Vale Bundle
Who Really Owns Vale Company?
Unraveling the ownership structure of Vale S.A. is essential for understanding its global influence. From its roots as a Brazilian state-owned enterprise to its current status as a publicly traded mining giant, Vale's journey reflects significant shifts in global market dynamics. Understanding Vale SWOT Analysis can provide valuable insights into its strategic positioning.

This exploration into Vale ownership is crucial for investors, analysts, and anyone interested in the mining industry. Understanding who owns Vale, including its major shareholders and the evolution of its ownership, provides critical insights into its strategic direction and future performance. This analysis will delve into the intricacies of Vale's ownership, from its initial government control to its current shareholder base, offering a comprehensive view of this global leader in iron ore and nickel production. Keywords like Vale SA, Vale shareholders, and Vale mining will be explored.
Who Founded Vale?
The story of Vale, formerly known as Companhia Vale do Rio Doce (CVRD), began on June 1, 1942. It was established as a state-owned enterprise by the Brazilian federal government. This marked the beginning of its journey as a key player in the mining industry.
As a state-owned entity, the initial ownership structure of Vale was straightforward. The Brazilian Union held 100% of the company's equity. This setup reflected the government's strategic vision for developing Brazil's mineral resources, particularly iron ore.
Unlike private ventures, Vale did not have individual founders in the traditional sense. Instead, the company was created through a government decree. This approach ensured that the company's early direction and investments were aligned with national development goals.
During its initial phases, Vale operated under direct governmental control. Decisions regarding strategy, investments, and operations were made by government ministries and appointed officials.
There were no early backers or angel investors. The state provided all the capital. Early agreements common in private ventures, such as vesting schedules, were not applicable.
The founding team's vision was tied to national development. Control was centralized within the Brazilian government. This ensured alignment with broader economic objectives.
The creation of Vale was a strategic initiative to develop Brazil's vast mineral resources. The focus was primarily on iron ore, a key commodity.
As a state-owned enterprise, Vale's operations were directly influenced by government policies. This setup ensured alignment with national interests.
The initial ownership structure was simple: the Brazilian Union held 100% of the company's equity. This setup provided a solid foundation for its operations.
The early years of Vale were characterized by its status as a state-owned entity. This meant that the Brazilian government had complete control over the company's operations and strategic direction. For a deeper dive, you can explore the Brief History of Vale. This structure allowed the government to focus on developing Brazil's mineral resources, particularly iron ore. The company's initial focus was on iron ore production, with the government providing all the necessary capital. In 2024, Vale's iron ore production reached approximately 306.1 million metric tons, a slight increase from the 300.8 million metric tons produced in 2023.
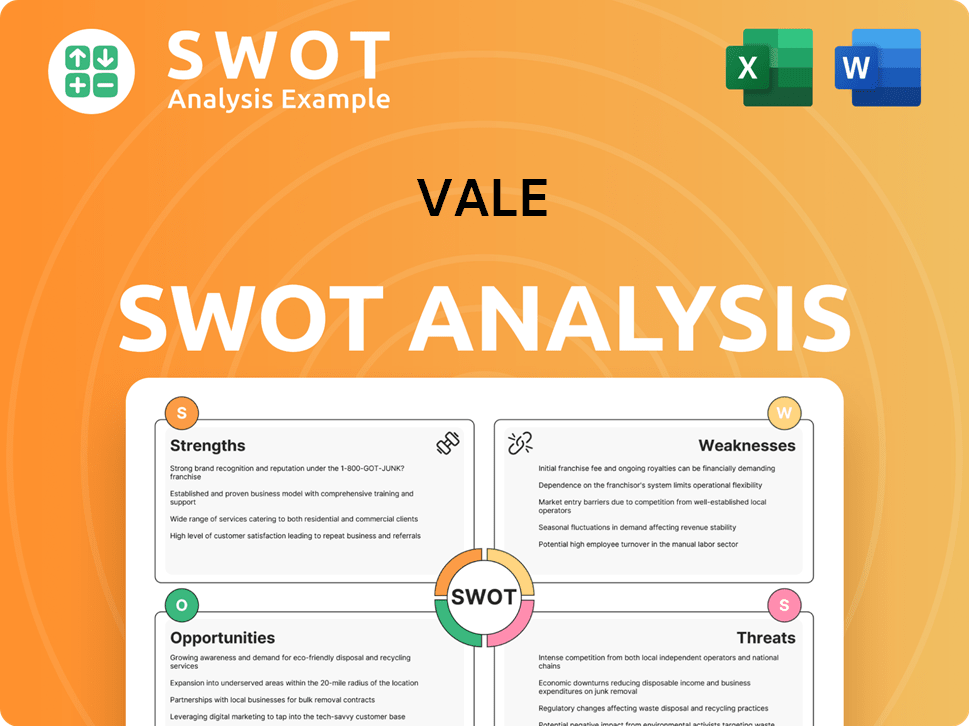
Vale SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Vale’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Vale's ownership is marked by a significant shift from state control to a publicly traded model. The privatization process, initiated in 1997, was a pivotal moment. This transition introduced a diverse shareholder base, fundamentally changing the company's structure and strategic direction. The initial public offering (IPO) was a key step in this transformation, opening up ownership to a broad range of investors.
Post-privatization, a consortium named Valepar S.A. initially held a controlling stake. This group included Brazilian pension funds like Previ, Petros, and Funcef, along with the Brazilian development bank BNDESPAR, and other strategic investors. Over time, Valepar's influence diminished. In 2017, a major restructuring dissolved Valepar, converting its shares into common shares of Vale S.A. This move aimed to enhance governance and improve liquidity for Vale shareholders.
| Event | Date | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Privatization | 1997 | Transition from state-owned to publicly traded. |
| Valepar Formation | Post-1997 | Consortium control by Brazilian pension funds and BNDESPAR. |
| Valepar Dissolution | 2017 | Simplified ownership structure; increased liquidity. |
As of early 2025, Vale's ownership is highly diversified. Institutional investors, including large asset managers and mutual funds, hold a significant portion of the shares. BlackRock Inc. and Capital Research Global Investors are consistently among the top institutional holders. Brazilian institutional investors, particularly pension funds, continue to maintain substantial stakes. Individual insider ownership, including executives and board members, represents a smaller percentage compared to institutional holdings. The Brazilian government, through BNDESPAR, still retains a relevant stake, which is often held through preferred shares or indirect means. This shift towards a market-driven strategy emphasizes shareholder returns and adherence to international governance standards. The Vale mining company's market capitalization, as of early 2024, was approximately $60 billion.
The ownership structure of Vale SA has evolved significantly since its privatization.
- Institutional investors, such as BlackRock, hold a significant portion of shares.
- Brazilian pension funds remain key stakeholders.
- The Brazilian government, through BNDESPAR, still has a relevant stake.
- The company's focus is on shareholder returns and international governance.
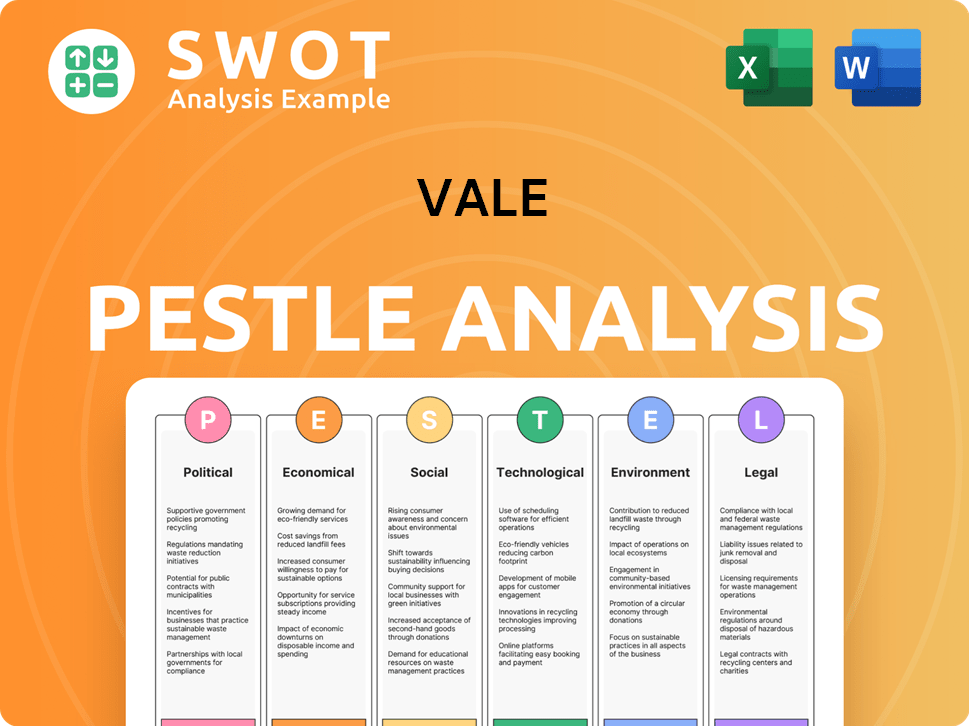
Vale PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Vale’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of the Vale company includes a mix of representatives from major shareholders, independent directors, and individuals with industry expertise. This composition reflects the diverse interests within the company, ensuring a balance between shareholder representation and independent oversight. The board typically includes members with backgrounds in finance, mining, and sustainability, reflecting the multifaceted nature of Vale's operations. The presence of independent directors is crucial for maintaining good governance and balancing the interests of various shareholder groups.
The board's composition is subject to change, but the inclusion of representatives from significant institutional investors is a common feature, reflecting their substantial ownership stakes. These investors often play an active role in shaping the company's strategic direction. The board's structure and the influence of its members are critical in overseeing the company's performance and ensuring accountability to all stakeholders. The Marketing Strategy of Vale also depends on the board's decisions.
| Board Member | Position | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Eduardo Bartolomeo | Chief Executive Officer | Vale |
| José Luciano Penido | Chairman of the Board | Independent |
| Alexander de Moraes | Board Member | Independent |
Vale operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for its common shares, which became more prevalent after the 2017 corporate restructuring. This structure promotes greater accountability to all common shareholders. While there are no longer 'golden shares' or specific founder shares granting outsized control, certain large institutional investors or long-term Brazilian entities may exert significant influence through their substantial holdings and active participation in shareholder meetings. Recent years have seen increased scrutiny on corporate governance within the mining sector, and Vale has faced activist investor campaigns or proxy battles related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues.
The voting power within Vale is primarily determined by share ownership, with a one-share-one-vote system in place. Major shareholders, including institutional investors and long-term Brazilian entities, wield significant influence. Shareholder meetings and proxy battles are key arenas for influencing corporate decisions.
- One-share-one-vote structure promotes accountability.
- Large institutional investors have significant influence.
- ESG issues are a focus for shareholder activism.
- Board independence is crucial for good governance.
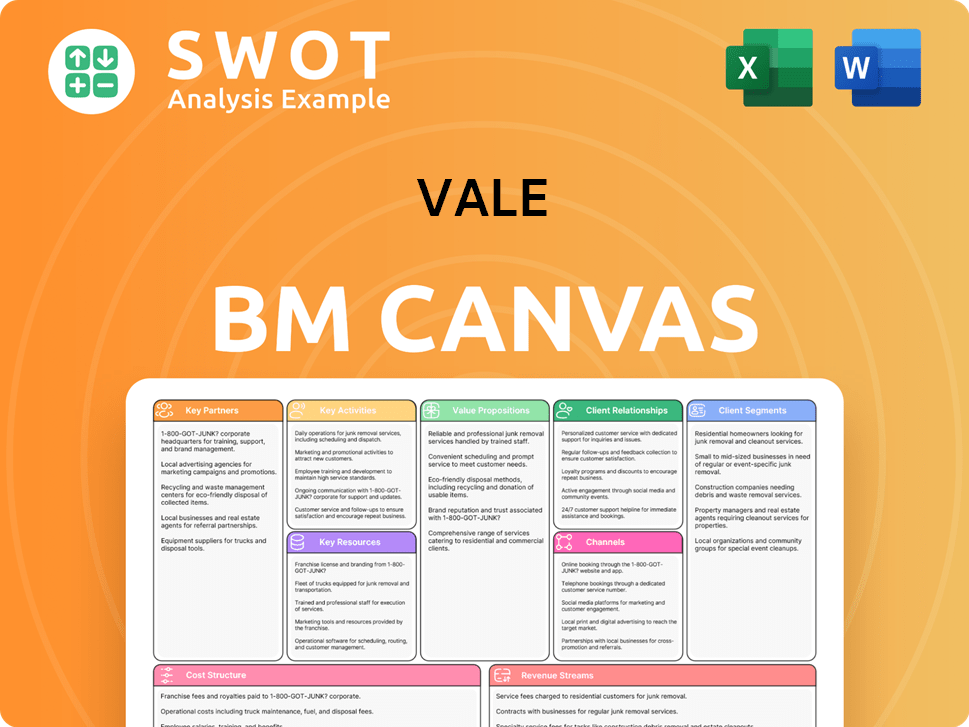
Vale Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Vale’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership of the Vale company has seen some interesting shifts. The company has been actively buying back its own shares, which is a move to give back to shareholders and improve its financial structure. While there haven't been any big changes in ownership due to mergers or acquisitions, the company has been selling off some of its non-core assets. These changes subtly affect who invests in the company and what they focus on.
Leadership changes have also played a role in investor sentiment. The departure of long-time executives and the arrival of new leaders can change how investors see the company. There's also a growing trend of institutional investors, like big asset managers, holding more shares due to the company's importance in global industries and the move towards renewable energy. Investors are increasingly focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, which influences the type of investors the company attracts. Vale has publicly stated its commitment to improving its ESG performance, a key factor for many current and prospective investors.
| Metric | Latest Data (2024-2025) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Approximately $60-70 billion USD | Financial News Outlets, Company Filings |
| Share Buyback Programs | Ongoing, with significant amounts allocated annually | Company Announcements |
| Institutional Ownership | Generally above 50% | Financial Data Providers |
The focus for Vale remains on improving its operations, boosting efficiency, and maintaining a strong financial position. These strategic moves will influence its appeal to various types of investors. Understanding the competitive landscape is also crucial for assessing Vale's position.
Vale's ownership is primarily institutional, with large asset managers and investment funds holding significant stakes. These institutional investors play a key role in shaping the company's strategic direction.
Major institutional investors include global asset management firms, pension funds, and sovereign wealth funds. These entities often have a long-term investment horizon.
Share buybacks and strategic divestitures are key trends. The company has been actively returning value to shareholders through share repurchases, reflecting confidence in its financial health.
ESG factors are increasingly important. Investors are prioritizing companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices, influencing ownership decisions.
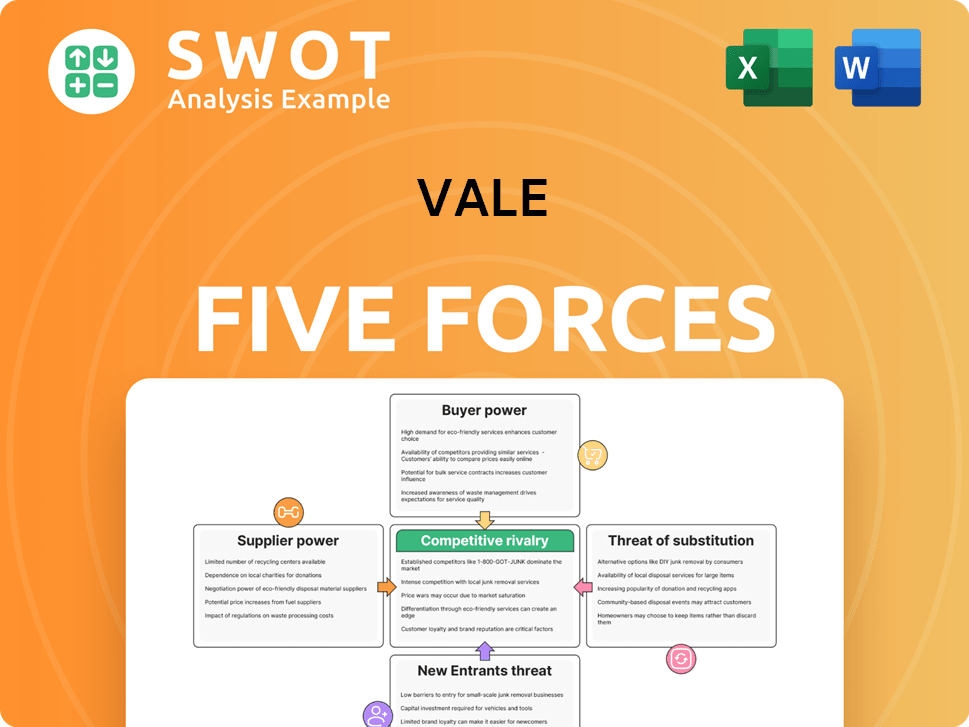
Vale Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Vale Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Vale Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Vale Company?
- How Does Vale Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Vale Company?
- What is Brief History of Vale Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Vale Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.