Sears Holdings Bundle
Can Sears Holdings Company Rise Again?
Once a retail behemoth, Sears Holdings Company's journey is a compelling case study of market evolution. From mail-order catalogs to dominating the American retail landscape, Sears's story is filled with innovation and influence. However, the tides of the Sears Holdings SWOT Analysis reveal a complex narrative of triumph and, ultimately, transformation.
While the concept of a traditional "growth strategy" is no longer relevant for Sears Holdings Company in its current state, understanding its past provides invaluable insights into the dynamics of the Retail Industry Analysis. Examining its business model, financial performance, and the impact of Market Trends offers crucial lessons for investors and business strategists alike. This exploration delves into the Sears Future and the factors that shaped its trajectory, providing a critical perspective on the challenges and opportunities within the evolving retail sector.
How Is Sears Holdings Expanding Its Reach?
Since Sears Holdings Company is no longer an active retail business, having gone through bankruptcy in 2018 and liquidated its assets, it does not have any current expansion initiatives. The company's historical expansion strategies, however, offer insights into its past approaches to growth and market positioning. Understanding these strategies is crucial for a comprehensive Retail Industry Analysis and assessing the company's legacy within the competitive environment.
Historically, the company's growth was significantly influenced by its mail-order catalog, which allowed it to reach customers across the United States without physical stores. This model was innovative for its time, especially in serving rural areas. Later, the company expanded into physical retail locations, establishing department stores that became key components of shopping malls. The company also diversified into financial services, real estate, and automotive services to capture more consumer spending and diversify revenue streams. This included the merger with Kmart in 2005, forming Sears Holdings Corporation, which was an attempt to create a stronger competitor in the discount retail sector by combining the two struggling chains.
These historical expansion strategies, however, ultimately proved inadequate to counter the changes in consumer behavior and the competitive landscape. The company faced challenges from shifting consumer preferences, the rise of e-commerce, and increased competition from other retailers. The decisions made during its expansion phases, including the acquisition of Kmart, were not enough to ensure long-term sustainability.
The initial expansion of Sears was primarily driven by its mail-order catalogs. This allowed the company to reach a broad customer base across the United States, especially in areas where physical stores were not readily available. The catalog model was a pioneering strategy that significantly expanded the company's reach and customer base.
Sears expanded into physical retail by opening department stores, which became anchor tenants in shopping malls across the country. These stores represented a shift from a catalog-based business to a multi-channel retail giant. The physical stores aimed to provide a more direct shopping experience for customers.
The company diversified its offerings by venturing into financial services, real estate, and automotive services. This move aimed to capture a larger share of consumer spending and create multiple revenue streams. This strategy was meant to hedge against the volatility of the retail sector.
The acquisition of Kmart in 2005 formed Sears Holdings Corporation, aiming to create a stronger competitor in the discount retail space. The merger was an attempt to combine two struggling chains to leverage their combined assets and market presence. This strategy, however, did not achieve the intended results.
Despite these expansion efforts, Sears faced significant challenges. The company struggled to adapt to changing consumer behaviors, the rise of e-commerce, and increased competition. The Sears Future was greatly impacted by these factors.
- Decline in Market Share: The company's market share steadily declined due to competition from online retailers and other brick-and-mortar stores.
- Store Closures: Numerous store closures occurred as the company struggled to maintain profitability.
- Bankruptcy Filing: Sears Holdings Corporation filed for bankruptcy in 2018, marking the end of its operations as a major retail entity.
- Impact of E-commerce: The company's failure to effectively compete in the e-commerce space contributed to its decline.
The historical expansion initiatives of Sears Holdings Company provide valuable insights into the Growth Strategy and challenges faced by the company. The company's past attempts at expansion, including diversification and acquisitions, ultimately proved insufficient to overcome the rapidly changing retail landscape. For a deeper understanding of the competitive environment Sears faced, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Sears Holdings.
Sears Holdings SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Sears Holdings Invest in Innovation?
Given that the entity is no longer an operating retail business, the concept of a current innovation and technology strategy for Sears Holdings Company is non-existent. The company's historical approach to technology and innovation provides insights into its past strategies and challenges. Understanding this history is crucial for any analysis of the Sears Holdings Company's business model and its ultimate decline.
Historically, Sears was a pioneer in retail innovation. Its mail-order catalog, launched in 1893, was a technological marvel for its time. It utilized print technology and an advanced logistics network to deliver a wide array of goods directly to consumers' homes. This innovation democratized access to products, especially in rural areas, showcasing the company's early leadership in leveraging technology for growth.
In later years, Sears attempted to adapt to new technological trends, including early ventures into e-commerce. However, these efforts lagged behind more agile competitors. The company invested in point-of-sale systems and inventory management technologies common in large-scale retail. However, the company struggled to fully embrace digital transformation and leverage cutting-edge technologies like AI, IoT, or advanced data analytics to the same extent as its more successful rivals.
Sears' early adoption of the mail-order catalog in 1893 was a groundbreaking innovation. This catalog utilized advanced printing and distribution technologies for its time. It allowed the company to reach a vast customer base, especially in areas with limited access to retail stores.
Sears made early forays into e-commerce, attempting to capitalize on the growing online market. These efforts, however, were not as successful as those of competitors that were more agile and adaptable. The company struggled to keep pace with the rapid changes in the digital retail landscape.
The company invested in point-of-sale (POS) systems and inventory management technologies. These systems aimed to improve operational efficiency and customer service. Despite these investments, Sears did not fully integrate these technologies to the same extent as its competitors.
Sears faced significant challenges in fully embracing digital transformation. It struggled to leverage cutting-edge technologies such as AI, IoT, and advanced data analytics. These limitations hindered its ability to compete effectively in the rapidly evolving retail sector.
Sears had a rich history of in-house product development and brand creation. Brands like Kenmore appliances and Craftsman tools were key to its success. However, the ability to innovate and integrate new technologies into core retail operations diminished over time.
The company's inability to keep pace with technological advancements contributed to its decline. Rapid changes in consumer expectations and the retail sector's technological landscape left Sears struggling to compete. This ultimately impacted its market share and financial performance.
Sears' failure to fully embrace digital transformation and advanced technologies significantly impacted its ability to compete in the retail industry. This led to a decline in market share and financial performance. Understanding these failures provides insights into the company's challenges and the broader Target Market of Sears Holdings.
- E-commerce Lag: Sears' e-commerce efforts lagged behind competitors like Amazon and Walmart, which invested heavily in online platforms and logistics.
- Data Analytics: The company did not effectively leverage data analytics to understand customer behavior, optimize inventory, or personalize marketing.
- Supply Chain: Sears' supply chain management was not as efficient or technologically advanced as its competitors, leading to higher costs and slower delivery times.
- Store Experience: The in-store experience did not keep pace with technological advancements, lacking features like interactive displays and mobile checkout options.
Sears Holdings PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What Is Sears Holdings’s Growth Forecast?
As the entity known as Sears Holdings Company no longer operates as a retail business, having gone through bankruptcy in 2018 and subsequently liquidated its assets, there isn't a current financial outlook or projections for its future growth. The Marketing Strategy of Sears Holdings in its final years was marked by significant revenue decline, increasing losses, and mounting debt, ultimately leading to its inability to meet financial obligations.
Prior to its bankruptcy filing, Sears Holdings consistently reported substantial net losses. For instance, in the fiscal year ending February 3, 2018, the company reported a net loss of $2.2 billion. This was preceded by a loss of $2.2 billion in the previous fiscal year. Revenue also saw a sharp decline, with sales falling by 28.5% in 2017 to $16.7 billion. These figures highlight a consistent downward trend in financial performance, driven by declining store traffic, intense competition from e-commerce giants and discount retailers, and a heavy debt load.
The company's financial struggles were further worsened by its inability to generate sufficient cash flow from operations to fund its ongoing business and debt servicing. This resulted in repeated store closures and asset sales in an attempt to raise liquidity. Ultimately, these measures were not enough to reverse the negative financial trajectory, culminating in the bankruptcy filing and the eventual cessation of its retail operations. The factors contributing to the company's downfall included a failure to adapt to changing market trends, heavy debt, and intense competition.
Sears Holdings experienced significant revenue decline in its final years, with sales dropping by 28.5% in 2017. This decline reflects the company's struggle to compete with online retailers and changing consumer preferences. The company's financial performance was consistently negative, marked by substantial net losses.
The company's inability to generate sufficient cash flow led to repeated store closures and asset sales. These measures were insufficient to reverse the negative financial trajectory. The heavy debt load further exacerbated financial difficulties, contributing to the eventual bankruptcy filing.
Intense competition from e-commerce giants and discount retailers significantly impacted Sears Holdings. Changing consumer preferences and the rise of online shopping created challenges. The company struggled to adapt to these shifts in the retail landscape.
The culmination of financial struggles led to the bankruptcy filing and the eventual cessation of retail operations. The bankruptcy marked the end of an era for a once-dominant retailer. The company's inability to adapt ultimately led to its demise.
Sears Holdings Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Risks Could Slow Sears Holdings’s Growth?
When assessing the potential risks and obstacles faced by the former Sears Holdings Company, it's crucial to recognize that it is no longer an active retail entity. Instead, we can analyze the factors that contributed to its decline to understand the challenges within the retail industry. This analysis offers valuable insights for businesses navigating similar environments.
The primary challenge for Sears Holdings Company was intense competition. It struggled to differentiate itself effectively in a market dominated by giants like Walmart and Target, as well as the rapidly growing e-commerce sector led by Amazon. The inability to adapt to changing consumer preferences and integrate modern technologies further compounded its difficulties.
Another significant obstacle was the company's substantial debt burden. This, combined with declining sales, severely limited its capacity to invest in necessary upgrades and compete effectively. Internal issues, such as outdated IT infrastructure, also hampered the execution of any effective turnaround strategies.
Sears Holdings Company faced intense competition from both traditional brick-and-mortar retailers and e-commerce giants. The company struggled to maintain its market share against competitors offering more competitive pricing and a wider selection of products. The competitive landscape was a significant factor in the company's struggles.
Sears Holdings Company was slow to adapt to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. The company failed to invest adequately in its online presence and modern retail technologies. This led to a decline in customer experience and a loss of market share.
A substantial debt burden significantly constrained Sears Holdings Company's ability to invest in necessary modernizations. Declining sales and profitability exacerbated the financial strain, limiting the company's ability to compete effectively. The financial distress was a major obstacle.
Internal resource constraints, including outdated IT infrastructure and a fragmented business model, hindered effective turnaround strategies. These inefficiencies made it difficult for the company to execute strategic initiatives and adapt to market changes. These challenges were a major factor in the decline.
The company was slow to embrace digital transformation. This included a lack of investment in a robust online presence and modern retail technologies. This failure to adapt to the digital age significantly impacted its ability to compete. The disruption of the internet and e-commerce was a key factor.
Management faced immense pressure to manage liquidity and debt, which often overshadowed strategic investments. This focus on short-term financial survival hindered long-term planning and innovation. These challenges significantly impacted the company's ability to adapt and compete.
The retail industry is highly competitive, with companies like Walmart and Amazon dominating the market. As of 2024, Amazon's net sales continue to grow, reflecting the ongoing shift towards e-commerce. The Sears Holdings Company struggled to compete against these giants.
The company's financial performance was a significant challenge. Declining sales and a heavy debt burden created a cycle of financial distress. The company's bankruptcy in 2018 highlighted the severity of its financial problems. For more details, you can explore Brief History of Sears Holdings.
The rapid advancements in technology, particularly in e-commerce and digital marketing, posed a challenge. Companies needed to invest heavily in online platforms and customer experience. The lack of investment in this area hampered the company's ability to compete effectively.
Consumer preferences have evolved significantly, with a growing demand for convenience, personalized shopping experiences, and value. Retailers must adapt to these trends to remain relevant. Sears Holdings Company struggled to meet these evolving demands.
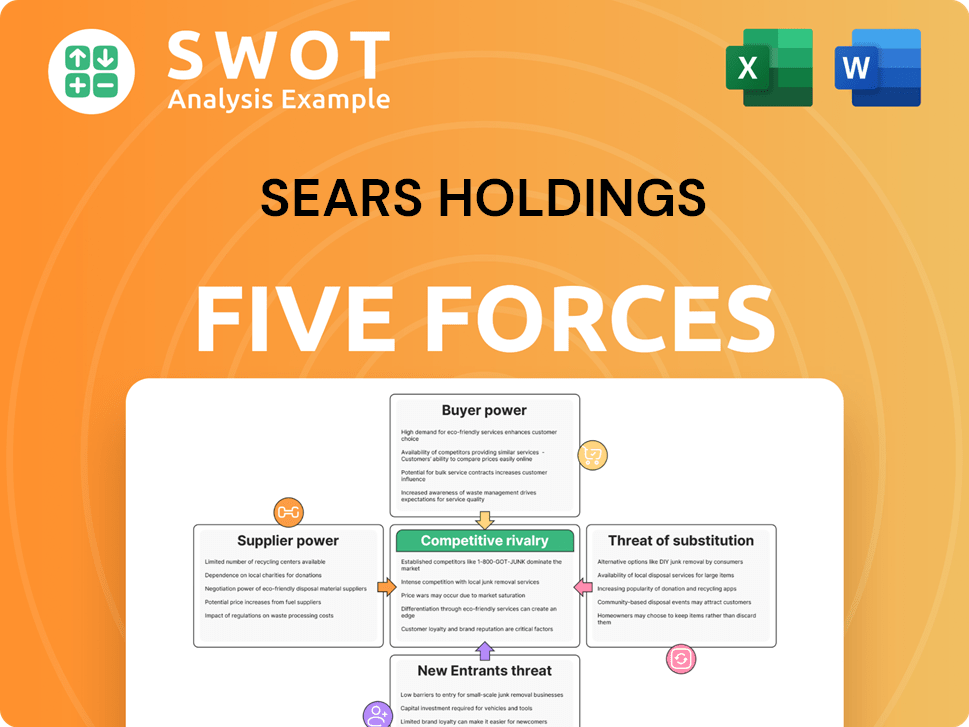
Sears Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Sears Holdings Company?
- How Does Sears Holdings Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Brief History of Sears Holdings Company?
- Who Owns Sears Holdings Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sears Holdings Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.