Bendigo Bank Bundle
Who Really Owns Bendigo Bank?
Understanding the ownership of a financial institution like Bendigo and Adelaide Bank is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike. The ownership structure dictates everything from strategic direction to community engagement. Unraveling the complexities of Bendigo Bank SWOT Analysis, from its humble beginnings to its current status, offers valuable insights into its enduring success.

This exploration into Bendigo Bank ownership will examine the bank's history, from its roots as a building society to its evolution into a publicly traded entity. We'll delve into the influence of Bendigo Bank shareholders, the dynamics of its ownership structure, and how these factors have shaped its commitment to community banking. Discover the key players, from major shareholders to the impact of its unique model, and understand how this impacts its financial performance and strategic decisions. Learn about the Bendigo Bank and Adelaide Bank merger and the current ownership and control.
Who Founded Bendigo Bank?
The story of Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, a significant player in the Australian financial landscape, begins with the Bendigo Mutual Permanent Land and Building Society. Founded in 1858 in Bendigo, Victoria, this marked the genesis of what would become a prominent financial institution. Understanding the early Bendigo Bank ownership structure is crucial to grasping its foundational principles.
The initial ownership of the society was not structured in the same way as modern corporations. Instead, it operated under a mutual ownership model. This meant that the members, comprising depositors and borrowers, collectively owned the institution. This structure prioritized community benefit over individual profit, shaping the bank's ethos from its inception.
The founders' vision centered on providing financial services to the local community. Their aim was to foster homeownership and support regional development. This community-focused approach inherently influenced the early Bendigo Bank shareholders and operational model. There were no traditional investors in the modern sense. The capital came from community deposits and member contributions.
The initial ownership was based on a mutual model, where members (depositors and borrowers) owned the institution.
The founders aimed to provide financial services to the local community, supporting homeownership and regional development.
Early capital came from community deposits and member contributions, not from external investors.
Any early disputes would have been disagreements among members regarding the society's direction.
The distributed, member-centric control reflected the founding team’s vision of community empowerment.
Unlike modern startups, there were no angel investors or venture capital in the early days.
The early Bendigo Bank history is characterized by its mutual structure, where members were the owners, emphasizing community service. The bank's focus on local development and homeownership set it apart. The absence of traditional investors and the reliance on community deposits highlight its unique approach. For further insights into the bank's current operations, consider its Target Market of Bendigo Bank.
- The mutual structure meant that early ownership was distributed among the community members it served.
- The founders' vision was rooted in providing financial services to the local community.
- Early capital came from community deposits and member contributions.
- The founding team’s vision of community empowerment and financial accessibility was directly reflected in this distributed, member-centric control.
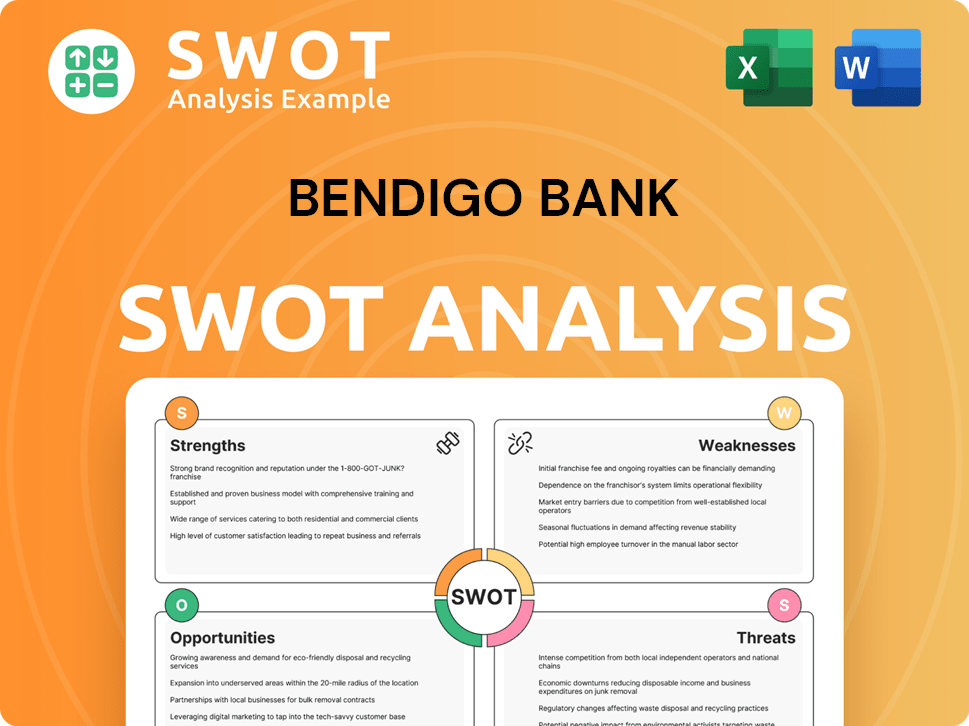
Bendigo Bank SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Bendigo Bank’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's ownership reflects a significant transformation from its origins as a mutual building society to a publicly listed entity. The pivotal moment occurred in 1995 when the bank demutualized and listed on the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) under the ticker symbol BEN. This strategic move opened doors to broader capital markets, fueling its growth and expansion ambitions. This transition fundamentally shifted the ownership structure from member-based to a model driven by public shareholders, marking a new era for the institution.
As of early 2025, the ownership of Bendigo and Adelaide Bank is characterized by a diverse mix of institutional and individual shareholders. Major institutional investors, including superannuation funds, managed funds, and index funds, hold substantial portions of the bank's shares. These institutional investors, such as Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street Corporation, are typically among the largest holders in major Australian listed companies, including Bendigo and Adelaide Bank. The bank's 2024 Annual Report and recent ASX filings provide the most accurate breakdown of major shareholders.
| Shareholder Type | Approximate Holding (as of late 2024/early 2025) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Typically exceeding 60-70% | Includes superannuation funds, managed funds, and index funds. |
| Retail Shareholders | Significant portion | Often comprises customers and community members. |
| Major Institutional Holders | Fluctuates; Top holders often include Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street | Specific percentages change; collectively represent a large portion of the free float. |
The blend of institutional and retail ownership shapes the bank's strategy, balancing shareholder returns with its community-focused approach. Changes in major shareholdings, such as large block trades by institutional investors, can influence share price and market perception. For more detailed information, you can refer to an article about the bank's financial performance and ownership structure to understand the nuances of its current standing.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank's ownership structure has evolved from mutual to public. Institutional investors hold a significant portion of shares, influencing the bank's strategic direction. Retail shareholders, including customers, also play a notable role in the bank's ownership.
- Demutualization in 1995 was a key change.
- Institutional investors include superannuation and managed funds.
- Retail shareholders represent a significant segment.
- The bank balances shareholder returns with community focus.
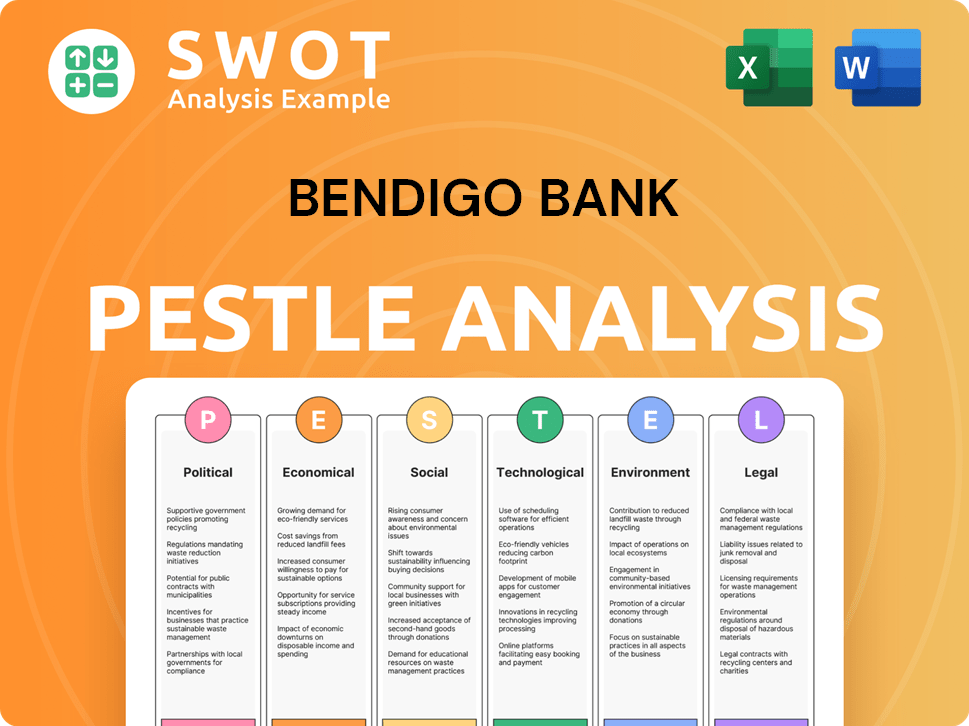
Bendigo Bank PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Bendigo Bank’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Bendigo and Adelaide Bank oversees the governance of the institution, balancing shareholder interests with its community-focused mission. As of late 2024 and early 2025, the board typically includes a mix of independent directors and those with extensive experience in the financial sector. The structure generally includes a Chair, a Managing Director (CEO), and several independent non-executive directors. Board members are chosen for their expertise in areas such as banking, finance, risk management, technology, and community engagement. For those interested in the Growth Strategy of Bendigo Bank, understanding the board's composition is key.
The board's composition and the 'one-share-one-vote' system ensure that decision-making is broadly distributed among shareholders, with the board acting as fiduciaries for all. While specific board members may change due to retirements or new appointments, the bank's commitment to transparent governance practices has generally mitigated significant conflicts. The bank's emphasis on its community bank model further supports this stability. Any governance controversies would typically revolve around executive remuneration, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives, or strategic direction, all addressed through regular shareholder meetings and board oversight.
| Board Role | Description | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Chair | Leads the board, ensuring effective governance. | Overseeing board meetings, setting agendas, and facilitating discussions. |
| Managing Director (CEO) | Chief Executive Officer, responsible for the bank's day-to-day operations. | Implementing the board's strategies, managing the executive team, and ensuring financial performance. |
| Independent Non-Executive Directors | Directors without executive responsibilities, providing independent oversight. | Overseeing risk management, reviewing financial performance, and ensuring compliance. |
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank operates under a 'one-share-one-vote' voting structure. There are no known dual-class shares, special voting rights, or golden shares that would grant outsized control to any individual or entity. This ensures that voting power is proportional to shareholding, providing a fair and transparent process for all Bendigo Bank shareholders. The bank's ownership structure is designed to promote equitable decision-making and accountability.
The Board of Directors plays a crucial role in the governance of Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, balancing shareholder interests with the bank's community-centric mission. The bank's structure generally includes a Chair, a Managing Director (CEO), and several independent non-executive directors.
- Board members are selected for their expertise in banking, finance, and risk management.
- The bank operates under a 'one-share-one-vote' system.
- The board ensures decision-making is broadly distributed among shareholders.
- Bendigo Bank's ownership structure promotes equitable decision-making.
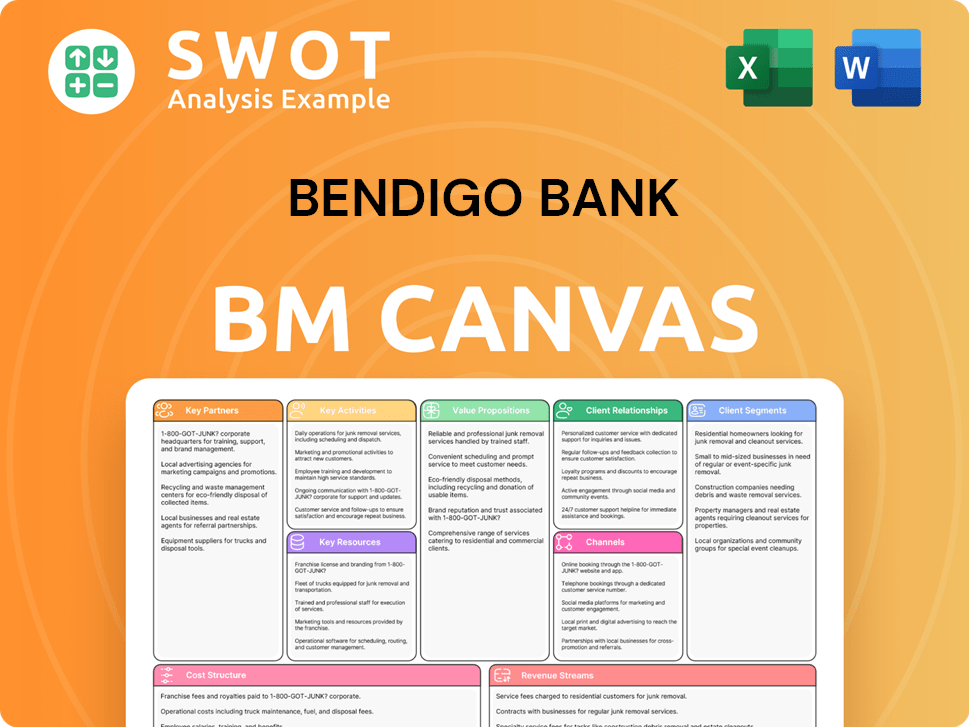
Bendigo Bank Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Bendigo Bank’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership structure of Bendigo and Adelaide Bank, often referred to as Bendigo Bank, has remained relatively stable. The bank, being a publicly listed entity, demonstrates a dispersed ownership model, with a significant portion held by institutional investors. There haven't been any major shifts like large-scale acquisitions or significant changes in the founding family's stake. Instead, the focus has been on capital management and adapting to the evolving financial landscape.
Share buybacks are a common tool used to optimize capital and boost shareholder value. However, secondary offerings are less typical for established banks unless they're pursuing substantial growth initiatives. Mergers and acquisitions are always a possibility in the banking sector, but no significant M&A activity that would drastically alter the ownership structure has been publicly announced recently. The bank's strategy continues to emphasize organic growth, digital transformation, and community engagement, which is reflected in its ownership stability.
| Metric | Value (Approximate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization (2024) | ~$5.5 Billion AUD | Reflects the overall value of the company. |
| Institutional Ownership (2024) | ~60-70% | Indicates a significant portion of shares are held by institutions. |
| Dividend Yield (2024) | ~5-6% | Provides an indication of returns for shareholders. |
Industry trends show an increase in institutional ownership and the influence of ESG-focused investors. Bendigo and Adelaide Bank already has high institutional ownership. The rise of activist investors hasn't significantly impacted the bank due to its stable performance and community-focused approach. Future changes in ownership would likely come from market dynamics, investment strategies, and potential strategic partnerships.
Bendigo Bank shareholders include a mix of institutional investors and retail shareholders. The ownership structure is typical for a publicly traded company. The bank's annual reports provide detailed information about its shareholder base.
The CEO of Bendigo Bank plays a crucial role in the company's strategy and performance. The current CEO and other key executives are listed in the bank's annual reports. Their decisions influence the bank's direction and financial outcomes.
The Bendigo Bank ownership structure is primarily composed of institutional and retail investors. There is no single controlling shareholder. This dispersed ownership model is common among large financial institutions.
Bendigo Bank's financial performance influences investor sentiment. The bank's financial results are available in its annual reports. Key metrics include revenue, profit, and return on equity.
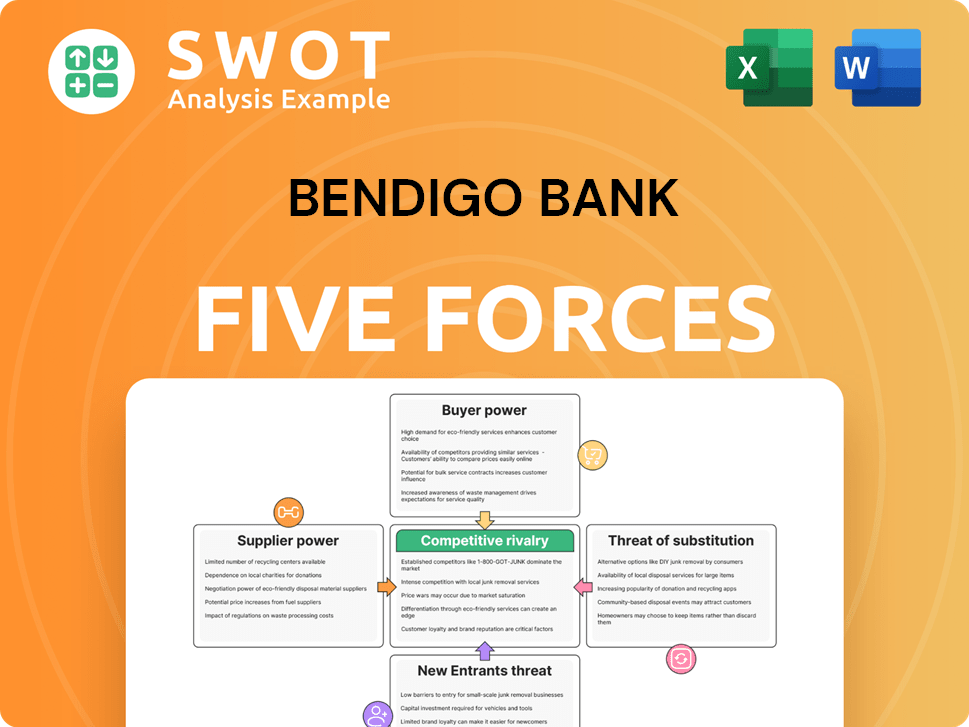
Bendigo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Bendigo Bank Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Bendigo Bank Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Bendigo Bank Company?
- How Does Bendigo Bank Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Bendigo Bank Company?
- What is Brief History of Bendigo Bank Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Bendigo Bank Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.