reti S.p.A., controlled by Cassa Depositi e Prestiti (CDP), is the major stakeholder.
- Institutional investors like BlackRock and Vanguard hold significant shares.
- The Italian state maintains influence through CDP, ensuring strategic alignment.
- Major shareholders influence Snam's strategy through governance and financial performance demands.
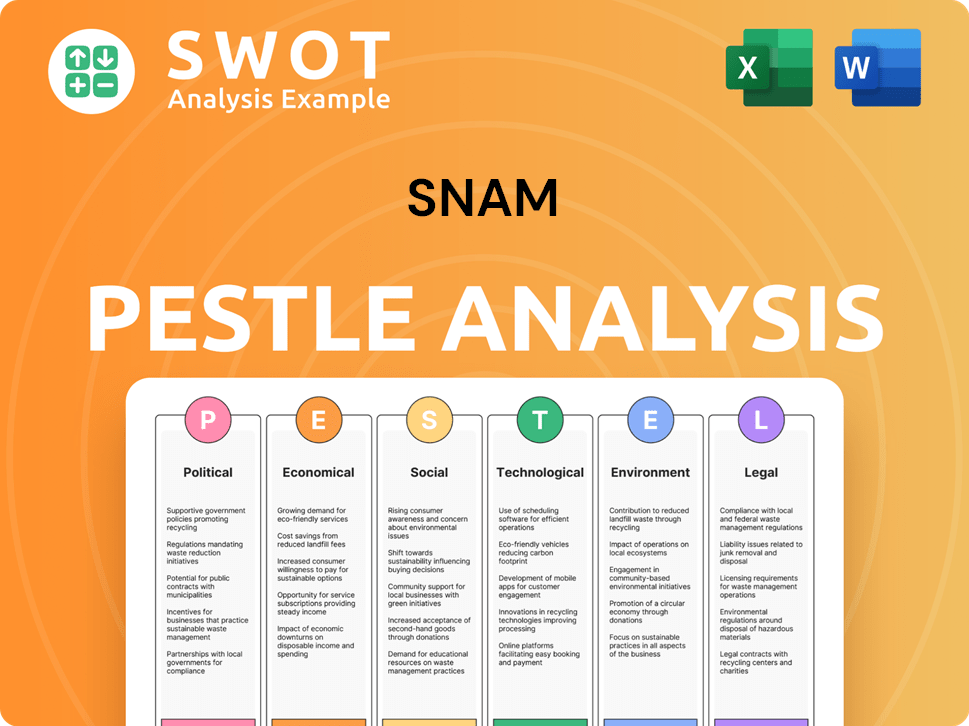
Snam PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Snam’s Board?
As of April 2025, the Board of Directors of the Snam company is composed of individuals representing major shareholders and independent members. This structure is designed to ensure good governance within a company of strategic national importance. The specific names and affiliations of the board members would be detailed in the latest annual report or corporate governance statement for 2024. Generally, board members representing CDP Reti S.p.A. would hold key positions, reflecting their significant ownership stake. Independent directors are appointed to ensure objectivity and protect the interests of all shareholders, contributing to a balanced governance framework.
The board's composition and decisions are regularly scrutinized by analysts and investors, ensuring accountability and adherence to market best practices. The presence of independent directors and the scrutiny from analysts and investors contribute to a more transparent and market-responsive decision-making process within Snam. For detailed information about the current board members, it's recommended to consult Snam's official reports.
| Board Role | Representative | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Chairman | (Details available in Snam's 2024 report) | (Details available in Snam's 2024 report) |
| CEO | (Details available in Snam's 2024 report) | (Details available in Snam's 2024 report) |
| Independent Director | (Details available in Snam's 2024 report) | (Details available in Snam's 2024 report) |
Snam operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for its ordinary shares. This means each share carries equal voting rights. This democratic voting structure means that while CDP Reti holds a significant block of shares, decisions are also influenced by the collective voting power of other institutional and individual Snam shareholders. The absence of outsized control mechanisms contributes to a more transparent decision-making process within Snam. To understand more about the company, you can also read about the Growth Strategy of Snam.
Snam's governance structure emphasizes transparency and equal voting rights, ensuring all shareholders have a voice. The board includes independent directors to maintain objectivity. The company's decisions are subject to scrutiny by analysts and investors.
- One-share-one-vote system.
- Independent directors for objectivity.
- Regular scrutiny by analysts and investors.
- Transparent decision-making process.
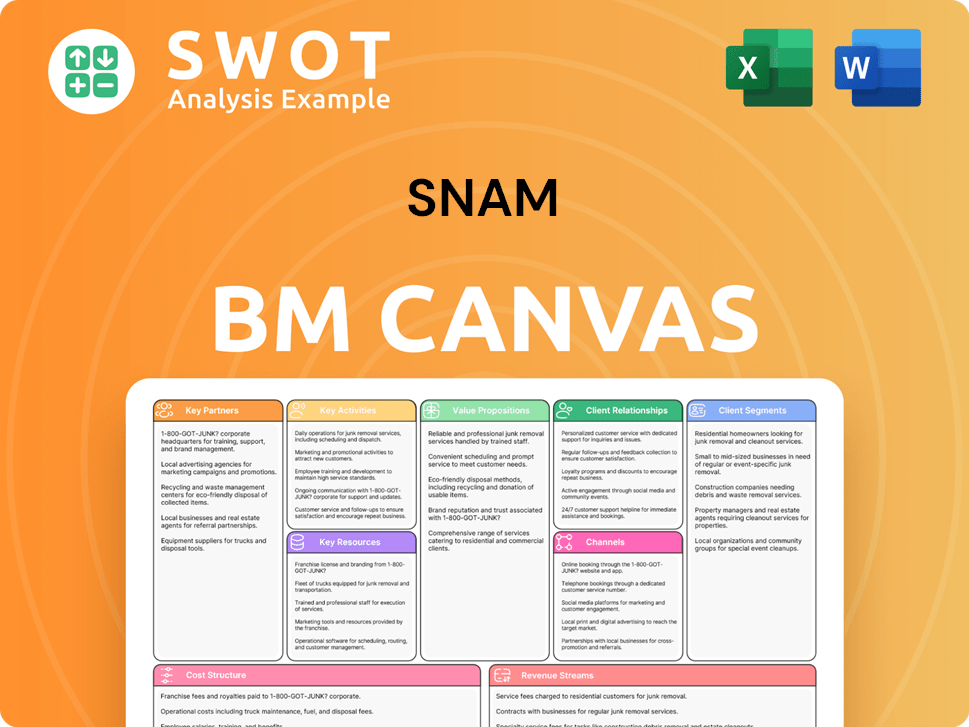
Snam Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Snam’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past three to five years (2022-2025), the Snam company has seen a continuation of its ownership trends, with a focus on institutional investment. The Italian state maintains strategic oversight. While major acquisitions haven't drastically changed the ownership structure, Snam Italy has been involved in strategic partnerships and minor acquisitions, particularly in new energy sectors like hydrogen and biomethane. These moves aim to attract investors interested in green energy transitions.
Industry trends show an increasing emphasis on ESG factors, which has led to a rise in institutional ownership from funds with sustainable investment mandates. This trend encourages further investments in decarbonization and sustainable infrastructure. Public statements from Snam management and analysts in 2024 and 2025 have highlighted the company's commitment to energy transition projects. These projects could attract further long-term strategic investors and potentially influence future ownership trends as the company diversifies its asset base. For more information on Snam's operations, consider reading about the Target Market of Snam.
| Year | Key Developments | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-2023 | Strategic partnerships in hydrogen and biomethane projects | Attracted investors focused on green energy and sustainable infrastructure. |
| 2024 | Increased focus on ESG initiatives and reporting | Enhanced appeal to institutional investors with sustainable investment mandates. |
| 2025 | Continued investments in decarbonization projects | Potential for attracting long-term strategic investors and influencing future ownership trends. |
The evolution of Snam shareholders reflects broader market dynamics, including potential shifts in major institutional holdings based on the company's performance and strategic direction. The company's focus on energy transition projects could further attract long-term strategic investors. The company's commitment to sustainable practices, as highlighted in its 2024 and 2025 reports, is likely to influence future ownership patterns.
Snam has formed strategic partnerships to expand its footprint in new energy vectors like hydrogen and biomethane. These partnerships aim to diversify its asset base. This strategic move attracts investors interested in green energy transitions and sustainable infrastructure.
The increasing focus on ESG factors has led to a rise in institutional ownership from funds with sustainable investment mandates. This trend encourages further investment in decarbonization and sustainable infrastructure. Snam's commitment to ESG is attracting investors.
The ownership profile of Snam continues to be influenced by institutional investment. The Italian state maintains strategic oversight. The company's commitment to energy transition projects could attract further long-term strategic investors.
Future ownership trends may be influenced by Snam's performance and strategic direction. The focus on energy transition projects could attract further long-term strategic investors. The diversification of the asset base is also a key factor.
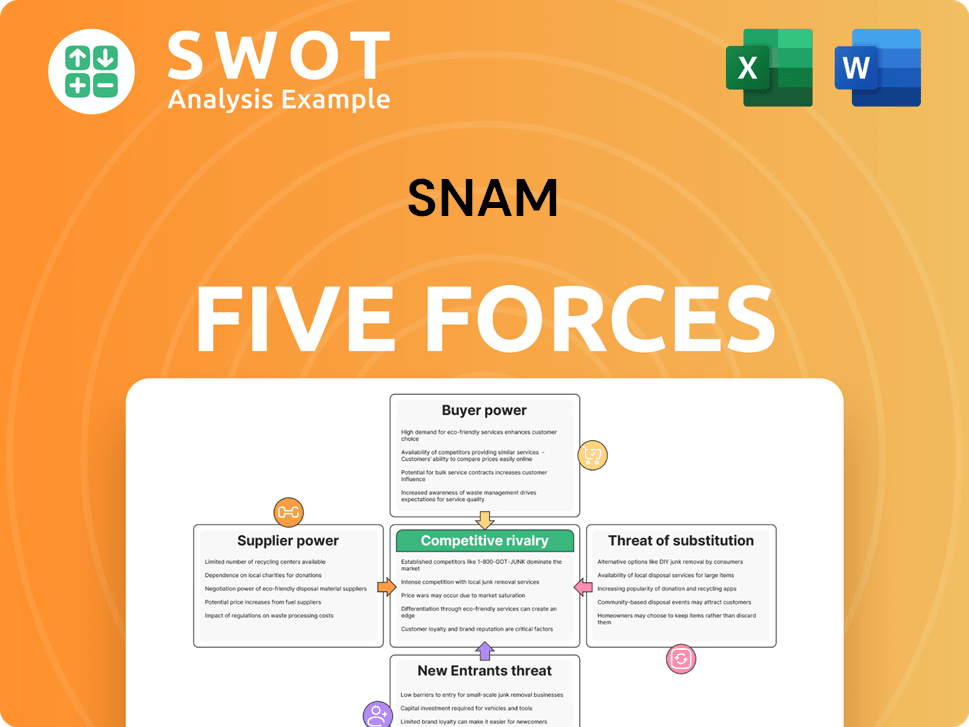
Snam Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Snam Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Snam Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Snam Company?
- How Does Snam Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Snam Company?
- What is Brief History of Snam Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Snam Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.