Hong Kong Exchanges Bundle
Who Really Controls the Hong Kong Stock Exchange?
Unraveling the Hong Kong Exchanges SWOT Analysis is just the beginning; understanding HKEX ownership is key to grasping its future. The ownership structure of a financial powerhouse like HKEX dictates its strategic moves, governance, and influence on global markets. Knowing who owns HKEX provides vital insights into its operational priorities and responsiveness to market demands.

The evolution of HKEX ownership, from its constituent entities to its current diverse shareholder base, is a fascinating journey. This exploration will examine the influence of key investors, the dynamics of its board of directors, and recent trends that are shaping its ownership landscape. Understanding who owns HKEX and the HKEX shareholders provides a comprehensive understanding of the forces that govern this vital financial market operator, including its ownership structure.
Who Founded Hong Kong Exchanges?
The concept of 'founding ownership' for the Hong Kong Exchanges Company (HKEX) is unique because it was formed through a merger of three existing entities in 2000: the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong (SEHK), the Hong Kong Futures Exchange (HKFE), and Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company (HKSCC). Therefore, there isn't a traditional set of individual 'founders' in the way a startup would have. Instead, the early HKEX ownership structure was a conversion of the memberships and shareholdings of these pre-existing exchanges and clearing houses into shares of the newly formed HKEX.
Prior to the merger, the SEHK and HKFE were member-owned organizations, meaning their ownership was held by their respective brokers and participants. The HKSCC was a wholly-owned subsidiary of SEHK. Upon the merger, members of SEHK and HKFE received shares in HKEX in exchange for their memberships and existing shares. For instance, SEHK members received HKEX shares based on their membership rights. The specific equity split at the company's inception was determined by the agreed-upon valuation and conversion ratios of these legacy entities.
The initial ownership was distributed among the former members of the constituent exchanges. There were no traditional 'angel investors' or 'friends and family' in the initial phase of HKEX's formation, as it was a corporatization and merger of existing, established market infrastructures. Early agreements revolved around the legal and financial frameworks of the merger, ensuring a smooth transition of operations and ownership rights from the previous member-based structures to a publicly listed corporate entity.
The initial ownership of HKEX was a direct result of the merger of SEHK, HKFE, and HKSCC. Members of the former exchanges received shares in the newly formed HKEX.
Unlike startups, HKEX did not have individual founders in the traditional sense. The formation was a consolidation of existing market infrastructures.
The equity split was determined by the valuation and conversion ratios of the merging entities. The initial ownership was distributed to the former members of the exchanges.
The merger was driven by the Hong Kong government's goal to enhance market competitiveness.
The merger resulted in a publicly listed corporate entity, transforming the ownership model from member-based structures.
Early agreements focused on the legal and financial aspects of the merger to ensure a smooth transition of operations and ownership.
The initial focus was on integrating the existing market infrastructures under a unified structure. The HKEX shareholders today include institutional investors and public shareholders. For those interested in the long-term vision, you can find more information on the Growth Strategy of Hong Kong Exchanges. Understanding the ownership structure is key to grasping how Who owns HKEX and how it operates. The Hong Kong Stock Exchange is a publicly traded company, and its ownership is widely distributed among various institutional and individual investors. As of the latest available data, major shareholders include large institutional investors and investment funds. The HKEX ownership history reflects a transition from a member-based structure to a publicly traded entity, with ongoing regulatory oversight to ensure market integrity. Key stakeholders include the Hong Kong government, institutional investors, and the general public. The HKEX major investors play a significant role in shaping the company's strategic direction. The HKEX board of directors oversees the company's operations, ensuring compliance and strategic alignment. For anyone looking to buy HKEX shares, they can do so through the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
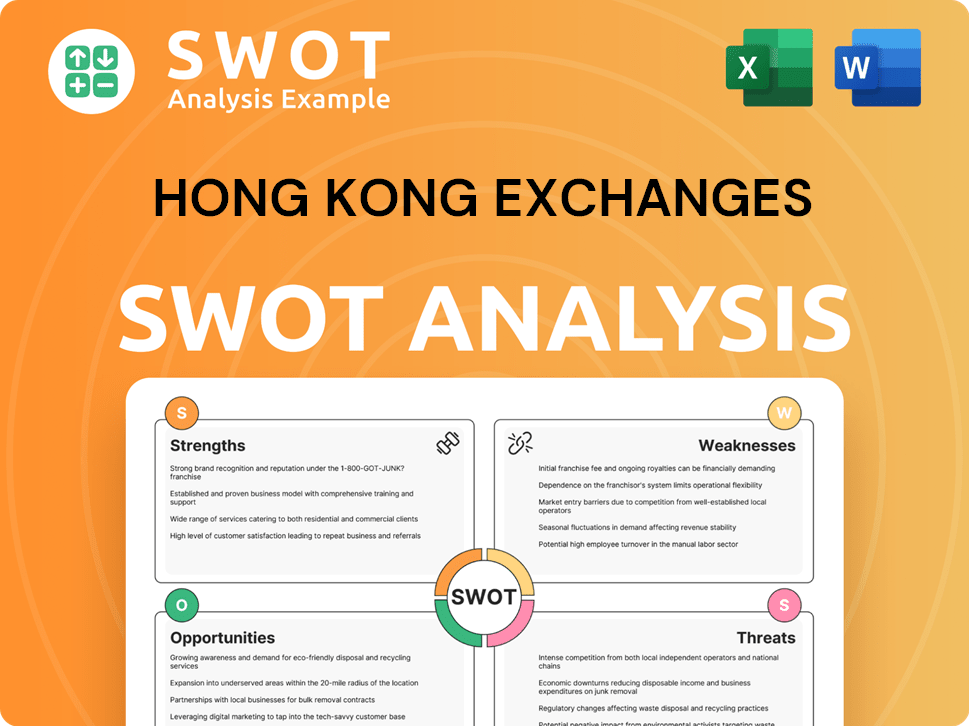
Hong Kong Exchanges SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Hong Kong Exchanges’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The Hong Kong Exchanges Company (HKEX) transitioned into its current ownership structure through a pivotal initial public offering (IPO) in 2000. This followed the merger of the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong, the Hong Kong Futures Exchange, and Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company. This IPO marked a significant shift, transforming the entity into a publicly traded company. This move allowed for broader investor participation and set the stage for the evolution of its shareholder base over time. The IPO's success and subsequent market performance have been crucial in shaping HKEX's growth and influence in the global financial landscape.
The ownership structure of HKEX is primarily characterized by its status as a publicly traded company. This means that its shares are held by a diverse group of institutional and individual investors. The major stakeholders include large institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds. The absence of a single dominant founder or family stake reflects its origins as a merger of several entities. The HKEX ownership has evolved through market dynamics, including institutional portfolio adjustments and strategic investments. This has subtly influenced the company's strategic direction, especially regarding capital allocation and international expansion.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Merger of Exchanges | Creation of HKEX as a publicly traded entity; Initial public offering (IPO). | 2000 |
| Market Fluctuations | Changes in institutional holdings; Influence on share prices. | Ongoing |
| Strategic Investments | Potential shifts in major shareholder composition; Influence on company strategy. | Ongoing |
The HKEX shareholders include a variety of institutional investors, such as asset management firms, sovereign wealth funds, and mutual funds. These entities hold significant portions of the outstanding shares. The Hong Kong government also plays a critical role, although it is not a direct shareholder. It influences HKEX through the appointment of board members and regulatory oversight via the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC). This ensures that HKEX's operations align with broader public policy objectives for Hong Kong's financial markets. For a deeper understanding of how HKEX operates, you can refer to this article: Revenue Streams & Business Model of Hong Kong Exchanges.
Understanding the ownership structure of HKEX is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike.
- Institutional Investors: Major asset managers and funds hold substantial shares.
- Hong Kong Government: Exerts influence through board appointments and regulation.
- Individual Shareholders: Contribute to the overall ownership distribution.
- Regulatory Bodies: Ensure market integrity and compliance.
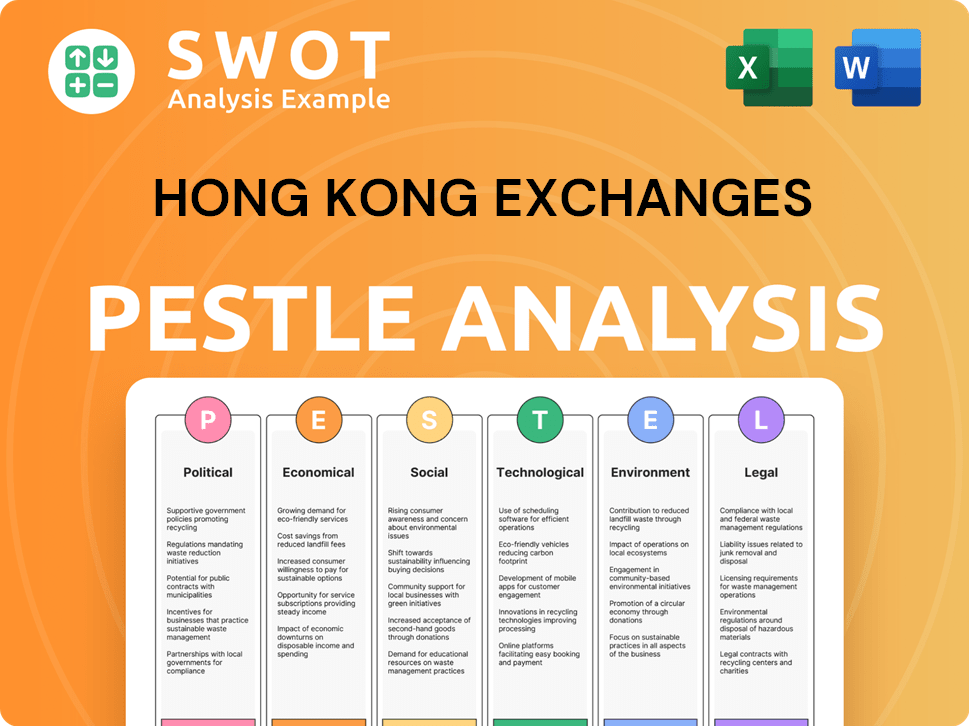
Hong Kong Exchanges PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Hong Kong Exchanges’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (HKEX) oversees the operations of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. As of late 2024 and early 2025, the board typically includes a mix of executive and non-executive directors. The Chairman, often appointed with government backing, plays a crucial role in ensuring that the exchange aligns with public interests. The composition of the board reflects HKEX's status as a publicly listed company with a vital public function.
The board's structure incorporates a significant number of Independent Non-Executive Directors (INEDs), often constituting over 50% of the board members. This structure promotes good corporate governance and impartiality. The board's diversity ensures a range of expertise and perspectives in decision-making. The board's composition is designed to balance commercial objectives with public policy considerations, reflecting the unique nature of HKEX's role in the financial ecosystem.
| Director Type | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Directors | Individuals involved in the day-to-day management of HKEX. | Oversee and implement the company's strategy. |
| Non-Executive Directors | Individuals with diverse backgrounds, providing independent oversight. | Offer strategic guidance and ensure good corporate governance. |
| Independent Non-Executive Directors (INEDs) | Non-executive directors without any material relationship with the company. | Ensure impartiality and protect the interests of all shareholders. |
HKEX operates under a one-share-one-vote principle, promoting fairness among shareholders. The voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held, ensuring that all shareholders have a voice in the company's direction. The governance framework of HKEX balances commercial objectives with public policy considerations, ensuring alignment with the broader financial development goals of the Special Administrative Region. The Hong Kong government's influence is primarily exercised through the appointment of the Chairman and several directors, ensuring that the exchange's strategic direction aligns with the broader financial development goals of the Special Administrative Region.
HKEX is a publicly traded company, and its ownership is distributed among various shareholders. The ownership structure is designed to ensure fair representation and adherence to good corporate governance practices. The government's influence is primarily through the appointment of the Chairman and directors.
- The board includes Executive and Non-Executive Directors.
- INEDs constitute a significant portion of the board.
- One-share-one-vote principle is in effect.
- The government appoints the Chairman and several directors.
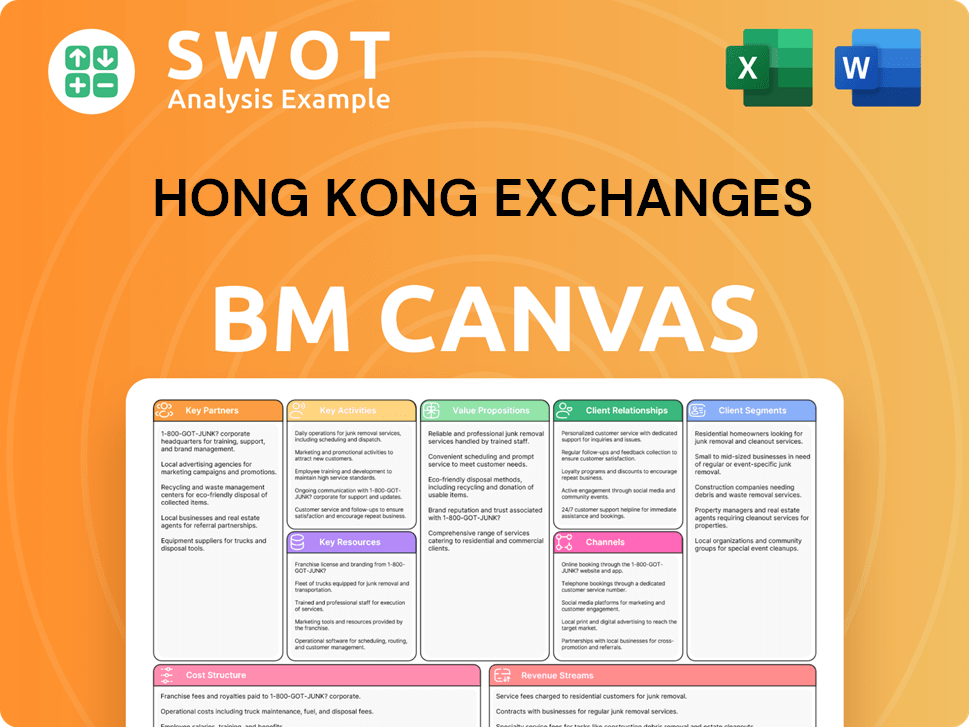
Hong Kong Exchanges Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Hong Kong Exchanges’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the Hong Kong Exchanges Company (HKEX) has seen developments primarily focused on strategic initiatives rather than dramatic shifts in its core HKEX ownership structure. A key area of focus has been enhancing connectivity with mainland China's capital markets, particularly through programs like Stock Connect and Bond Connect. These efforts aim to attract long-term investors looking to capitalize on the growth potential of China's financial markets, influencing the composition of its institutional shareholder base.
In terms of capital management, HKEX has engaged in share buybacks, which can incrementally reduce the number of outstanding shares. Any share buyback programs announced in 2024 or 2025 would be detailed in their financial reports, highlighting a commitment to returning value to shareholders. The increasing influence of large institutional investors and index funds also affects HKEX shareholders. As passive investing strategies gain traction, index funds and ETFs tracking major Asian or global indices often become significant shareholders. This can lead to a more dispersed ownership base, with greater scrutiny from institutional asset managers regarding ESG factors and long-term value creation. For more insights, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Hong Kong Exchanges.
| Metric | Data (2024/2025) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Approximately $50 billion USD (as of late 2024) | Financial News Outlets |
| Share Buyback Programs | Announcements in 2024/2025 | HKEX Financial Reports |
| Stock Connect Turnover | Daily average trading volume (recent figures) | HKEX Reports |
The ownership structure of HKEX remains relatively stable, with a mix of institutional and individual investors. The company's strategic focus on integrating with mainland China's markets and managing capital efficiently continues to be a key factor influencing Who owns HKEX. The increasing importance of ESG factors and the rise of passive investing are also reshaping the landscape of HKEX ownership structure.
Major institutional investors hold significant stakes in HKEX. Index funds and ETFs tracking major Asian indices are also key shareholders. Ownership is relatively dispersed, with no single dominant shareholder.
HKEX is governed by a board of directors. The board is responsible for strategic direction and oversight. Regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC), oversee HKEX.
HKEX's stock performance reflects market conditions. The company's financial reports provide detailed information on trading volumes. Investors closely monitor the company's performance.
HKEX's future hinges on its integration with mainland China. The company's ability to adapt to regulatory changes is crucial. Diversification of product offerings is also a key strategy.
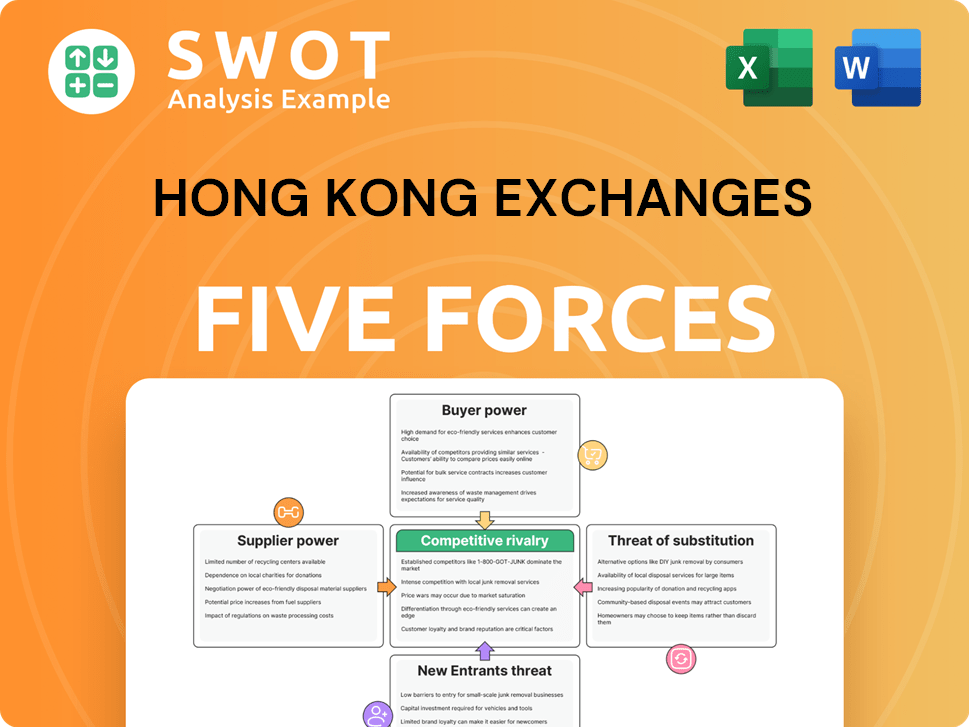
Hong Kong Exchanges Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Hong Kong Exchanges Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Hong Kong Exchanges Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Hong Kong Exchanges Company?
- How Does Hong Kong Exchanges Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Hong Kong Exchanges Company?
- What is Brief History of Hong Kong Exchanges Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Hong Kong Exchanges Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.