Tenet Health Bundle
What's the Story Behind Tenet Health?
Embark on a journey through time to uncover the fascinating Tenet Health SWOT Analysis, a leading healthcare provider with a story as complex as the industry it serves. From its humble beginnings in 1969, Tenet Healthcare, initially known as National Medical Enterprises, has navigated a dynamic landscape of mergers, acquisitions, and evolving healthcare paradigms. Discover the pivotal moments that shaped this Hospital System into a healthcare powerhouse.
This brief history of Tenet Healthcare Corporation reveals a remarkable transformation, from its early days acquiring medical facilities to its current status as a major player in the healthcare industry. The company's strategic moves, including its significant investments in ambulatory surgery centers, reflect its commitment to adapting and thriving. Explore the timeline of Tenet Healthcare's growth, its impact on healthcare, and its ongoing evolution as a prominent Healthcare Provider.
What is the Tenet Health Founding Story?
The story of Tenet Healthcare, a significant healthcare provider, begins in 1969. Originally named National Medical Enterprises (NME), the company was established by Richard Eamer, Leonard Cohen, and John Bedrosian. Their vision was to bring standard business practices to the healthcare industry.
NME's initial headquarters were in Los Angeles, California. This marked the start of what would become a major player in the hospital system landscape. The founders aimed to manage hospitals like retail or hotel chains, focusing on efficiency and patient satisfaction.
The company's early strategy involved acquiring and managing hospitals to improve efficiency and profitability. This approach quickly led to significant growth and expansion within the healthcare sector.
NME started with a $7 million investment, which was used to purchase five hospitals.
- In May 1969, NME acquired four general hospitals, including Doctors Medical Center of Modesto, and real estate for future hospital development.
- By 1975, NME had grown to own, operate, and manage 23 hospitals and a home healthcare business.
- The company focused on providing cost-efficient, well-managed hospitals to satisfy doctors and patients.
- By 1981, NME owned or managed 193 hospitals and nursing homes, becoming the third-largest healthcare company in the U.S.
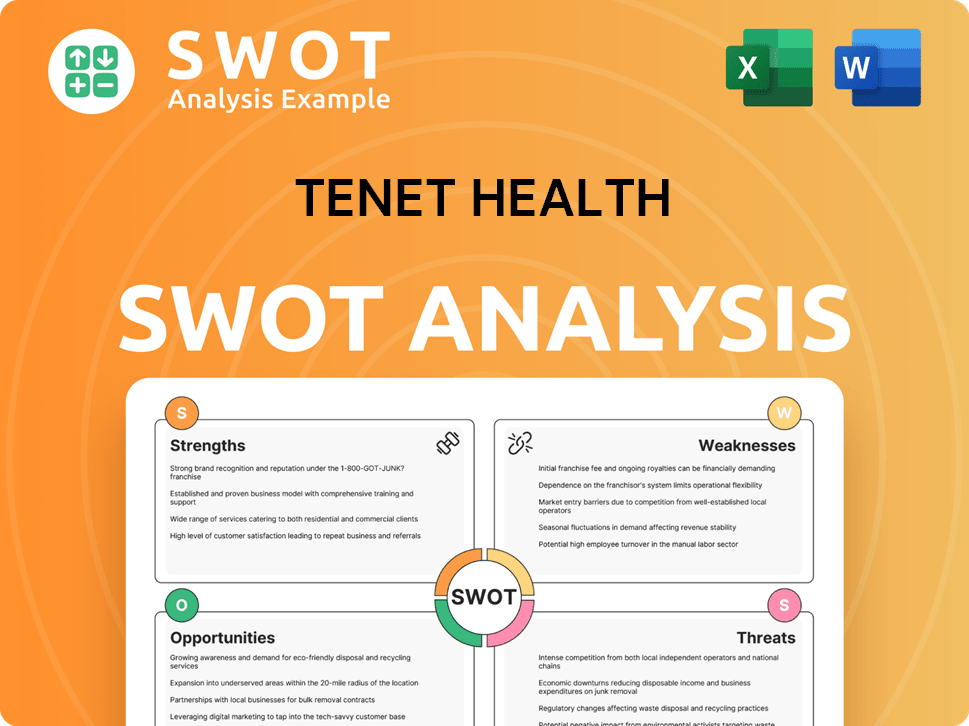
Tenet Health SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Tenet Health?
The early growth and expansion of the Tenet Health company, formerly known as National Medical Enterprises (NME), marked a period of significant acquisitions and strategic moves. NME's initial focus was on rapid expansion beyond its California base, quickly increasing its hospital network. This period laid the foundation for Tenet Healthcare's future as a major healthcare provider.
In 1971, NME initiated seven construction projects and acquired another hospital, tripling its size within a year. The company expanded outside California in 1973, acquiring a hospital in Seattle, Washington, and building one in El Paso, Texas. By 1974, NME established domestic and international divisions for management services, with significant income from managing other hospitals and equipment rental.
By the end of 1979, NME was the fourth-largest publicly owned hospital chain in the U.S. A notable international contract was signed in 1980, a five-year, $150 million agreement with Saudi Arabia. By the end of 1981, NME's sales exceeded $1 billion, demonstrating substantial financial growth and international reach.
In 1982, NME acquired National Health Enterprises, becoming the second-largest nursing home owner. In 1986, NME restructured into subdivisions, divesting acute-care hospitals. The acquisition of American Medical Holdings in 1994 for $3.35 billion was a pivotal moment, leading to the rebranding as Tenet Healthcare Corporation.
In 1996, Tenet acquired OrNda, followed by further acquisitions, including eight Philadelphia hospitals in 1998. The 2013 acquisition of Vanguard Health Systems for $4.3 billion significantly expanded Tenet's operations, making it the third-largest investor-owned hospital company in the U.S. by revenue and hospital count. For more details on the company's target market, you can read this article: Target Market of Tenet Health.
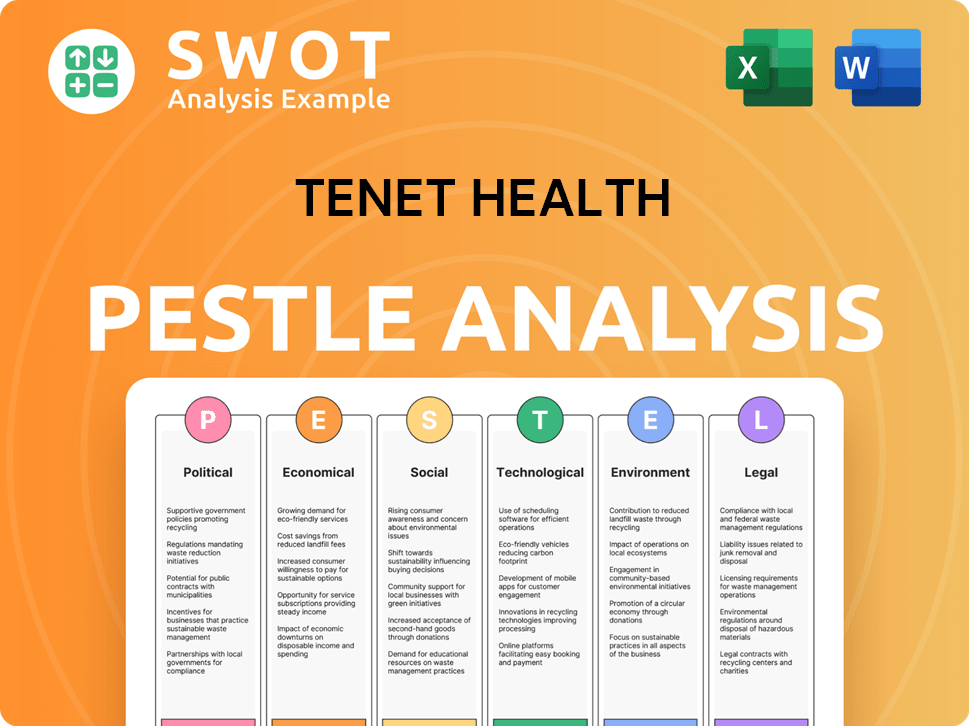
Tenet Health PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Tenet Health history?
The brief history of Tenet Healthcare reveals a journey marked by strategic shifts and significant developments. Tenet Health's evolution includes pivotal acquisitions and expansions, shaping its position in the healthcare sector. The Tenet Company History is a story of growth, adaptation, and facing industry challenges.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2015 | Tenet Healthcare acquired a majority stake in United Surgical Partners International (USPI), becoming the largest operator of outpatient surgery centers in the United States. |
| 2024 | USPI's adjusted EBITDA grew by 17%, and Tenet Health added nearly 70 ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) to its portfolio through acquisitions and openings. |
| 2024 | Tenet Healthcare divested 14 hospitals and related operations, including hospitals in Alabama, South Carolina, and California. |
| 2024 | Tenet exited the year with a leverage ratio of 2.54x EBITDA, reflecting significant balance sheet deleveraging. |
| 2025 (Projected) | Tenet plans to add 10 to 12 de novo ASCs, with an investment of approximately $250 million earmarked for M&A in the ambulatory space. |
Tenet Health has embraced innovation, particularly in surgical robotics, which are now in almost 150 programs across the country. The company leverages AI-driven technologies to streamline clinical and administrative processes.
Tenet Healthcare has expanded the use of surgical robotics, integrating them into nearly 150 programs nationwide. This technology enhances surgical precision and patient outcomes.
Tenet Health invests in AI to streamline clinical and administrative functions. This investment aims to reduce costs and improve patient satisfaction.
Launched in 2008, Conifer Health Solutions provides revenue cycle management and value-based care services. This subsidiary supports Tenet Healthcare's financial and operational efficiency.
Tenet Healthcare has faced challenges, including scrutiny over past surgical practices and stock price volatility. The healthcare provider also faces ongoing challenges such as policy uncertainty and labor market pressures.
The potential expiration of Affordable Care Act (ACA) exchange subsidies at the end of 2025 and possible changes to Medicaid funding could pose a 2-10% EBITDA headwind for Tenet Health. This uncertainty requires strategic adaptation.
Clinical staff retention and potential shortages pose ongoing concerns for the Hospital System. Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency.
Tenet Healthcare's stock price experienced significant volatility, with a peak in 2002 followed by a dip in 2009. The company has since focused on strategic financial management.
Tenet Health focuses on operational excellence, cost discipline, and continued investment in high-acuity service lines and the ambulatory segment to navigate these challenges. This approach aims to ensure long-term sustainability and growth.
For a deeper dive into Tenet Health's financial workings, explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Tenet Health.
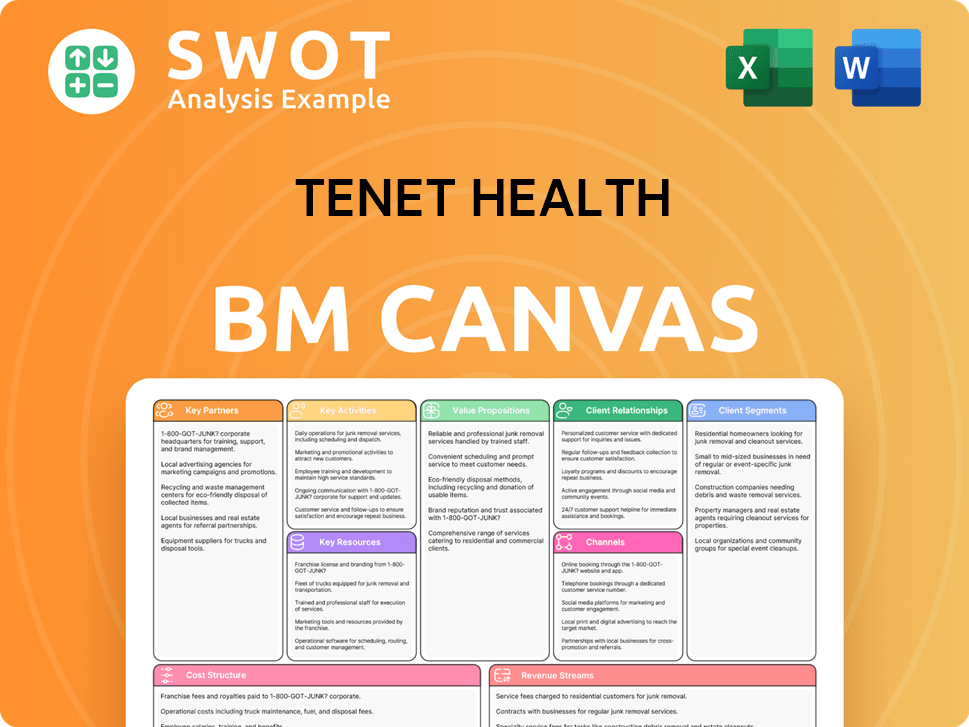
Tenet Health Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Tenet Health?
The Growth Strategy of Tenet Health is a journey marked by strategic acquisitions, expansions, and a focus on ambulatory care. Initially incorporated in 1969 as National Medical Enterprises (NME), the company rapidly grew through acquisitions, expanding beyond California by 1973. A significant pivot occurred in 1994 when NME acquired American Medical Holdings and was renamed Tenet Healthcare Corporation. Further expansion included the founding of United Surgical Partners International (USPI) in 1998, which later merged with Tenet. The acquisition of Vanguard Health Systems in 2013 and the combination with USPI in 2015 solidified its position in the healthcare market. More recently, Tenet has focused on ambulatory acquisitions, including SurgCenter Development, and divesting hospital assets to bolster its ambulatory surgery center portfolio.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1969 | Incorporated as National Medical Enterprises (NME) in California, initiating with an IPO to acquire four hospitals. |
| 1973 | Expanded outside California through acquisitions in Washington and Texas. |
| 1980 | Signed a $150 million contract with Saudi Arabia for healthcare facility development. |
| 1994 | NME acquired American Medical Holdings and changed its name to Tenet Healthcare Corporation. |
| 1998 | United Surgical Partners International (USPI) was founded. |
| 2008 | Launched Conifer Health Solutions. |
| 2013 | Acquired Vanguard Health Systems, significantly expanding hospital operations. |
| 2015 | Combined with USPI to create the largest ambulatory surgery platform in the U.S. |
| 2020-2021 | Completed transformative ambulatory acquisitions with SurgCenter Development. |
| 2024 | Divested 14 hospitals and added nearly 70 new ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) to USPI's portfolio. |
In 2024, Tenet Healthcare's net operating revenues reached approximately $20.7 billion, with USPI contributing $4.5 billion. The company reported a net income of $318 million and an Adjusted EBITDA of $1.048 billion in Q4 2024. These figures reflect a strong performance driven by strategic initiatives and market adjustments.
The first quarter of 2025 saw Tenet Health reporting a net income of $406 million and an Adjusted EBITDA of $1.163 billion. Ambulatory Care Adjusted EBITDA increased by 15.7% compared to Q1 2024, highlighting the success of the ambulatory strategy. This growth underscores the company’s focus on expanding its ambulatory footprint.
For 2025, Tenet anticipates an Adjusted EBITDA between $3.975 billion and $4.175 billion, with net operating revenues projected between $20.6 billion and $21 billion. The company plans to invest approximately $250 million annually in ambulatory M&A, aiming to add 10 to 12 de novo centers. A new medical campus in Florida is also slated for completion by late 2025.
Tenet's strategic focus remains on expanding its ambulatory footprint and maintaining robust free cash flow. It continues to emphasize high-acuity service lines. The company expects stable surgical case volumes and sustained higher patient acuity levels in 2025, particularly in procedures like total joint replacements and cardiovascular interventions.
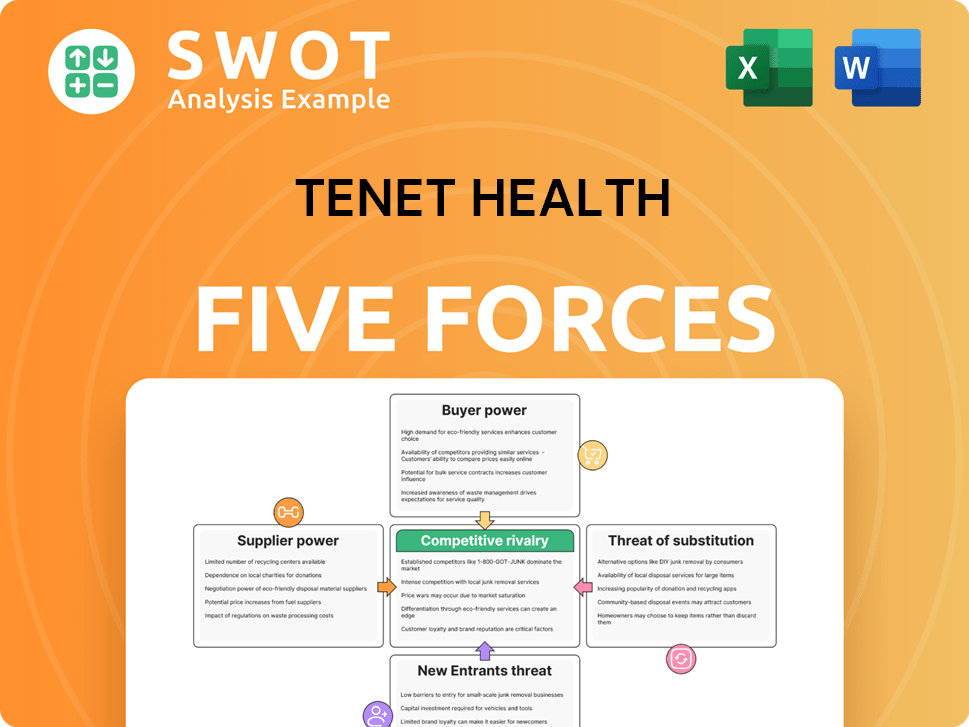
Tenet Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Tenet Health Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Tenet Health Company?
- How Does Tenet Health Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Tenet Health Company?
- What is Brief History of Tenet Health Company?
- Who Owns Tenet Health Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Tenet Health Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.