Sears Holdings Bundle
Who Owns Sears Holdings Company Now?
Unraveling the story of 'Who owns Sears Holdings Company?' is essential to understanding the downfall of a retail legend. From its humble beginnings to its eventual bankruptcy, the evolution of Sears' ownership reveals the critical role it played in the company's strategic decisions and ultimate fate. This investigation into Sears ownership offers a compelling case study of how shifts in the business landscape can reshape even the most established enterprises.
The journey of Sears, from mail-order catalogs to sprawling department stores, is a fascinating tale of American retail. Understanding the Sears Holdings SWOT Analysis is key to understanding the strategic decisions that led to its current state. The company's bankruptcy and subsequent liquidation underscore the importance of adapting to changing consumer preferences and maintaining a sustainable business model. Exploring the current owner of Sears and the decisions made during its final years provides valuable insights into the dynamics of corporate ownership and the impact on a company's survival.
Who Founded Sears Holdings?
The story of Sears, Roebuck and Company begins with Richard Warren Sears, who launched a watch company in 1886. Alvah Curtis Roebuck joined him in 1887, forming the foundation of what would become a retail giant. Their early collaboration set the stage for the mail-order business that would revolutionize American commerce.
In 1893, the company was officially incorporated in Illinois. The initial ownership was primarily between Sears and Roebuck, with Sears focusing on sales and marketing, and Roebuck managing the technical aspects. The company's rapid growth was fueled by its innovative catalog sales model, attracting capital and attention.
A pivotal moment came in 1895 when Julius Rosenwald, a clothing manufacturer, bought out Roebuck's interest for $25,000. This marked a significant shift in the early ownership structure, with Rosenwald becoming a key partner alongside Sears. This early reshuffling of ownership reflected new visions and financial injections that were crucial for the company's expansion.
Richard Warren Sears started a watch company in 1886, which evolved into Sears, Roebuck and Company. Alvah Curtis Roebuck joined Sears in 1887, contributing to the company's early development. Their partnership was key to the initial success of the mail-order business.
The early ownership revolved around Richard Sears and Alvah Roebuck. While specific equity splits aren't fully documented, Sears held the dominant stake. The company's incorporation in 1893 marked a formalization of its structure.
In 1895, Julius Rosenwald bought out Alvah Roebuck's interest. Rosenwald's involvement transformed Sears into a modern retail enterprise. This shift was crucial for the company's growth and strategic direction.
Sears's focus on direct-to-consumer sales and Rosenwald's emphasis on efficiency shaped the company. These strategies were instrumental in the company's initial growth. The early decisions influenced the company's expansion.
The innovative catalog sales model was a key factor in Sears's early success. This approach allowed the company to reach a vast customer base. The catalog was a critical tool for driving sales and growth.
The company's rapid growth attracted early capital and attention. This financial support was essential for scaling the business. The early investments fueled the company's expansion efforts.
The early ownership of Sears, Roebuck and Company was defined by the partnership of Richard Sears and Alvah Roebuck, followed by the significant addition of Julius Rosenwald. These individuals shaped the company's strategy and growth. Understanding the early ownership structure provides context for the evolution of Sears Holdings Company.
- Richard Sears and Alvah Roebuck were the original founders.
- Julius Rosenwald became a key partner in 1895.
- The mail-order catalog was a critical innovation.
- Early ownership decisions influenced the company's future.
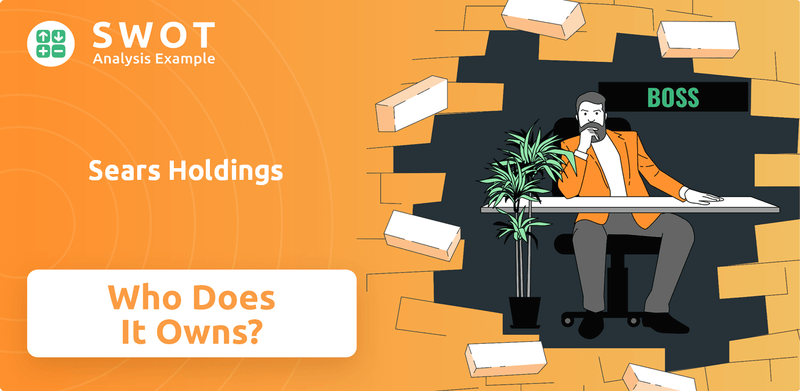
Sears Holdings SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Sears Holdings’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of Sears, Roebuck and Company evolved significantly over time, starting with its initial public offering in 1906, which broadened its shareholder base. For many years, Sears operated as a publicly traded company, attracting a diverse range of investors. However, a pivotal change occurred in 2005 when Kmart and Sears merged to form Sears Holdings Corporation. This merger, orchestrated by Edward S. Lampert through his hedge fund ESL Investments, marked a turning point in the company's ownership structure, as ESL Investments became the dominant shareholder.
The merger of Kmart and Sears, and subsequent strategic decisions, significantly impacted the company's trajectory. Lampert's strategy focused on leveraging real estate assets and streamlining operations. This approach, coupled with the challenges facing the retail industry, eventually led Sears Holdings to file for bankruptcy. The bankruptcy process resulted in a restructuring where ESL Investments, through Transformco, acquired the remaining assets of Sears and Kmart. This transition shifted the ownership from a publicly held company to one largely controlled by a private entity, ESL Investments.
| Timeline | Event | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 1906 | Sears goes public | Broadened public shareholding |
| 2005 | Merger of Kmart and Sears | ESL Investments becomes dominant shareholder |
| 2018 | Sears Holdings files for bankruptcy | Restructuring and asset acquisition by Transformco (ESL Investments) |
As of early 2024, the primary owner of the residual assets of Sears Holdings, including the remaining Sears and Kmart assets, is ESL Investments, led by Edward Lampert, through Transformco. This shift reflects a strategic focus on asset monetization and a reduced retail footprint. The Brief History of Sears Holdings provides additional context on the company's evolution. Major stakeholders now primarily include ESL Investments and its affiliates, who have provided substantial financing and equity during and after the bankruptcy process. The current status of Sears Holdings Company indicates a significant transformation in its ownership and operational strategy.
The ownership of Sears has dramatically changed, from a publicly traded company to one controlled by ESL Investments.
- ESL Investments, led by Edward Lampert, now owns the remaining assets through Transformco.
- The company's strategy has shifted towards asset monetization and a smaller retail presence.
- Sears's history includes significant events like the 2005 merger and the 2018 bankruptcy filing.
- The current ownership structure reflects a major restructuring of the company.
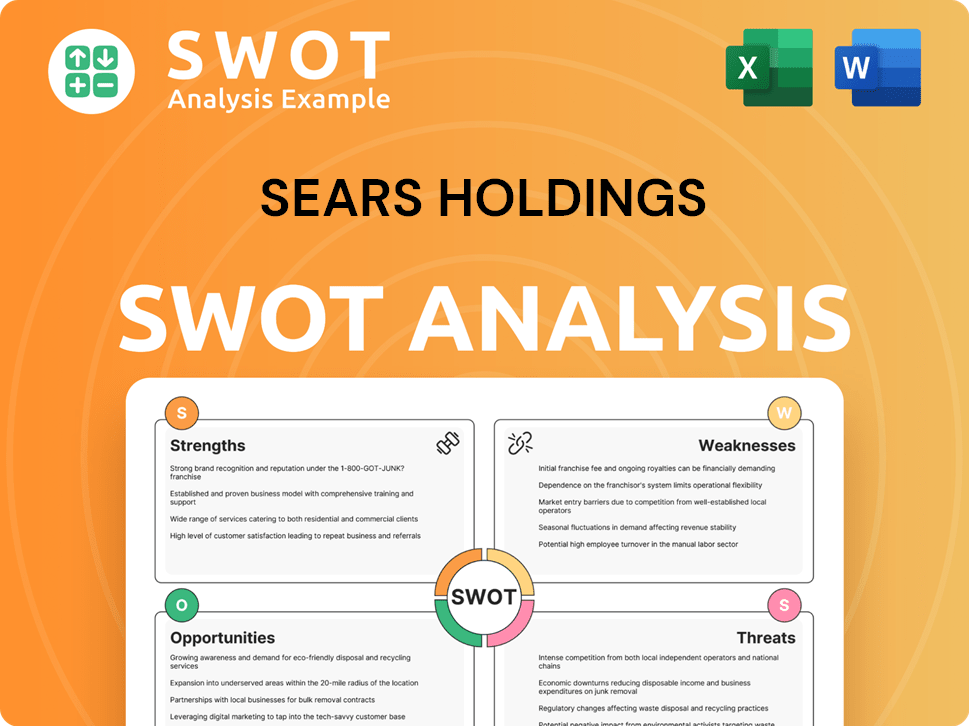
Sears Holdings PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Sears Holdings’s Board?
Given the liquidation of Sears Holdings Company, the traditional board of directors structure no longer applies in the same way. The remaining assets are primarily controlled by Transformco, an entity owned by Edward S. Lampert's ESL Investments. Before the liquidation, during its public and pre-liquidation phases, the board of directors reflected the influence of its major shareholders, especially Edward Lampert.
During its operational years, Edward Lampert, as the largest shareholder through ESL Investments, exerted significant control over the board. He served as Chairman and later CEO, with many board members affiliated with ESL Investments or aligned with Lampert's strategic vision. This raised concerns about the board's independence, especially regarding asset sales and the declining retail operations. In the post-bankruptcy and liquidation phase, governance of the remaining assets under Transformco would be more akin to a privately held entity, with control concentrated in ESL Investments.
| Aspect | Details | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Primary control of remaining assets | Transformco, owned by ESL Investments |
| Board of Directors | Structure | Determined by ESL Investments |
| Public Trading | Stock | No longer publicly traded |
The control is primarily vested in Edward Lampert and ESL Investments, reflecting the outcome of the bankruptcy and asset acquisition. The Marketing Strategy of Sears Holdings evolved significantly as the company faced financial challenges and ultimately, liquidation.
Edward S. Lampert, through ESL Investments, currently owns Sears. This control stems from the Sears bankruptcy and asset acquisition. Transformco, owned by ESL Investments, manages the remaining assets.
- Edward Lampert's ESL Investments controls the remaining assets.
- Sears is no longer publicly traded.
- The board structure is now determined by ESL Investments.
- Sears filed for bankruptcy in 2018.
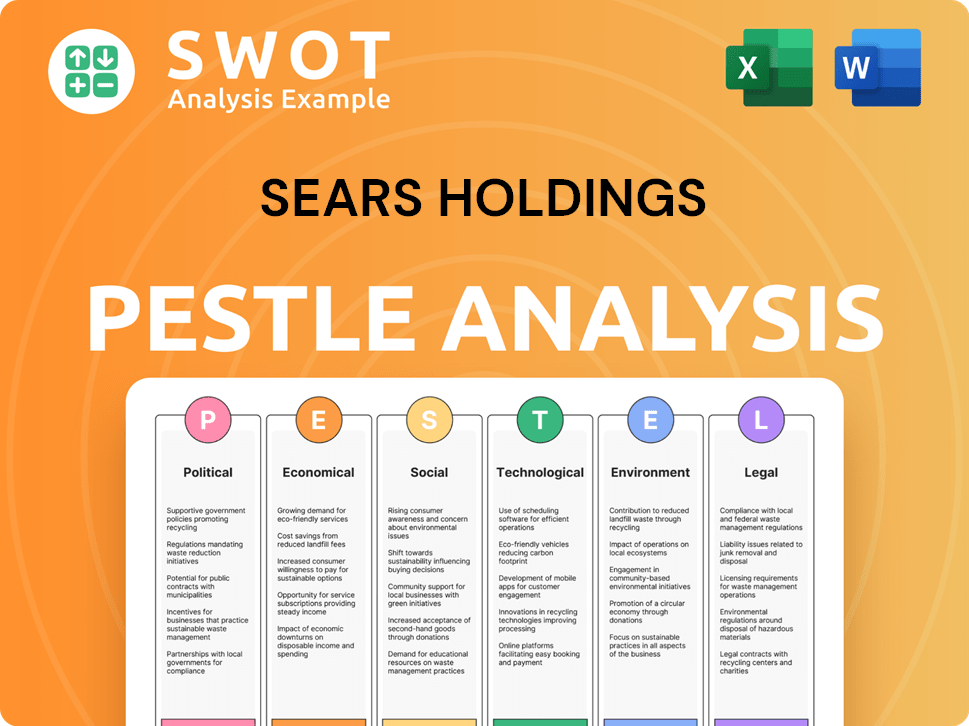
Sears Holdings Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Sears Holdings’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years, the most significant development in Sears Holdings Company's ownership has been its transition from a publicly traded entity to a privately held one. Following the 2018 bankruptcy filing, Edward S. Lampert's ESL Investments, operating through Transformco, acquired most of the remaining assets, including the Sears and Kmart brands. This acquisition, finalized in early 2019 for approximately $5.2 billion, effectively removed Sears and Kmart from public ownership.
Since the acquisition, Transformco has focused on downsizing the physical retail footprint of Sears and Kmart. The number of operational stores has significantly decreased. This shift reflects broader industry trends towards e-commerce and challenges faced by traditional brick-and-mortar retailers. As of early 2024, the number of operational stores has dwindled significantly, with only a handful remaining compared to hundreds just a few years prior.
| Metric | Data | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Price | Approximately $5.2 billion | 2019 |
| Estimated Store Count (Early 2024) | Fewer than 20 | 2024 |
| Bankruptcy Filing Date | October 15, 2018 | 2018 |
The rise of activist investors, like Edward Lampert, has influenced changes in company strategy, often involving asset sales and restructuring. While Sears's situation is extreme due to bankruptcy, it highlights how concentrated ownership can lead to aggressive strategic shifts. There have been no public statements about future ownership changes or a potential re-listing for Sears or Kmart as retail operations; the focus remains on asset management and the continued operation of the remaining brands under Transformco. For more details on the competitive landscape, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of Sears Holdings.
Sears transitioned from a publicly traded company to a privately held entity under Transformco. This change occurred after the bankruptcy filing, with ESL Investments acquiring the assets.
Sears and Kmart store numbers have significantly decreased, focusing on asset management and a smaller retail footprint. The focus is on monetization and the remaining brands.
Sears is now primarily controlled by Edward S. Lampert's ESL Investments through Transformco. This shift reflects the influence of activist investors and strategic restructuring.
There are no current plans for public re-listing or significant ownership changes. Transformco's focus remains on managing assets and operating the remaining stores.
Sears Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Sears Holdings Company?
- How Does Sears Holdings Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Brief History of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sears Holdings Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.