AIG Bundle
Who Really Owns AIG?
Understanding the intricate web of AIG SWOT Analysis is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of the financial world. From its humble beginnings in Shanghai to its current status as a global insurance leader, AIG's ownership structure has undergone dramatic transformations. The
The evolution of
Who Founded AIG?
The American International Group (AIG) was established in 1919. The founder, Cornelius Vander Starr, launched the company in Shanghai, China. His initial focus was on providing insurance to businesses and individuals in Asia.
Starr, an American entrepreneur, started the firm as American Asiatic Underwriters. He played a crucial role in the company's early expansion. There is limited public information on the exact ownership structure or early investors beyond Starr's significant control.
The early years of AIG were marked by rapid growth across Asia. Starr's vision of a globally diversified insurance business was evident from the beginning. The company's expansion strategy and the control Starr maintained over its development reflect this vision.
Founded in 1919 in Shanghai, China, by Cornelius Vander Starr. The initial business focused on selling insurance in Asia.
Expanded rapidly throughout Asia. Driven by Starr's entrepreneurial spirit and his ability to spot opportunities in untapped markets.
Starr maintained significant control and ownership. Specific equity splits or initial shareholding percentages are not widely available.
No widely publicized information about early ownership disputes or buyouts. Suggests a relatively stable founding period under Starr's leadership.
Starr's vision for a globally diversified insurance business. Reflected in the company's expansion strategy and control over its early development.
Initially named American Asiatic Underwriters. Later evolved into the American International Group.
Understanding the early ownership of AIG is crucial for grasping its history. The company, now known as American International Group, started with a clear vision. For more insights into the competitive landscape, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of AIG. Here are some key points:
- Founded in 1919 in Shanghai, China.
- Cornelius Vander Starr was the founder.
- Focused on insurance for Chinese businesses and individuals.
- Early expansion across Asia.
- Starr maintained significant control.
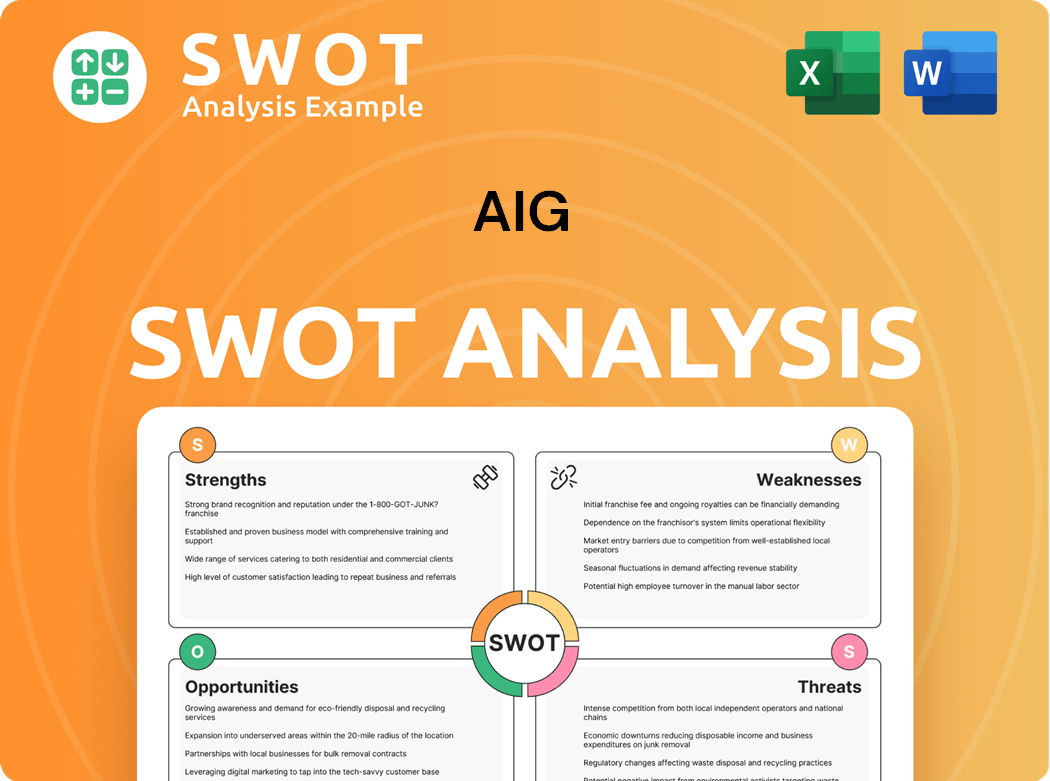
AIG SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has AIG’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of the American International Group (AIG) has seen significant changes over time. Initially, AIG operated as a public company, listed on the New York Stock Exchange. However, the 2008 financial crisis dramatically altered this, leading to substantial government intervention. The U.S. Treasury and the Federal Reserve provided a bailout, resulting in the U.S. government becoming the majority owner, controlling nearly 80% of AIG's stock.
Following the financial crisis, the U.S. government divested its stake in AIG through a series of stock sales, completed by December 2012. This returned the company to private ownership. Understanding AIG's ownership structure is crucial for assessing its strategic direction and financial health. As of early 2025, AIG's ownership is primarily held by institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual shareholders. Major institutional investors, such as Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., and State Street Corp., typically hold significant percentages of the outstanding shares. These entities collectively wield substantial voting power due to their large investment portfolios. For more details, one can refer to AIG's annual reports and SEC filings, such as 10-K reports, which provide detailed breakdowns of major shareholders and their holdings.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | AIG becomes a publicly traded company. | Prior to 2008 |
| 2008 Financial Crisis | U.S. government bailout; government becomes majority owner. | 2008 |
| Government Divestiture | U.S. government sells its stake, returning AIG to private ownership. | Completed by December 2012 |
The shift in ownership has had a direct impact on AIG's strategic focus, particularly in streamlining operations and strengthening its core insurance businesses. The company has aimed to enhance shareholder value by divesting non-core assets and adjusting to the dynamics of private ownership. To learn more about AIG's financial operations, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of AIG.
AIG's ownership has evolved significantly, from a public company to one largely controlled by the government and back to private ownership.
- Institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock are key shareholders.
- Government intervention during the 2008 financial crisis was a major turning point.
- Understanding the ownership structure is vital for evaluating AIG's strategic direction.
- AIG's current ownership is primarily distributed among institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual shareholders.
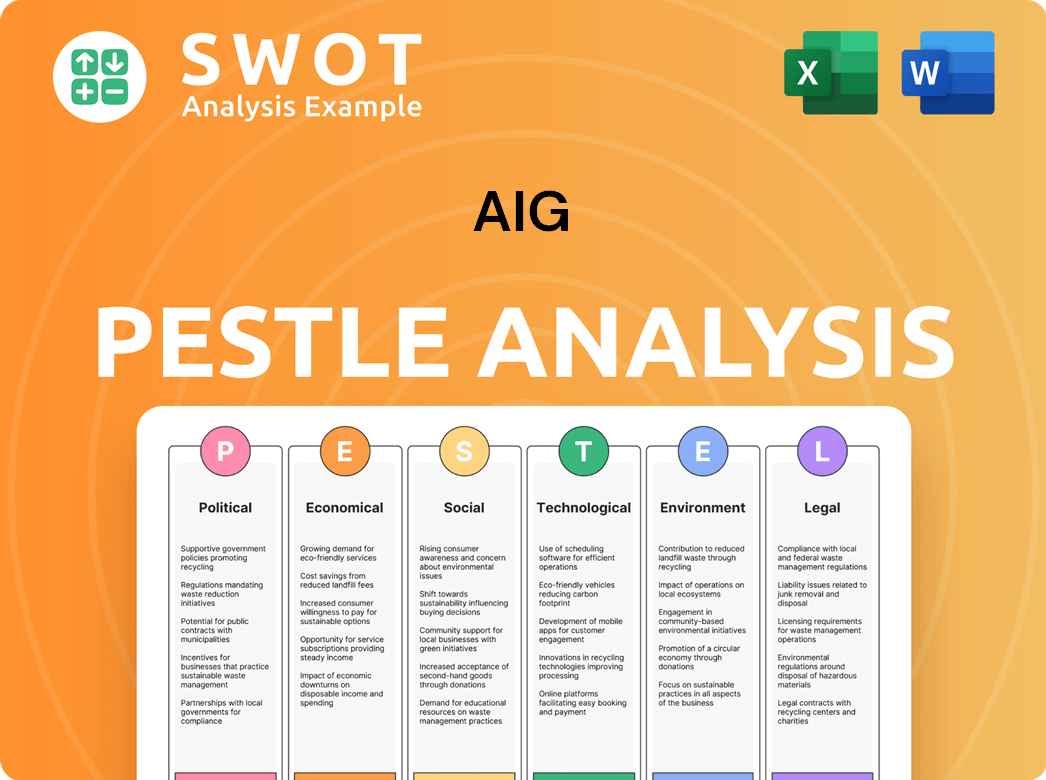
AIG PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on AIG’s Board?
The Board of Directors at American International Group (AIG), plays a critical role in overseeing the company's strategic direction and ensuring good corporate governance. As of early 2025, the board typically comprises a mix of independent directors and executives. These individuals bring a wealth of experience from various sectors, including finance, insurance, and corporate governance, ensuring a well-rounded perspective in decision-making. The composition of the board reflects a commitment to representing the interests of AIG shareholders and maintaining robust oversight of the company's operations.
The board's composition is regularly updated to reflect the evolving needs of the company and the interests of its shareholders. While the exact individuals may change, the focus remains on maintaining a board that is both independent and capable of providing strategic guidance. The board's structure is designed to promote transparency and accountability, which is essential for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the long-term success of AIG. The board's decisions are crucial in shaping the company's future, including its financial performance and strategic initiatives. For more insights into AIG's approach to its market presence, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of AIG.
| Board Member | Title | Key Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Peter Zaffino | Chairman & CEO | Extensive experience in insurance and financial services. |
| Amy L. Schioldager | Lead Independent Director | Significant experience in corporate governance and financial oversight. |
| Christopher Swift | Director | Former CEO of AIG, bringing deep industry knowledge. |
AIG operates under a one-share-one-vote structure, meaning each share of common stock generally entitles its holder to one vote on matters brought before shareholders. This structure ensures that voting power is proportional to share ownership, promoting fairness and transparency in the company's decision-making processes. The absence of dual-class shares or other arrangements that would grant disproportionate voting rights to certain individuals or entities underscores AIG's commitment to shareholder democracy. Institutional investors and major AIG shareholders exert influence through their voting power and engagement with management on key issues, although they may not always hold direct board seats.
AIG's board is composed of independent directors and executives, ensuring diverse expertise. The one-share-one-vote structure provides equal voting rights to all shareholders. Major institutional investors influence decisions through voting and engagement.
- Board members bring diverse backgrounds in finance and insurance.
- Shareholders vote on matters such as director elections.
- Activist investors can influence strategy and governance.
- Institutional investors' voting power shapes key decisions.
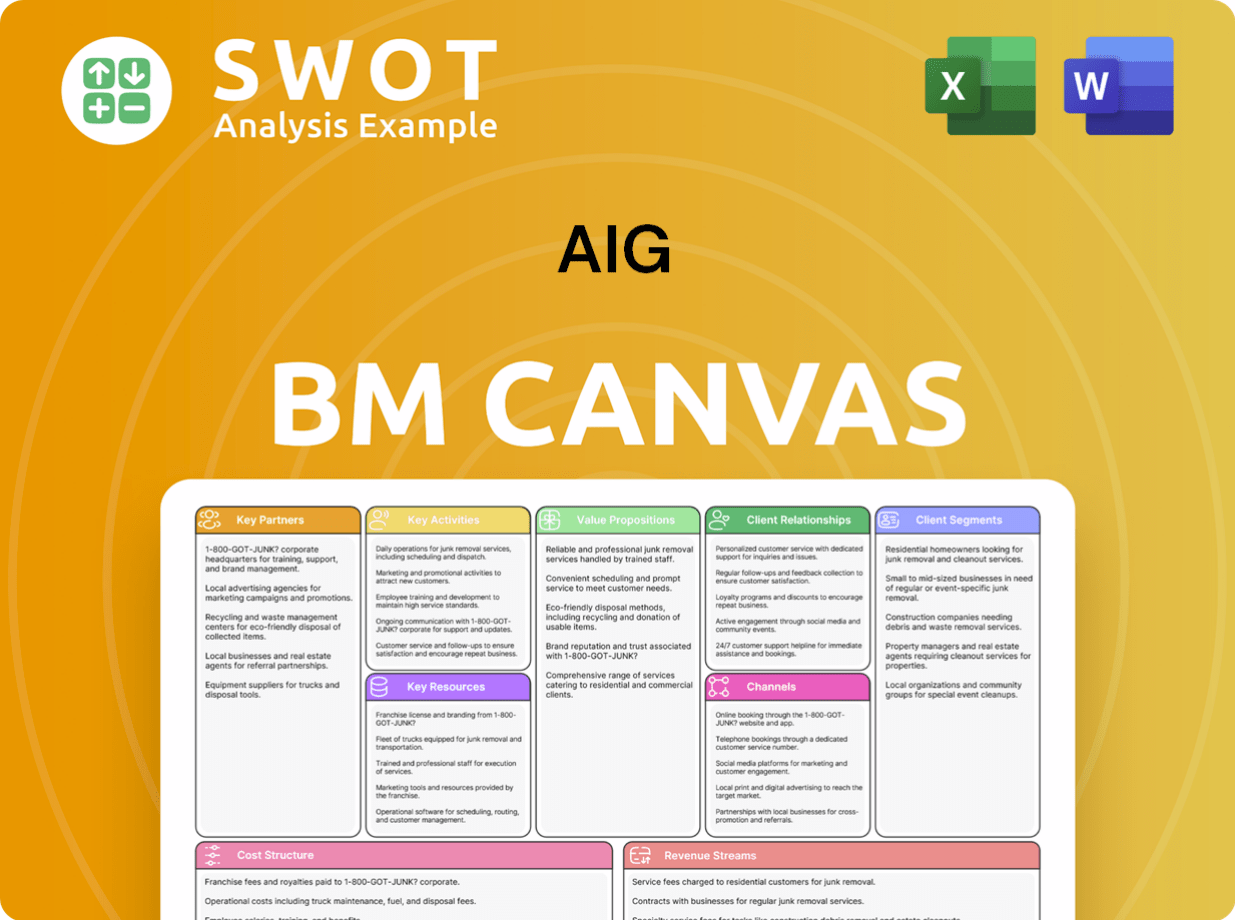
AIG Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped AIG’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the AIG company has undergone significant changes in its ownership structure. A major move was the separation of its life and retirement business, now known as Corebridge Financial, Inc., through an initial public offering in September 2022. AIG initially retained a majority stake in Corebridge but has since been gradually reducing its holdings. This strategic shift aims to streamline AIG's operations and concentrate on its property-casualty insurance business, also known as General Insurance.
In May 2024, AIG announced a secondary offering of Corebridge Financial common stock, further decreasing its stake to approximately 48.3%. This ongoing process reflects AIG's commitment to focusing on its core business and returning capital to shareholders. The company's focus on its 'AIG 200' strategy also indicates a continuous effort to streamline operations and improve profitability, which indirectly influences its attractiveness to investors and thus, its ownership trends.
| Ownership Change | Details | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Corebridge Financial IPO | Separation of life and retirement business | September 2022 |
| Secondary Offering | Reduction of AIG's stake in Corebridge Financial | May 2024 |
| Share Buybacks | Returning capital to shareholders | Ongoing |
Industry trends also play a role in shaping AIG's ownership landscape. The increasing institutional ownership in large-cap companies, alongside the general trend toward consolidation in the insurance sector, influences AIG's strategic decisions. Public statements by AIG management consistently highlight a dedication to optimizing its portfolio and enhancing shareholder value, which may involve further divestitures or strategic acquisitions. For more details on the company's growth strategy, you can read about the Growth Strategy of AIG.
The separation of Corebridge Financial and subsequent reduction of AIG's stake. This move streamlines operations.
AIG is actively returning capital to shareholders through share buyback programs. This enhances shareholder value.
AIG aims to optimize its portfolio and potentially make strategic acquisitions. This improves overall performance.
Institutional ownership and consolidation trends in the insurance sector influence AIG's decisions. This shapes the market.
AIG Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of AIG Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of AIG Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of AIG Company?
- How Does AIG Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of AIG Company?
- What is Brief History of AIG Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of AIG Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.