ASX Bundle
How has the ASX shaped Australia's financial destiny?
The Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) isn't just a place to trade stocks; it's the backbone of Australia's financial system. From its humble beginnings to its current global prominence, the ASX has continually evolved, reflecting the nation's economic growth and technological advancements. Understanding the ASX SWOT Analysis is crucial for grasping its strategic positioning.

The ASX company history reveals a fascinating journey of the Australian Securities Exchange history, starting with the amalgamation of state-based exchanges in 1987. This pivotal moment marked the beginning of the modern share market history in Australia. The evolution of the ASX listed companies mirrors the broader financial market evolution, adapting to global trends and technological leaps to become a leading exchange.
What is the ASX Founding Story?
The Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) was officially established on April 1, 1987. This marked a significant milestone in the Mission, Vision & Core Values of ASX, consolidating six independent state-based stock exchanges into a single, unified entity.
The primary goal of this consolidation was to boost market efficiency, enhance liquidity, and strengthen Australia's position in the increasingly interconnected global financial markets. Prior to this, each state exchange operated independently, leading to fragmentation and inefficiencies.
The formation of the ASX was a collective effort, driven by the leadership and members of the merging exchanges, supported by government legislation. The initial business model focused on providing a centralized marketplace for trading equities and, subsequently, other financial products, along with essential post-trade services.
The ASX was formed on April 1, 1987, by merging six state-based stock exchanges.
- The amalgamation aimed to improve market efficiency and enhance Australia's standing in global finance.
- The initiative was driven by the leadership of the merging exchanges and supported by government legislation.
- The initial focus was on creating a centralized marketplace for equities trading and post-trade services.
- The initial funding came from the assets of the merged exchanges.
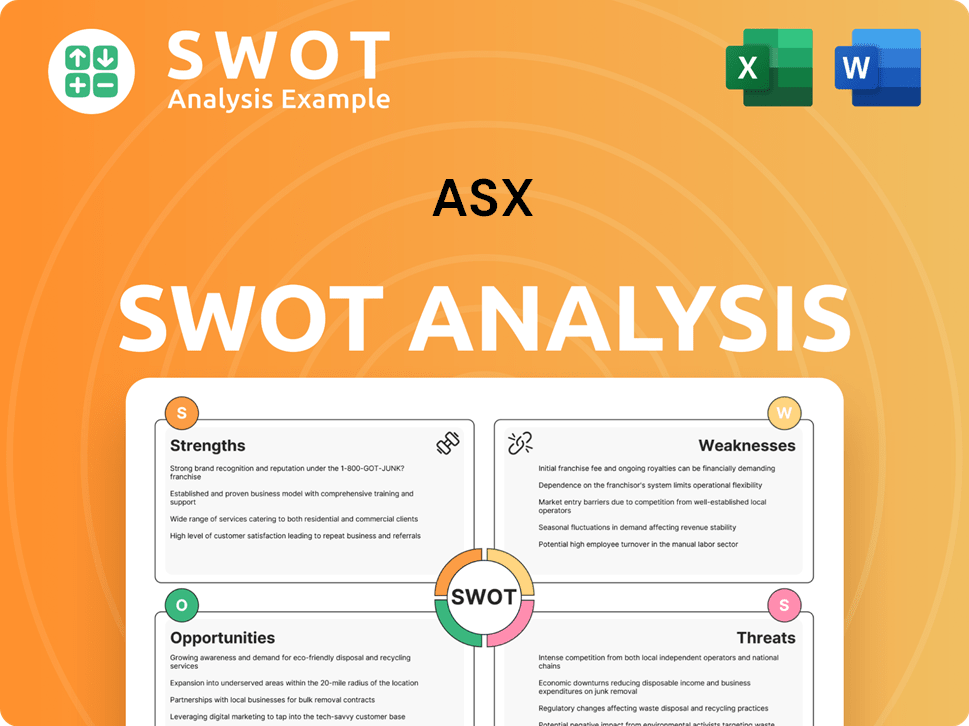
ASX SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of ASX?
The early years of the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) were marked by significant growth and technological advancements. Following its establishment in 1987, the exchange quickly adapted to new technologies, transforming the way shares were traded. This period saw the introduction of electronic trading systems and the expansion of financial products, laying the groundwork for its future success. For those interested in the Growth Strategy of ASX, understanding this early evolution is key.
A pivotal moment in the ASX company history was the introduction of the Stock Exchange Automated Trading System (SEATS) in 1990. This replaced the traditional open outcry system, marking a shift towards electronic trading. The implementation of SEATS significantly increased efficiency and accessibility for investors, setting the stage for further technological upgrades.
The early 1990s saw the ASX expanding its offerings beyond equities. New financial products, including options and futures, were introduced. This diversification attracted a broader range of market participants and increased the exchange's overall appeal, contributing to the evolution of trading on the ASX.
In 1996, the ASX underwent demutualization and became a publicly traded company. This was a significant milestone, transforming the exchange from a member-owned organization to a for-profit entity. This change aligned its interests more closely with its shareholders, influencing the share market history.
A major event in the Australian Securities Exchange history occurred in 2006 when the ASX merged with the Sydney Futures Exchange (SFE). This merger created ASX Limited, establishing it as a multi-asset class exchange. This strategic move provided integrated trading, clearing, and settlement services, attracting both domestic and international participants.
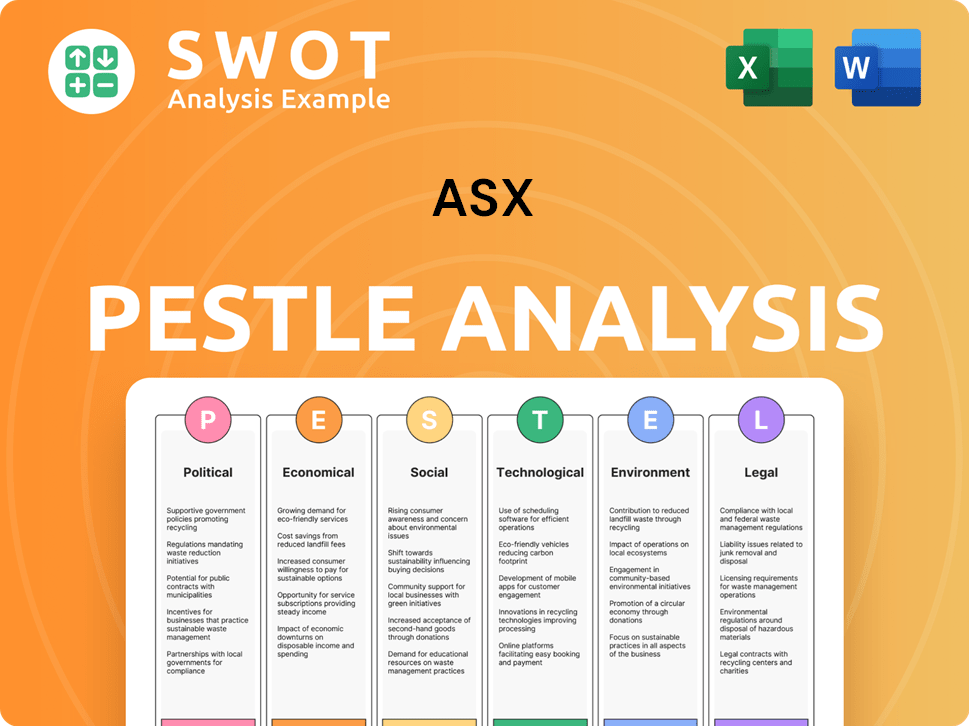
ASX PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in ASX history?
The Australian Securities Exchange history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped the ASX into a leading financial market. These pivotal moments reflect the evolution of the ASX and its role in the Australian economy, showcasing its growth and adaptation over time.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1990 | Full transition to electronic trading with the implementation of SEATS, revolutionizing market access and efficiency. |
| 1994 | Introduction of CHESS (Clearing House Electronic Subregister System), streamlining clearing and settlement of share transactions. |
| 2006 | Merger with the Sydney Futures Exchange, creating a diversified multi-asset exchange and expanding derivatives offerings. |
| 2022 | Cancellation of the DLT-based CHESS replacement project after facing significant challenges. |
Technological advancements have been central to the ASX's evolution, driving efficiency and expanding market capabilities. These innovations have transformed the ASX into a modern financial hub.
The shift to electronic trading with SEATS in 1990 significantly improved market access. This transition enhanced the speed and transparency of trading on the ASX.
CHESS, introduced in 1994, streamlined clearing and settlement processes. It reduced risk and improved the efficiency of share transactions.
The merger with the Sydney Futures Exchange broadened the ASX's product offerings. This expansion provided investors with access to a wider range of financial instruments.
Continuous investments in data and analytics capabilities have improved market surveillance. These tools help in monitoring trading activities and ensuring market integrity.
The ASX has faced several challenges, including global financial crises and technological setbacks. These experiences have shaped the ASX's resilience and strategic direction.
The 2008 global financial crisis led to increased market volatility and regulatory scrutiny. The ASX responded by enhancing its risk management frameworks and regulatory compliance.
Competition from alternative trading venues and global exchanges has intensified. The ASX continues to innovate to maintain its market position.
Operational resilience and cybersecurity are critical challenges requiring continuous investment. The ASX has implemented robust risk management frameworks to address these threats.
The cancellation of the DLT-based CHESS replacement project highlighted the complexities of large-scale technology transformations. This setback led to a re-evaluation of the ASX's technology strategy.
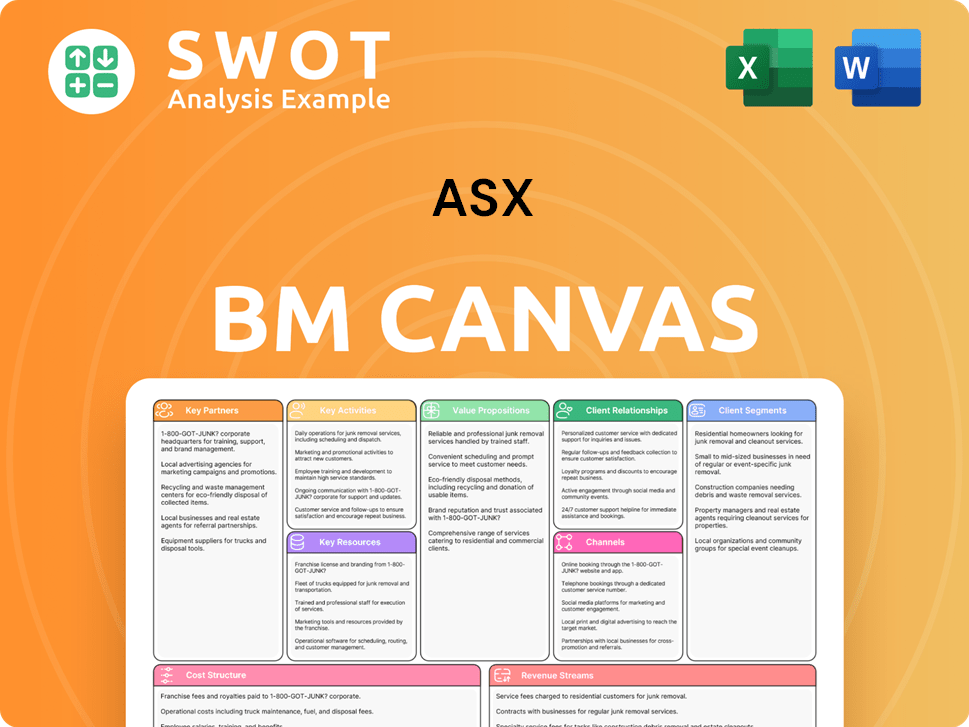
ASX Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for ASX?
The ASX company history is a narrative of strategic mergers, technological advancements, and adaptation to global financial trends. From its inception in 1987 through the merging of state exchanges to its current status, the Australian Securities Exchange has consistently evolved to meet the demands of a dynamic financial landscape. Key milestones include the introduction of electronic trading systems and the implementation of CHESS, which have significantly improved market efficiency.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| April 1, 1987 | Formation of the Australian Stock Exchange Limited through the merger of six state exchanges. |
| 1990 | Introduction of the Stock Exchange Automated Trading System (SEATS), marking the shift to electronic trading. |
| 1994 | Implementation of the Clearing House Electronic Subregister System (CHESS) for electronic settlement. |
| 1996 | Demutualization and listing of ASX on its own exchange. |
| 2006 | Merger of Australian Stock Exchange and Sydney Futures Exchange to form ASX Limited. |
| 2010s | Continued investment in data services and technology infrastructure. |
| 2017 | Announcement of plans to replace CHESS with a distributed ledger technology (DLT) system. |
| Late 2022 | Cancellation of the DLT-based CHESS replacement project due to significant challenges and delays. |
| 2023-2024 | Focus on enhancing the existing CHESS system and exploring alternative modernization pathways. |
The Australian Securities Exchange history includes a strong emphasis on strengthening its core operations. This involves refining existing infrastructure, particularly the CHESS system, and ensuring its resilience. The goal is to provide a stable and efficient clearing and settlement solution for the Australian market.
Technological advancements are key to the future of the ASX. This includes exploring innovative solutions to improve market efficiency, enhance data analytics capabilities, and bolster cybersecurity measures. The exchange is committed to adapting to the evolving technological landscape.
Key strategic initiatives include optimizing trading platforms and expanding data and analytics services. ASX may also explore new opportunities in emerging financial technologies. These initiatives aim to foster growth and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
The ASX is focused on adapting to evolving global financial market trends. This includes maintaining a strong regulatory standing and responding to the increasing demand for sustainable finance products. The exchange aims to remain relevant and competitive.
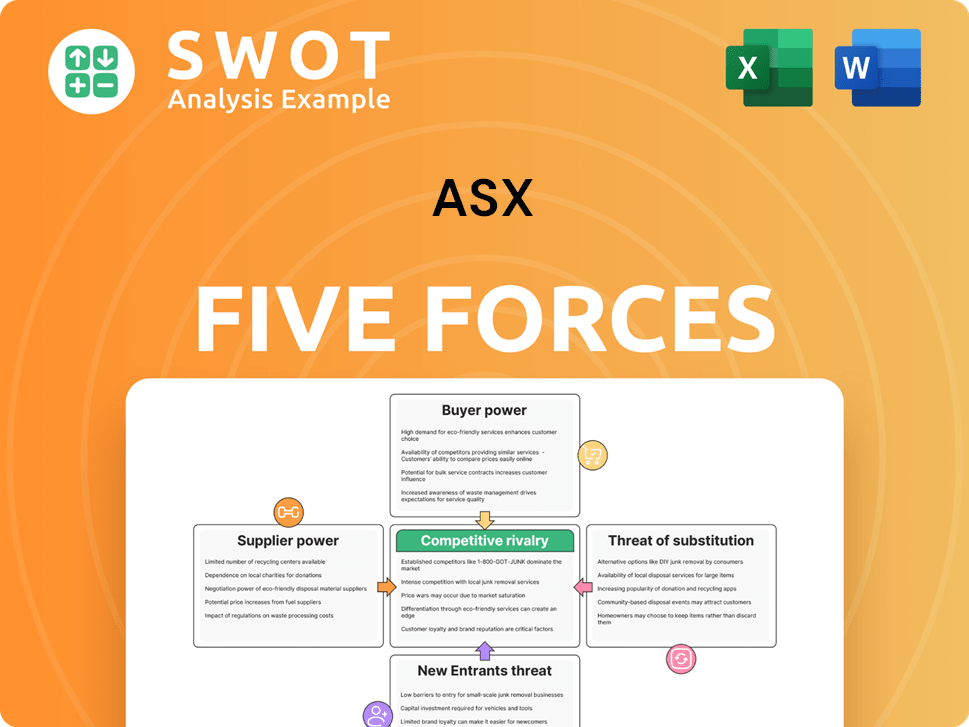
ASX Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of ASX Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of ASX Company?
- How Does ASX Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of ASX Company?
- What is Brief History of ASX Company?
- Who Owns ASX Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of ASX Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.