United Parcel Service Bundle
Who Really Controls United Parcel Service?
Unraveling the United Parcel Service SWOT Analysis is just the beginning. Understanding UPS ownership unveils the forces shaping its future, from strategic decisions to financial performance. Knowing "Who owns UPS?" is crucial for anyone looking to understand the global logistics landscape and its key players.

From its inception as a small messenger service to its current status as a global logistics leader, the UPS company's ownership has undergone a fascinating evolution. This exploration will delve into the UPS shareholders, the impact of the UPS stock, and the key players who have shaped the United Parcel Service ownership structure. We'll examine the CEO's influence, the public versus private aspects, and the implications for investors and stakeholders alike. This deep dive will answer the question: "Who owns UPS?"
Who Founded United Parcel Service?
The story of United Parcel Service (UPS) begins in 1907, with its roots in the American Messenger Company. The founders, James E. Casey, then just 19 years old, and Claude Ryan, 18, started the business with a modest investment. Casey's initial capital of $100, borrowed from a friend, marked the beginning of what would become a global logistics giant.
Early on, the company's growth was fueled by the dedication of its founders and early employees. While specific equity splits aren't publicly detailed from the very beginning, Casey's leadership was pivotal. Key figures like Casey's brother George and Evert McCabe joined the team, contributing to the company's expansion and operational improvements.
The initial focus of the American Messenger Company was on providing messenger services, evolving over time to include package delivery. This shift laid the groundwork for the future of UPS. The company's early years were characterized by a hands-on approach, with the founders deeply involved in all aspects of the business.
James E. Casey and Claude Ryan founded the American Messenger Company in 1907. Casey provided the initial capital of $100.
George Casey, James' brother, and Evert McCabe were also important in the company's early development.
The company initially focused on messenger services before expanding into package delivery.
For decades, UPS remained privately held, with ownership primarily among employees and management.
Growth was largely self-funded through retained earnings and employee investments.
This structure fostered a strong company culture and a long-term strategic outlook.
The early UPS ownership structure was unique, focusing on employee ownership. This model, which lasted for many years, fostered a strong company culture. The company's growth was mostly self-funded, with employees having a direct stake in the company's success. This approach differed from traditional businesses, as there were no external angel investors or family members acquiring stakes. If you want to know more about the competitive landscape, you can check out the Competitors Landscape of United Parcel Service.
- Who owns UPS? Primarily, the employees and management held ownership for a long time.
- Is UPS a public company? No, it was a privately held company for decades.
- Who are the major shareholders of UPS? Before going public, the major shareholders were the employees.
- What is the history of UPS ownership? The history of UPS company ownership is rooted in a private, employee-centric model.
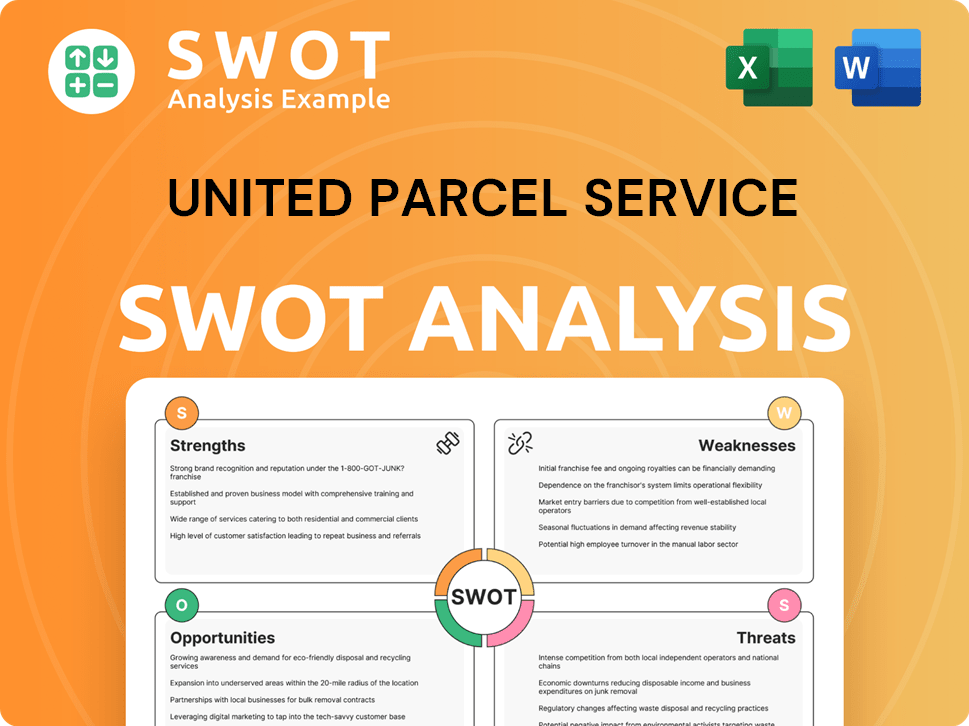
United Parcel Service SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has United Parcel Service’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The most significant change in the ownership of United Parcel Service (UPS) occurred on November 10, 1999, with its initial public offering (IPO). This IPO was a landmark event, raising approximately $5.47 billion, which was the largest in U.S. history at the time. This transition marked a shift from a privately held, employee-owned business to a publicly traded company, opening the door for wider investment and providing substantial capital for global expansion. The IPO allowed the company to access capital markets more easily, which fueled its growth and strategic initiatives.
Before the IPO, UPS was primarily owned by its employees and a small group of private investors. The decision to go public was driven by the need for capital to fund expansion plans and to provide liquidity for employee shareholders. The move to public ownership has significantly influenced UPS's strategic focus, emphasizing shareholder value, quarterly earnings, and transparency. This shift also enabled UPS to make strategic acquisitions and investments, accelerating its growth in the competitive logistics market.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| IPO | November 10, 1999 | Transitioned from private, employee-owned to publicly traded company. |
| Public Trading | November 10, 1999 - Present | Allowed for broader investment from institutional and individual investors. |
| Ongoing | Early 2025 | Institutional investors hold a majority of the shares. |
As of early 2025, the UPS ownership structure is largely dominated by institutional investors. Major shareholders include large asset management firms and mutual funds. Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., and State Street Corp. are consistently among the top institutional holders, collectively controlling a significant portion of UPS stock. These firms manage extensive portfolios on behalf of their clients, making their holdings in UPS a reflection of broader market investment trends. While individual insiders, including executives and board members, hold shares, their collective ownership represents a much smaller percentage compared to institutional investors. Understanding the UPS ownership structure explained is crucial for investors looking to understand the dynamics of the UPS company.
The shift to public ownership in 1999 was a pivotal moment for UPS, transforming its financial structure and strategic direction. The majority of UPS shareholders today are institutional investors, reflecting the company's integration into the broader financial market. For more details, check out the Brief History of United Parcel Service.
- The IPO in 1999 was a major turning point.
- Institutional investors are the primary stakeholders.
- This structure influences strategic decisions.
- Understanding the ownership is key for investors.
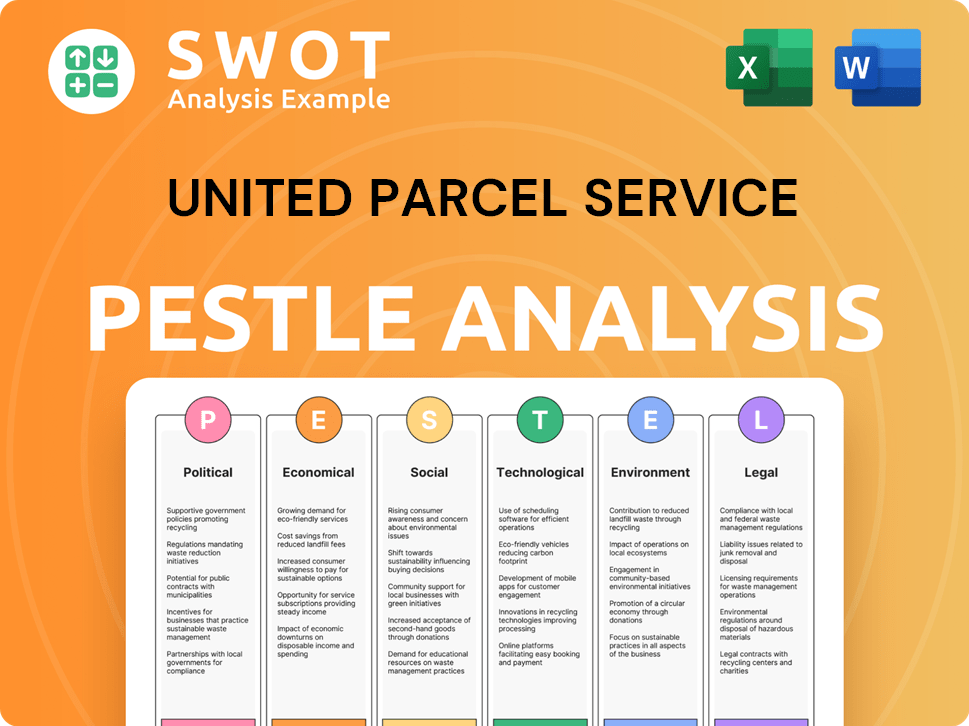
United Parcel Service PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on United Parcel Service’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of United Parcel Service (UPS) is composed of a mix of independent directors and executives, reflecting a commitment to corporate governance. The board typically includes the Chief Executive Officer and Chairman, alongside a majority of independent directors. This structure is designed to ensure oversight of the company's strategic direction and financial performance. The board's decisions are made through a collaborative process among its members, acting in the best interests of UPS shareholders.
The board members generally have diverse backgrounds in finance, logistics, technology, and global business. While specific board members representing major shareholders are not explicitly designated, the composition aims to bring varied expertise to the table. The board's role is to oversee the Target Market of United Parcel Service, ensure sound financial performance, and act in the best interests of its shareholders.
| Board Role | Description | As of Early 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Chief Executive Officer (CEO) | Leads the company's operations and strategic direction. | Carol B. Tomé |
| Chairman of the Board | Oversees the board's activities and ensures effective governance. | Carol B. Tomé |
| Independent Directors | Provide oversight and represent shareholder interests. | Majority of the Board |
UPS operates under a one-share, one-vote structure for its common stock, meaning each share of Class B common stock (the publicly traded class) entitles the holder to one vote. There are no known special voting rights that grant outsized control to any individual or entity beyond their proportional ownership of shares. In recent years, UPS has not been subject to significant public proxy battles or activist investor campaigns that have fundamentally reshaped its governance or decision-making processes. This structure ensures that all UPS shareholders have a proportional say in the company's direction.
The board of directors oversees UPS, ensuring strategic direction and financial health. The one-share, one-vote structure gives equal voting power to all shareholders. Understanding the board's composition and voting rights is key for anyone interested in UPS ownership or how to invest in UPS stock.
- Board members include the CEO, Chairman, and independent directors.
- Each share of Class B common stock gets one vote.
- No special voting rights exist.
- The board focuses on shareholder interests.
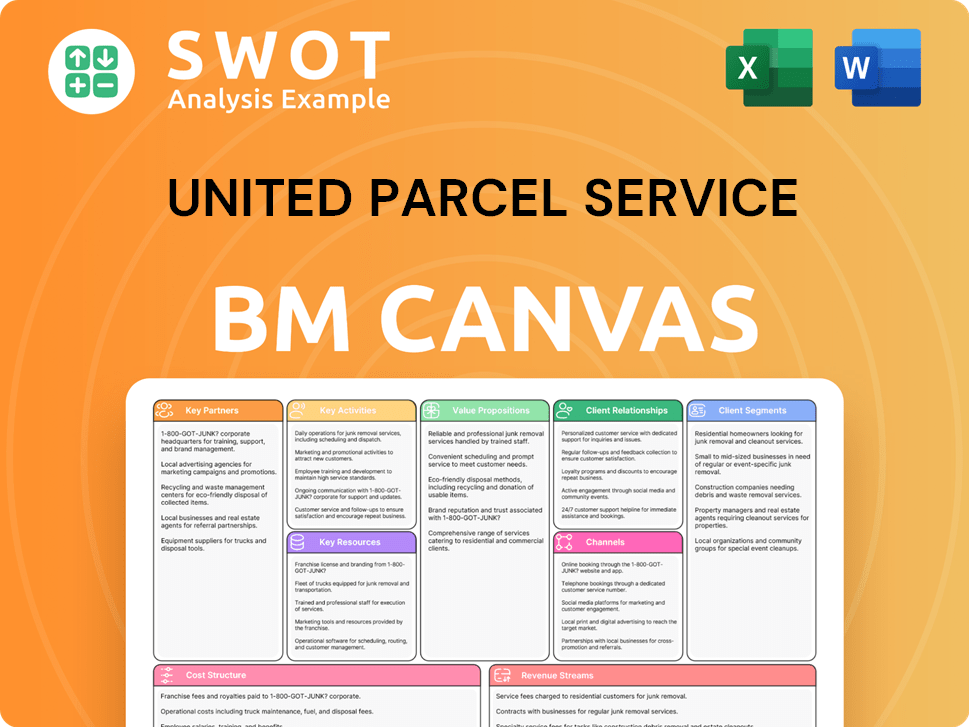
United Parcel Service Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped United Parcel Service’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (roughly 2022-2025), the ownership structure of United Parcel Service (UPS) has remained relatively stable, with institutional investors continuing to hold a significant portion of the company's shares. This trend reflects the company's established position in the logistics industry and its consistent financial performance. The focus of UPS company analysis often centers on operational efficiency and market share, with less emphasis on dramatic shifts in ownership. The stability in UPS ownership is typical for a mature, publicly traded company.
Significant share buyback programs could influence the proportional ownership of existing UPS shareholders, but these are not always implemented. Secondary offerings, which would dilute ownership, are less common for established companies like UPS. Strategic moves, such as investments in healthcare logistics or technological advancements, are usually funded through internal capital or debt, rather than through significant equity dilution. The primary focus remains on the company's ability to adapt to industry trends, such as the growth of e-commerce, and to maintain its competitive edge. For more details on the business model, check out the Revenue Streams & Business Model of United Parcel Service.
| Metric | Data | Source/Year |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Approximately $145 billion | Yahoo Finance, May 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership | Approximately 70-75% | Various financial data providers, 2024 |
| Dividend Yield | Around 3.5% | Yahoo Finance, May 2024 |
The ownership of UPS stock is largely influenced by the company's financial health and the broader economic environment. The company's stock symbol is UPS. Investors looking to invest in UPS stock should consult with a financial advisor. The history of UPS ownership is tied to the company's growth from its founding to its current status as a global logistics leader. The company's headquarters is located in Atlanta, Georgia. UPS is a publicly traded company, and has been since it went public in 1999. Understanding the UPS ownership structure is important for anyone considering investing in the company.
Institutional investors hold a substantial portion of UPS shares. This indicates a level of confidence in the company's long-term prospects and financial stability. The consistent returns and dividend payments make UPS an attractive investment for many institutional investors.
Major shareholders of UPS include large asset management firms and index funds. These entities often seek stable, dividend-paying stocks. Analyzing the holdings of these major players offers insights into market sentiment.
Share buyback programs, if implemented, can increase the proportional ownership of remaining shareholders. Such actions often signal confidence in the company's future performance. This can positively influence the stock price.
Increased e-commerce demand and supply chain diversification are driving factors in the logistics sector. These trends make UPS an appealing investment for institutional investors. Staying informed on industry trends is crucial.
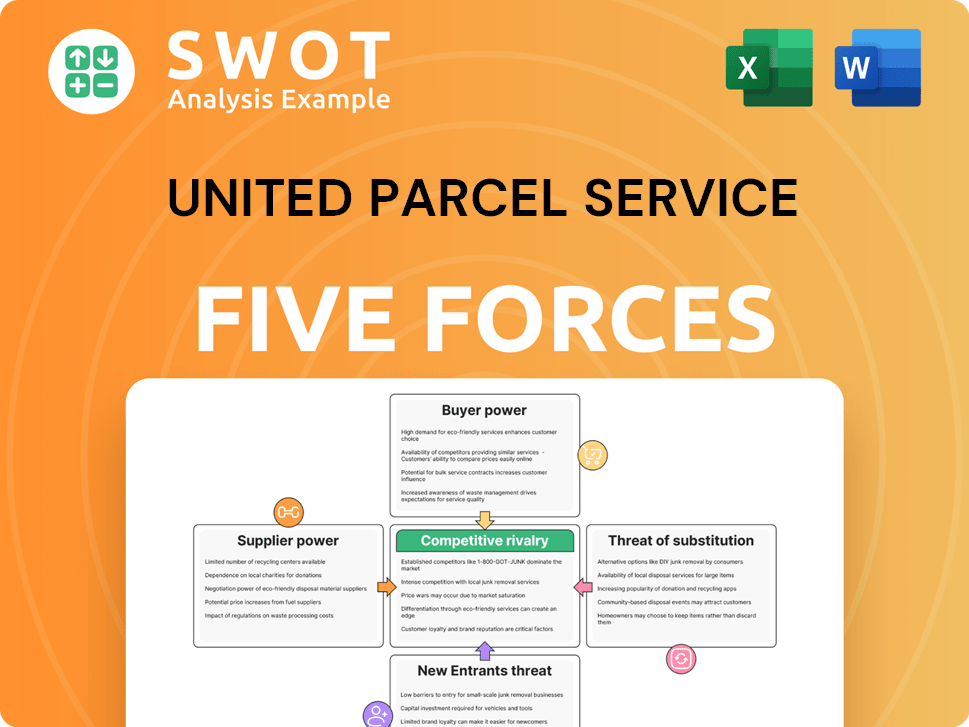
United Parcel Service Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of United Parcel Service Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of United Parcel Service Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of United Parcel Service Company?
- How Does United Parcel Service Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of United Parcel Service Company?
- What is Brief History of United Parcel Service Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of United Parcel Service Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.