Sears Holdings Bundle
What ultimately led to Sears' downfall?
The retail world is a battlefield, and few stories are as compelling as the rise and fall of Sears Holdings Company. From its humble beginnings as a mail-order catalog to its reign as a retail titan, Sears once defined American consumerism. But how did this iconic brand, a cornerstone of the Sears Holdings SWOT Analysis, ultimately lose its footing in the face of evolving market dynamics?

This analysis will dissect the Sears competitive landscape, examining Sears competitors and the strategies they employed. We'll explore the Sears Holdings Company and its struggle to adapt to the digital age, providing a comprehensive retail industry analysis. Understanding Sears market position compared to rivals and the competitive advantages of Sears competitors is crucial to understanding the challenges faced by Sears.
Where Does Sears Holdings’ Stand in the Current Market?
Prior to its bankruptcy and liquidation, Sears Holdings Company held a diminishing market position within the broader retail industry. The company's primary product lines encompassed a wide range of general merchandise, including apparel, home goods, appliances, and automotive services. Its geographic presence was primarily concentrated in the United States, with a significant footprint of department stores and Kmart locations across the country. Analyzing the Sears competitive landscape reveals a company struggling to maintain relevance.
Over time, the company experienced a substantial shift in its positioning, struggling to adapt to changes in consumer preferences and the rise of online retail. Once a dominant force in categories like appliances, its market share eroded significantly. The company's financial health was severely strained in its later years, marked by consistent losses and a substantial debt burden, contrasting sharply with the industry averages of more agile and profitable retailers. Understanding the Sears competitors is crucial for comprehending its decline.
Sears's position was particularly weak in urban and suburban areas where direct competition from big-box retailers and e-commerce giants was most intense. This decline is well-documented in a related article that explores the Growth Strategy of Sears Holdings. The challenges faced by the company highlight the need for retail industry analysis to understand the broader market dynamics.
By 2017, Sears's share of the appliance market had reportedly fallen to around 10%, a dramatic decrease from its previous dominance. This significant drop illustrates the impact of competition and changing consumer behavior. The company's inability to adapt led to a decline in its overall market share.
The company's financial performance was consistently negative in its later years, with substantial losses and a growing debt burden. This financial instability limited its ability to invest in improvements and compete effectively. The contrast with more profitable retailers was stark.
Sears was primarily concentrated in the United States, with a large network of stores. This geographic focus meant it was highly vulnerable to local competition and shifts in regional economic conditions. The reliance on physical stores also became a disadvantage.
The company's general merchandise focus, including apparel, home goods, and appliances, made it susceptible to competition from specialized retailers and online platforms. The inability to differentiate its product offerings further weakened its position. This is a key aspect of Sears business strategy.
The key challenges for Sears included adapting to changing consumer preferences, the rise of e-commerce, and intense competition from big-box retailers and online giants. These factors contributed to its declining market position. Understanding these challenges is vital for a detailed Sears competitive landscape analysis.
- Inability to compete with online retailers like Amazon.
- Failure to innovate and adapt to changing consumer demands.
- High debt burden and financial instability.
- Intense competition from established retailers.
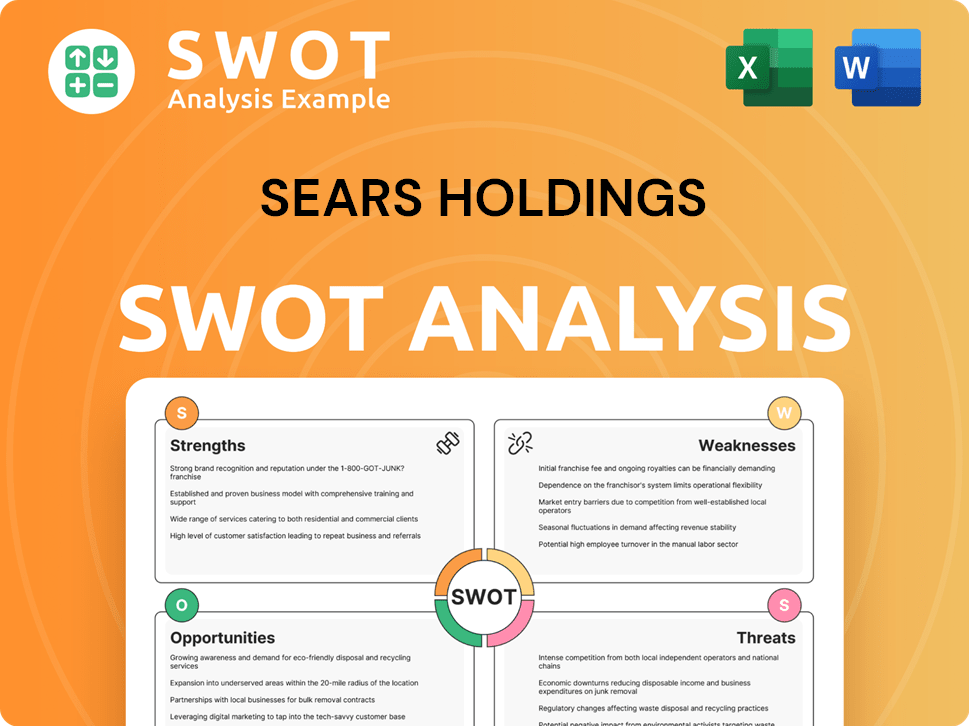
Sears Holdings SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging Sears Holdings?
The Sears competitive landscape was complex, with Sears Holdings Company facing a wide array of rivals across different retail segments. Understanding these competitors is crucial for any retail industry analysis of the company. The challenges faced by Sears highlight the intense competition and evolving dynamics of the retail sector.
The company had to contend with both direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors included department stores like Macy's, J.C. Penney, and Kohl's, while indirect competitors encompassed big-box retailers such as Walmart and Target, home improvement stores like Lowe's and The Home Depot, and the rapidly growing e-commerce sector, particularly Amazon. These various competitors each brought their own strengths and strategies to the table, making it difficult for Sears to maintain its market share.
The competitive pressure intensified over time, with the rise of e-commerce significantly impacting Sears's business. The company's ability to adapt to these challenges and differentiate itself from its rivals became critical for its survival. Exploring the strategies of its competitors provides insights into the broader retail environment and the factors influencing success in the industry.
Macy's, J.C. Penney, and Kohl's were direct competitors, vying for the same customer base. They offered similar product assortments and competed through store format updates and loyalty programs.
Walmart and Target provided a broad selection of goods at competitive prices. They often had more efficient supply chains and distribution networks, giving them an advantage.
Lowe's and The Home Depot directly competed in categories like appliances and tools. Their specialized focus and customer service were key differentiators.
Amazon posed a significant threat due to its vast product selection, competitive pricing, and convenient delivery options. This impacted Sears' business strategy.
Sears struggled to maintain market share in key categories like appliances. Aggressive pricing and product innovation from competitors intensified these challenges.
Specialized online retailers offered niche products and services. Sears struggled to integrate these offerings, further complicating the competitive landscape.
The competitive landscape was constantly changing, with mergers and alliances among rivals strengthening their positions. For example, in 2024, Amazon's net sales increased by 12% year-over-year, highlighting the continued dominance of e-commerce. Understanding the strategies of these competitors, as well as the impact of e-commerce, is crucial. For more insights, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of Sears Holdings.
Sears faced several key challenges in the competitive landscape, including maintaining market share in key categories and adapting to the rise of e-commerce.
- Intense competition from department stores, big-box retailers, and specialized online retailers.
- The need to innovate and adapt to changing consumer preferences and shopping habits.
- The impact of store closures and their effect on the overall market position.
- The importance of brand perception and customer service in a competitive environment.
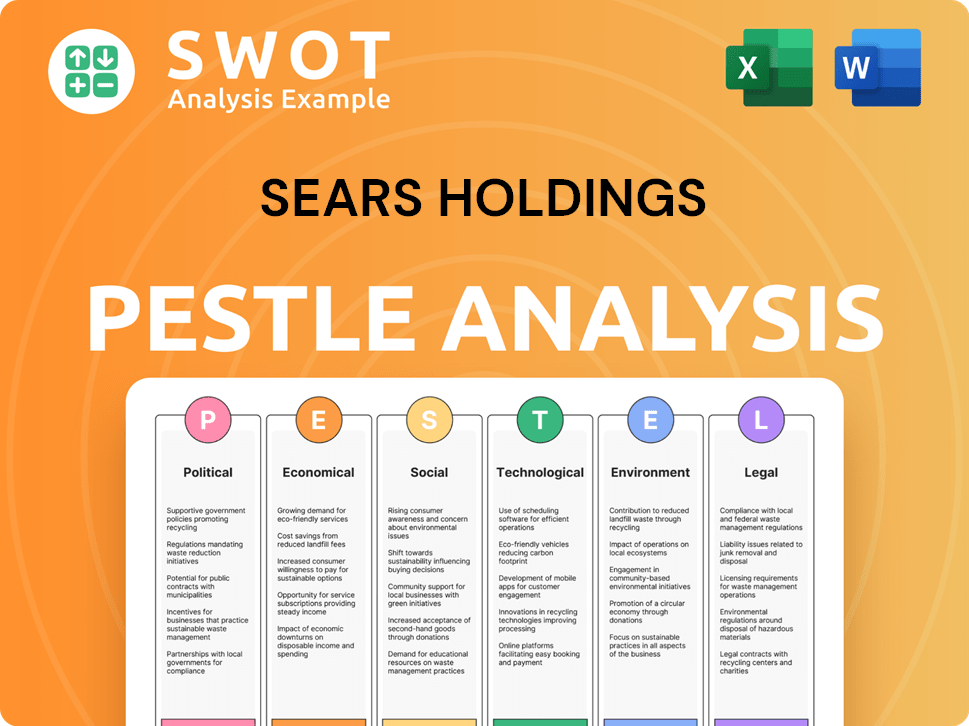
Sears Holdings PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What Gives Sears Holdings a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
To understand the Sears competitive landscape, it's essential to examine its historical advantages. Sears Holdings Company, in its prime, leveraged a vast network of department stores, providing widespread accessibility and convenience. The company also benefited from strong brand equity in its proprietary brands, such as Kenmore and Craftsman, which fostered customer loyalty for many years. These factors were key to its success in the retail industry analysis.
Historically, Sears's business strategy included economies of scale, stemming from its massive purchasing power and distribution network, enabling competitive pricing. Its catalog-based origins provided an early form of direct-to-consumer distribution. However, these advantages faced significant threats from competitors expanding their physical presence and the rise of e-commerce platforms. These shifts significantly impacted Sears's market share and its competitive position.
The erosion of these advantages highlights the challenges Sears Holdings Company faced. The extensive store network, once an asset, became a liability due to high overhead costs. The decline in brand equity for Kenmore and Craftsman, coupled with difficulties in adapting to e-commerce, further weakened its operational efficiencies. Understanding these shifts is crucial when analyzing Sears's competitive landscape.
Sears once boasted a vast network of physical stores, offering convenience and accessibility. This extensive presence was a key competitive advantage for many years. However, the cost of maintaining this network eventually became a significant burden as consumer preferences shifted.
Brands like Kenmore and Craftsman held strong brand equity and customer loyalty. These proprietary brands were a key differentiator, known for their quality and reliability. This contributed significantly to Sears's sales and market position for decades.
Sears benefited from economies of scale, derived from its massive purchasing power and distribution network. This allowed the company to offer competitive pricing and maintain operational efficiencies. The company's size was a significant advantage in the retail market.
Sears's catalog-based origins established an early form of direct-to-consumer distribution. This innovative approach provided a unique advantage in reaching customers. This model was revolutionary for its time, setting the stage for future retail strategies.
The Sears competitive landscape changed as other retailers expanded and e-commerce gained traction. Sears's store network became a liability due to high overhead. The brand equity of Kenmore and Craftsman diminished, and the company struggled to adapt its supply chain.
- Increased Competition: The rise of competitors with larger e-commerce presences.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Consumers gained access to a wider array of brands.
- Operational Challenges: Inability to adapt to the demands of e-commerce.
- Financial Performance: Sears Holdings Company faced significant financial challenges.
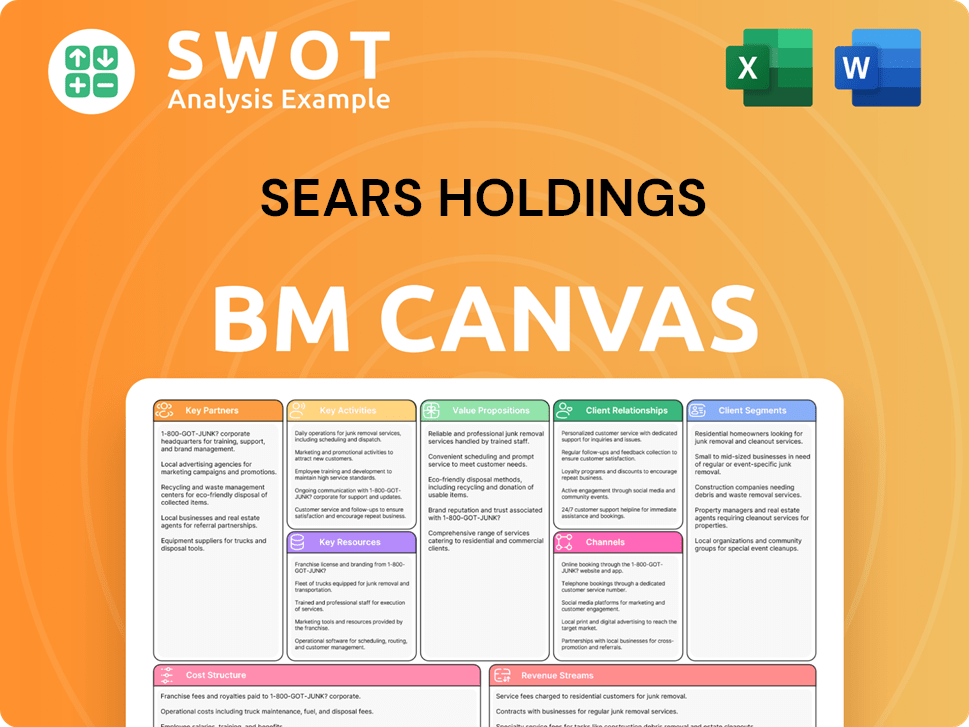
Sears Holdings Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping Sears Holdings’s Competitive Landscape?
The retail industry has undergone significant transformations, driven by the rise of e-commerce, the need for omnichannel strategies, and evolving consumer expectations. For a company like Sears Holdings Company, understanding the Sears competitive landscape and adapting to these shifts was crucial for survival. The company's struggles highlight the challenges faced by traditional retailers in a rapidly changing market.
The Sears competitors, particularly online giants, have reshaped the industry. The evolving retail environment demanded agility and innovation, making it challenging for companies that were slow to adapt. This chapter examines the industry trends, future challenges, and opportunities that shaped the trajectory of Sears Holdings Company.
Key trends include the growth of e-commerce, the importance of omnichannel retail, and the demand for personalized customer experiences. Technological advancements, such as AI and augmented reality, are redefining the retail experience. Regulatory changes, particularly regarding data privacy, also influence the industry.
Challenges for Sears Holdings Company included declining mall foot traffic and the expansion of online retailers. Changing consumer preferences for speed and convenience demanded significant investment in digital infrastructure. Increased regulation on product safety and environmental impact posed additional threats.
Opportunities in the retail landscape include growth in emerging markets and continued innovation in product offerings and retail technologies. Strategic partnerships could have provided avenues for revitalization. However, as Sears no longer operates, these opportunities are largely irrelevant to its current state.
The Sears market position compared to rivals was significantly impacted by the rise of e-commerce. The shift towards online shopping and the success of competitors like Amazon, which reported net sales of approximately $574.8 billion in 2023, created intense pressure. The ability to offer competitive pricing, efficient logistics, and a seamless online experience became critical.
The Sears business strategy faced significant hurdles due to its inability to adapt quickly to the changing retail environment. Sears competitors, such as Walmart, Target, and online retailers, invested heavily in e-commerce and supply chain optimization. For instance, Walmart's e-commerce sales grew by 23% in fiscal year 2023, demonstrating the importance of a strong online presence.
- The decline in demand for traditional department store offerings.
- Increased regulation on product safety and environmental impact.
- Aggressive new competitors in specialized online segments.
- Challenges in maintaining customer loyalty and brand perception.
For a deeper understanding of the company's financial structure and business model, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Sears Holdings. The Sears Holdings Company financial performance was negatively affected by these challenges, leading to store closures and a decline in market share. The impact of e-commerce on Sears' competitive landscape was profound, underscoring the need for retailers to embrace digital transformation and adapt to evolving consumer behaviors.
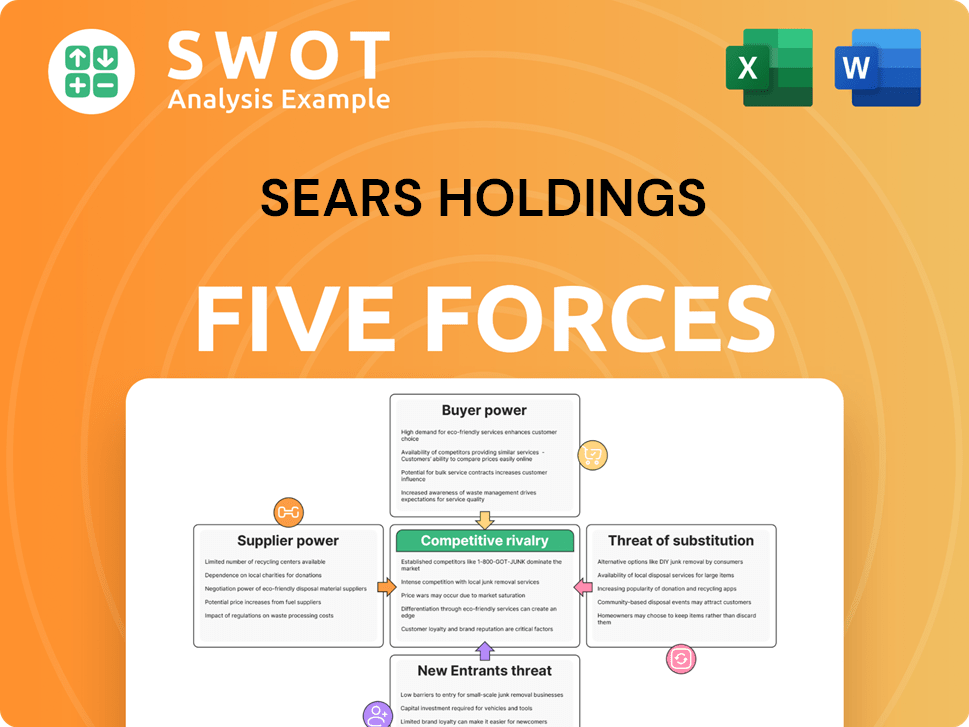
Sears Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Sears Holdings Company?
- How Does Sears Holdings Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Brief History of Sears Holdings Company?
- Who Owns Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sears Holdings Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.