SVB Bundle
What Defined SVB's Competitive Arena Before Its Fall?
The sudden demise of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in 2023 sent shockwaves through the financial world, prompting a deep dive into its competitive environment. Before its collapse, SVB was a crucial player in the venture capital landscape, deeply intertwined with the innovation economy. This analysis aims to dissect SVB's market position, its key rivals, and the strategic factors that shaped its trajectory.

This exploration of the SVB SWOT Analysis will provide a comprehensive understanding of the SVB competitive landscape and its SVB competitors. We'll examine the banking industry competition and the venture capital landscape to understand how SVB's unique focus impacted its performance. Furthermore, we'll analyze Silicon Valley Bank analysis to identify its strengths, weaknesses, and the financial services market dynamics that ultimately led to its downfall, offering insights into the SVB's main competitors 2024 and beyond.
Where Does SVB’ Stand in the Current Market?
Prior to its collapse, the bank, formerly known as Silicon Valley Bank, held a unique and dominant market position within the innovation economy. It catered to a significant portion of venture-backed technology and life science companies. The institution was widely recognized as the leading bank for startups, venture capital firms, and private equity firms in the U.S. and beyond.
Its primary offerings included commercial banking services tailored for startups, such as treasury management, debt financing, and venture debt. These were complemented by investment banking, private banking for founders and executives, and direct venture capital investments. Geographically, the bank had a strong presence in major innovation hubs like Silicon Valley, Boston, and New York, and expanded internationally into markets like the UK, Israel, and China.
Over time, the bank's positioning evolved from a purely transactional bank to a comprehensive financial partner, deeply integrating itself into the startup lifecycle from seed funding to IPO. This shift allowed it to capture a broader range of client needs and build strong, long-term relationships. For instance, at the end of 2022, it held over $200 billion in assets. The bank's strong position was particularly evident in its ability to attract deposits from a vast number of venture-backed companies, often holding a substantial portion of their operating capital. Its relatively weaker position was arguably its concentration risk, being heavily reliant on a single, albeit robust, sector.
The bank's core strength lay in its deep understanding of and specialization in the tech and life sciences sectors. This focus allowed it to offer tailored financial products and services that met the unique needs of startups and venture-backed companies. Its ability to attract and retain clients within this niche was a key factor in its success.
The bank positioned itself as a comprehensive financial partner, offering a range of services from seed funding to IPO support. This integrated approach allowed it to build strong, long-term relationships with clients, capturing a larger share of their financial needs over time. This strategy is also discussed in Growth Strategy of SVB.
The bank strategically established a strong presence in major innovation hubs across the United States and expanded internationally. This geographic diversification allowed it to serve a wider range of clients and tap into diverse markets. The international expansion included key markets like the UK, Israel, and China.
Prior to its collapse, the bank reported substantial assets and deposits, reflecting its significant scale within its specialized market. At the end of 2022, the bank held over $200 billion in assets, demonstrating its financial strength. This strong financial position was supported by its ability to attract deposits from a vast number of venture-backed companies.
The bank's strengths included its specialized focus, comprehensive service offerings, and strong relationships within the innovation ecosystem. However, its weaknesses included concentration risk, being heavily reliant on a single sector, and the potential for rapid deposit outflows. The competitive landscape for the bank involved both traditional banks and specialized financial institutions.
- Strengths: Deep industry knowledge, tailored financial products, strong client relationships, and a comprehensive service offering.
- Weaknesses: Concentration risk, reliance on a single sector, and vulnerability to rapid deposit outflows.
- Opportunities: Expansion into new markets, development of new financial products, and strategic partnerships.
- Threats: Increased competition, changes in the venture capital landscape, and economic downturns.
SVB SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format

Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging SVB?
The competitive landscape for SVB was characterized by a mix of direct and indirect rivals, all vying for a share of the innovation economy. While few could match SVB's specialization, the bank faced significant challenges from both larger, diversified institutions and smaller, niche players. Understanding these competitors is crucial for a comprehensive Silicon Valley Bank analysis.
Direct competitors included large commercial banks and niche players, while indirect competition came from non-bank lenders and fintech disruptors. The dynamics were further reshaped by mergers and acquisitions, such as the acquisition of First Republic Bank by JPMorgan Chase in May 2023. This consolidation highlights the ongoing evolution of the banking industry competition.
The competitive environment also involved high-profile 'battles' for lucrative tech IPO mandates and the banking relationships of rapidly scaling unicorns, illustrating the intense competition within the venture capital landscape. The emergence of fintech disruptors added another layer of complexity, offering streamlined digital banking services and specialized financial tools.
JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo increasingly targeted the tech sector. These banks leveraged their vast capital reserves and extensive branch networks.
Signature Bank and First Republic Bank (acquired by JPMorgan Chase) focused on personalized services. They often competed for smaller to mid-sized startups and venture capital firms.
Venture debt funds and private credit firms offered specialized financing solutions. Fintech disruptors provided streamlined digital banking services.
Fintech companies posed a growing competitive threat. These firms offered specialized financial tools and digital banking services, attracting tech-savvy customers.
The acquisition of First Republic Bank by JPMorgan Chase reshaped the landscape. This consolidation concentrated market share and expertise.
SVB's specialized focus and deep integration within the innovation economy set it apart. However, this focus also made it vulnerable to sector-specific risks.
Analyzing SVB's competitive position requires a deep dive into its strengths and weaknesses, as well as the strategies of its rivals. For example, JPMorgan Chase's acquisition of First Republic Bank increased its assets by approximately $228 billion, according to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). This move underscores the ongoing consolidation within the banking sector. The Target Market of SVB was heavily reliant on venture capital funding, making the bank susceptible to shifts in the venture capital landscape. The competitive advantages of SVB included its specialized expertise in the tech sector, but its financial performance was closely tied to the success of its clients. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for identifying SVB's key market rivals and assessing the impact of the collapse on the future of its competitors.
Several factors influenced the competition within the financial services market:
- Capital Strength: Larger banks had a significant advantage due to their vast capital reserves.
- Specialized Services: Niche players offered personalized services tailored to specific client needs.
- Technological Innovation: Fintech disruptors leveraged technology to offer streamlined services.
- Market Focus: SVB's focus on the innovation economy created both opportunities and risks.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Consolidation reshaped the competitive landscape, increasing market concentration.
SVB PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
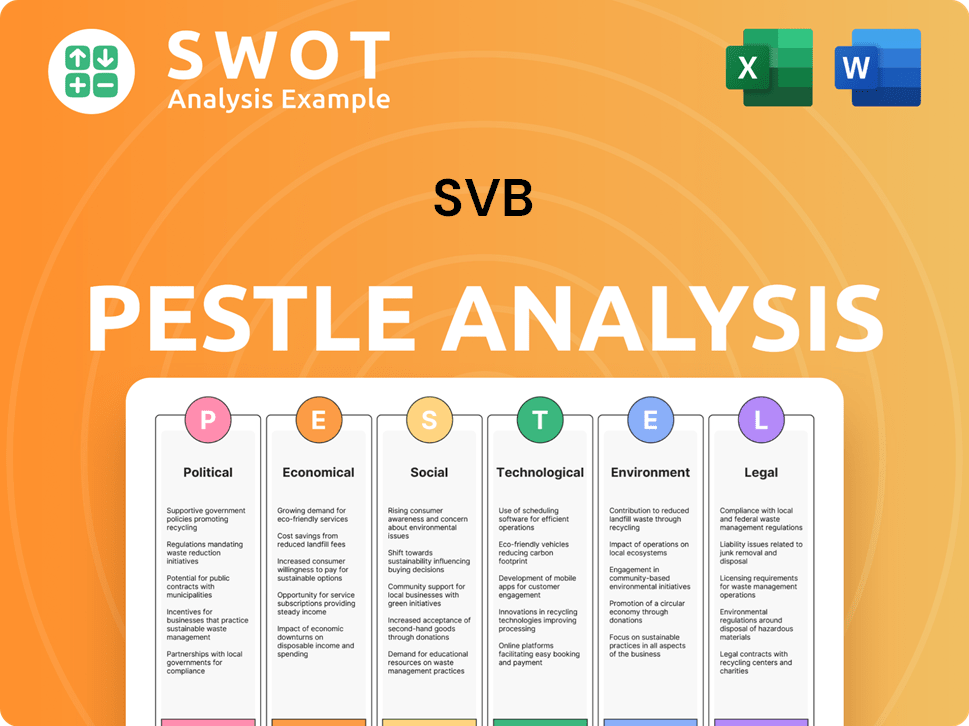
What Gives SVB a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
The competitive advantages of SVB, a key player in the financial services market, were deeply rooted in its specialization within the innovation economy. SVB's strategic focus on startups, venture capital firms, and tech companies allowed it to build a unique understanding of their financial needs. This specialization, combined with a strong network effect, gave SVB a significant edge over traditional banks.
SVB's competitive position was also bolstered by its brand equity and customer loyalty. Widely recognized as 'the bank for startups,' SVB fostered a sense of community and trust among its clientele. This loyalty was reinforced by dedicated relationship managers who understood the nuances of the tech industry. However, these advantages were ultimately vulnerable to systemic risks, as demonstrated by the bank's collapse, highlighting the impact of broader market challenges.
Understanding the SVB competitive landscape requires a deep dive into its unique strengths and how they stacked up against its rivals. A detailed Silicon Valley Bank analysis reveals a complex interplay of factors that contributed to its success and eventual downfall.
SVB's primary advantage was its deep understanding of the tech and venture capital sectors. This expertise allowed it to offer tailored financial products, such as venture debt, that were not readily available from other banks. This focus enabled SVB to build strong relationships and a loyal customer base within the innovation ecosystem.
SVB benefited significantly from its extensive network of relationships with venture capitalists, accelerators, and incubators. These connections often led to referrals, making SVB the go-to bank for many startups. This network effect created a powerful ecosystem that fueled SVB's growth within the venture capital landscape.
SVB's strong brand as 'the bank for startups' fostered high customer loyalty. Dedicated relationship managers who understood the tech industry's specific needs further strengthened these relationships. This customer-centric approach helped SVB maintain a competitive edge in the financial services market.
SVB invested in digital platforms to enhance client experience and streamline banking operations. While not reliant on proprietary technology, these platforms improved efficiency and client satisfaction. This investment in technology supported SVB's competitive position.
SVB's competitive advantages were built on specialization, network effects, and brand loyalty. These strengths allowed SVB to dominate the niche market of tech and venture-backed companies. However, the collapse highlighted the vulnerability of even strong competitive advantages to broader market risks. For a more in-depth analysis, consider reading this article on SVB's strategic partnerships and rivals.
- Specialization in the tech and venture capital sectors provided a significant competitive edge.
- Strong network effects, driven by relationships with venture capitalists, fueled growth.
- Brand equity and customer loyalty, fostered by a customer-centric approach, were crucial.
- Digital platforms enhanced client experience and streamlined operations.
SVB Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
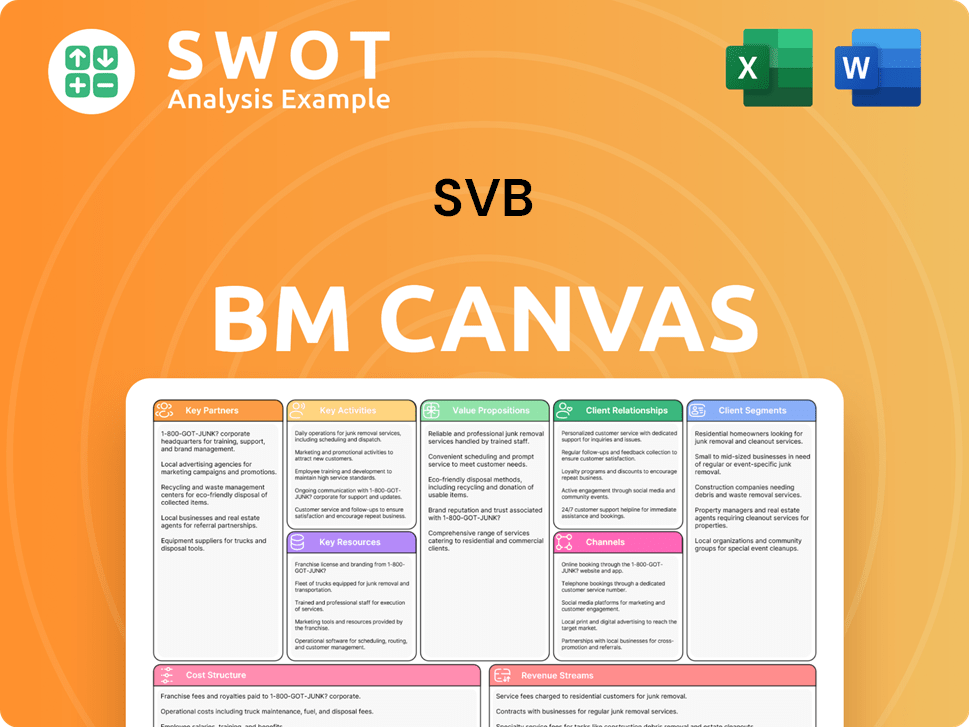
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping SVB’s Competitive Landscape?
The competitive landscape for financial institutions serving the innovation economy is undergoing significant shifts, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving client preferences. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any entity aiming to thrive in this specialized market. The collapse of SVB has reshaped the landscape, creating both challenges and opportunities for its competitors and new entrants.
The banking industry competition is intensifying, with traditional banks, fintech companies, and neobanks vying for market share. The venture capital landscape and overall financial services market are also key factors influencing the strategies and performance of institutions. As the industry adapts to the post-SVB era, understanding the competitive advantages of SVB and its rivals is essential for success.
Technological advancements, particularly in fintech and AI, are reshaping financial service delivery. Regulatory changes, such as stricter capital requirements, are impacting risk management. Shifting consumer preferences, with a demand for digital-first solutions, are also significant. Global economic shifts, including interest rate fluctuations, influence the sector.
Further consolidation among traditional banks and the rise of specialized neobanks are expected. A decline in venture capital funding poses a threat to deposit bases and lending opportunities. Increased regulatory scrutiny could stifle innovation. Adapting to the evolving needs of the innovation economy will be critical.
Growth opportunities exist in emerging markets for innovation, such as AI and biotech. Product innovations, like embedded finance solutions, offer avenues for growth. Strategic partnerships between banks and fintechs could create hybrid models. Adaptability and innovation are key to success.
The competitive environment is influenced by venture capital funding cycles. Market participants face threats like funding declines and increased regulatory scrutiny. Adaptability, regulatory compliance, and innovation will be crucial. The Revenue Streams & Business Model of SVB provides insights into its operations.
SVB's main competitors in 2024 face a landscape shaped by the bank's collapse. They must address increased regulatory scrutiny and evolving client needs. Understanding SVB's strengths and weaknesses, along with the impact of the collapse, is essential for strategic positioning.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Banks face stricter capital requirements and liquidity rules.
- Evolving Client Needs: Demand for digital-first solutions and integrated financial platforms is rising.
- Venture Capital Funding: Fluctuations in VC funding directly impact deposit bases and lending.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations between traditional banks and fintechs could create hybrid models.
SVB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
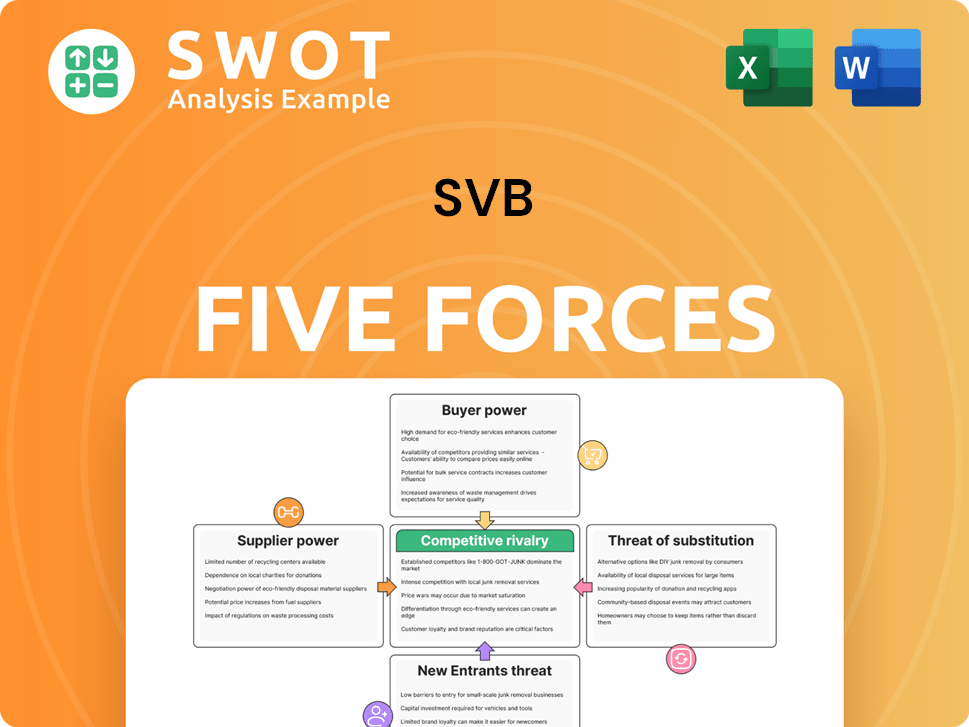
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of SVB Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of SVB Company?
- How Does SVB Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of SVB Company?
- What is Brief History of SVB Company?
- Who Owns SVB Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of SVB Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.