Fortum Bundle
How has Fortum, a Finnish energy company, shaped the European energy landscape?
From its roots in 1998, Fortum has evolved into a major player in the Fortum SWOT Analysis, a journey marked by strategic shifts and significant growth. This Finnish energy company's story is one of transformation, innovation, and adaptation within the dynamic energy sector. Understanding the Fortum SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its current standing.
This exploration into Fortum's history will uncover its early years, key milestones, and expansion history, providing insights into its impact on the energy market. Discover how Fortum, a prominent player in the energy sector, navigated challenges and embraced sustainability initiatives to become the company it is today. Learn about Fortum's founding date, its early years, and its current operations.
What is the Fortum Founding Story?
The Fortum history began on December 18, 1998. This marked a significant moment in the restructuring of Finland's energy sector. The company emerged from the merger of Imatran Voima Oy and Neste Oy, two major state-owned entities.
This strategic consolidation aimed to create a robust and competitive Finnish energy company. The goal was to operate effectively within the liberalized European energy markets. The Finnish state played a pivotal role in the formation of the new corporation.
The initial vision for Fortum company was to establish an integrated energy provider. It would have a diverse portfolio encompassing power generation, oil, and gas. This would serve both industrial and residential customers.
The genesis of Fortum is rooted in the late 1990s. It was a response to the evolving energy sector. The merger of Imatran Voima Oy and Neste Oy was a strategic move.
- The Finnish state was the primary architect of the company.
- The merger was driven by the need for greater efficiency and scale.
- The new entity aimed to leverage the combined expertise of its predecessors.
- The company's formation was a key step in adapting to the changing energy market.
In its early years, Fortum focused on expanding its operations. It aimed at both domestic and international markets. The company's early strategy involved strategic acquisitions and investments. This helped it to grow its portfolio of assets. For example, by 2000, Fortum had already begun to expand its presence in the Nordic countries and beyond. This included investments in power plants and distribution networks.
The company's expansion strategy included a focus on renewable energy. Fortum recognized the growing importance of sustainable energy sources. In 2002, Fortum acquired a stake in the Swedish hydropower company, which was a significant step. This move aligned with the company's long-term goals. It also helped it to reduce its carbon footprint. This was in response to increasing environmental concerns.
Fortum's commitment to sustainability has been a core part of its strategy. The company has invested heavily in renewable energy projects. This includes wind, solar, and hydro power. It has also implemented various initiatives to reduce its environmental impact. In 2023, Fortum produced around 60% of its electricity from carbon-free sources.
The financial performance of Fortum has been a key indicator of its success. The company has shown resilience and growth over the years. In 2024, Fortum's revenue was approximately EUR 5.2 billion. The company has also focused on optimizing its portfolio. This has involved divesting non-core assets and investing in strategic growth areas.
The company has undergone several leadership changes. These changes have influenced its strategic direction. The current CEO, Markus Rauramo, has been in office since 2020. He has been instrumental in steering the company towards sustainable energy solutions.
Fortum's headquarters are located in Espoo, Finland. The company's operations span across several countries. It has a significant presence in the Nordic region, as well as in other parts of Europe and Asia. Fortum continues to adapt to the changing energy landscape. It is focused on innovative technologies and sustainable practices. For more insights, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Fortum.
Fortum SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Fortum?
The early growth of the Finnish energy company, Fortum, was marked by strategic moves to solidify its presence in the Nordic energy market. Following its establishment in 1998, Fortum focused on both internal growth and strategic acquisitions. A key decision was divesting its oil business in 2005, allowing a sharper focus on power and heat generation. This shift helped align Fortum more closely with the evolving energy sector.
Fortum expanded its footprint across the Nordic region, particularly in Sweden and Norway. The company also made inroads into the Baltic region and Poland. Early capital raises supported these expansions and investments in infrastructure. These moves were crucial for establishing Fortum as a significant player in the European energy landscape.
The company's leadership transitions during this period emphasized efficiency and sustainability. By concentrating on its core energy business, Fortum aimed to optimize operations and strengthen its market share. This strategic focus was essential for navigating the competitive European energy market. For more details, see Revenue Streams & Business Model of Fortum.
In the early 2000s, Fortum's financial performance reflected its growth strategy. While specific figures from the late 1990s and early 2000s are not readily available, the company's focus on expanding its power and heat generation capabilities, along with strategic acquisitions, set the stage for future financial success. The divestment of the oil business in 2005 allowed Fortum to streamline its operations and focus on core energy activities.
Fortum's early years also laid the groundwork for its future sustainability initiatives. The company's emphasis on power and heat generation, along with investments in infrastructure, supported its long-term goals. While specific details on early sustainability projects are not available, the shift towards renewable energy sources became a key part of its strategy. This focus was vital for aligning with the evolving energy sector.
Fortum PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Fortum history?
The Fortum company has a rich history marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts within the energy sector. From its early years to its current operations, the Finnish energy company has evolved considerably, adapting to changing market dynamics and technological advancements. The company's journey reflects its commitment to innovation and sustainability.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1998 | Fortum was established through the merger of Imatran Voima Oy (IVO) and Neste. |
| 2000s | The company expanded its operations internationally, particularly in the Nordic and Baltic regions. |
| 2010s | Fortum increased its focus on renewable energy sources, including hydropower and wind power. |
| 2023 | Fortum completed the divestment of its Russian operations due to geopolitical circumstances. |
| 2024 | Fortum was recognized for its sustainability efforts and commitment to reducing emissions. |
A key area of innovation for Fortum has been its commitment to decarbonization and the development of renewable energy sources. The company has consistently invested in hydropower, wind, and solar energy projects, aligning with broader industry trends towards sustainability.
Fortum has made significant investments in renewable energy projects, expanding its portfolio of wind and solar power plants. This includes projects in the Nordic countries and other European markets.
The company has been developing smart energy solutions and district heating networks, offering efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling services. This includes advanced metering and energy management systems.
Fortum is actively working on decarbonization strategies to reduce its carbon footprint across its value chain. This involves phasing out coal-fired power plants and investing in cleaner energy sources.
Fortum is leveraging digital technologies to enhance its energy services, including the development of smart grids and digital platforms for customer engagement. This improves efficiency and customer experience.
The company is exploring and implementing energy storage solutions to improve grid stability and integrate renewable energy sources. This includes battery storage and pumped hydro storage projects.
Fortum is focusing on sustainable district heating solutions, including the use of renewable energy sources and waste heat recovery. This reduces emissions and improves energy efficiency in urban areas.
However, Fortum has also faced considerable challenges, including market downturns and fluctuating energy prices. The divestment of its Russian operations in 2023, driven by geopolitical circumstances, resulted in a significant financial impact.
The energy sector is subject to market volatility, including fluctuations in energy prices and demand. This can impact Fortum's financial performance and strategic planning.
Geopolitical events and regulatory changes can pose significant risks to Fortum's operations, as seen with the divestment of its Russian assets. These events can lead to financial losses and strategic adjustments.
Increasing regulatory pressures related to emissions and environmental standards require significant investments and adjustments. This includes complying with stricter environmental regulations and carbon pricing mechanisms.
Divestments, such as the one in Russia, can lead to substantial financial impacts, including write-downs and losses. This can affect the company's profitability and financial stability.
The energy market is highly competitive, with new entrants and evolving business models. This requires Fortum to continuously innovate and adapt to maintain its market position.
Technological advancements, such as the rise of renewable energy and smart grids, can disrupt traditional energy business models. Fortum needs to invest in new technologies to remain competitive.
Fortum Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Fortum?
The Fortum history showcases a series of strategic transformations and significant developments within the energy sector. Established in 1998 through a merger, the Finnish energy company has evolved from its initial focus on oil and power to a strong emphasis on clean energy and customer solutions. Key milestones include expansions into Russia, strategic partnerships, and a firm commitment to sustainability, culminating in the divestment of its Russian operations in 2023. These actions have positioned Fortum for continued growth in the renewable energy sector.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1998 | Fortum Corporation was established through the merger of Imatran Voima Oy and Neste Oy. |
| 2005 | The oil business was divested to concentrate on power and heat. |
| 2007-2010 | Expansion into Russia with substantial investments in power generation assets occurred. |
| 2013 | The 'Fortum 2020' strategy was launched, focusing on clean energy and customer solutions. |
| 2016 | A strategic partnership with Uniper led to acquiring a majority stake. |
| 2020-2022 | There was an increased focus on decarbonization and renewable energy investments. |
| 2023 | The divestment of Russian operations was completed. |
| 2024 | Fortum is recognized for its sustainability efforts and commitment to reducing emissions. |
Fortum's future strategy emphasizes growth within the Nordic and Baltic regions. The company plans to invest heavily in fossil-free power generation. This includes expanding its wind and solar energy capacity to meet the growing demand for renewable energy sources.
The company is actively exploring new technologies like hydrogen production and small modular reactors (SMRs). These investments are designed to diversify its energy portfolio and prepare for future energy needs. This aligns with the global trend towards cleaner energy solutions.
Fortum is dedicated to achieving carbon neutrality in its own production by 2030 in Europe. This commitment underscores its role in driving decarbonization. The company aims to provide reliable, clean energy.
Analysts predict continued growth in renewable energy sectors. This aligns with Fortum's strategic initiatives. Its focus on sustainable energy solutions positions it well in the evolving energy sector.
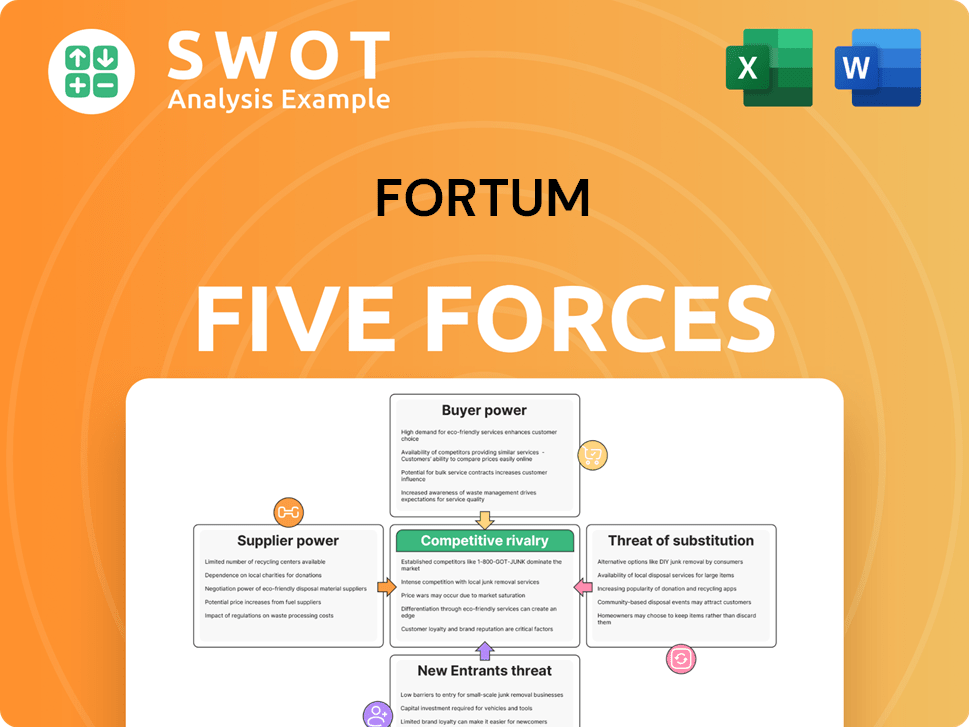
Fortum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Fortum Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Fortum Company?
- How Does Fortum Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Fortum Company?
- What is Brief History of Fortum Company?
- Who Owns Fortum Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Fortum Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.