SVB Bundle
Who Really Owns SVB Now?
The 2023 collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), the largest bank failure since 2008, sent shockwaves through the financial world. Understanding SVB SWOT Analysis is crucial, but even more critical is knowing the SVB ownership structure. This is because ownership profoundly impacts a company's strategy, accountability, and survival during crises. SVB, once a cornerstone of the tech industry, offers a compelling case study in the importance of ownership.
From its roots serving the tech and venture capital sectors, SVB's journey to its eventual acquisition by First Citizens Bank is a story of shifting ownership and strategic decisions. Unraveling the details of who owns SVB, from its initial stakeholders to its public shareholders and the entities involved in its takeover, provides invaluable insights. This exploration of the SVB bank ownership structure will shed light on the factors contributing to its downfall and the subsequent restructuring of the bank.
Who Founded SVB?
The story of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) began in 1983, with Bill Biggerstaff and Robert Medearis at the helm. Their vision was to create a financial institution specifically tailored to the needs of the tech industry. This focus on a niche market was a key factor in the bank's early success and its eventual significant role in the financial landscape.
Biggerstaff, with his banking expertise, and Medearis, bringing venture capital experience, saw a gap in the market. Traditional banks were not equipped to understand or support the unique financial demands of technology startups and venture capital firms. This insight became the cornerstone of SVB's strategy.
While the precise initial equity split between Biggerstaff and Medearis isn't publicly available, their combined efforts were crucial. They gathered early backing from local entrepreneurs and investors who believed in the burgeoning technology sector. These initial investments provided the essential capital for SVB's launch and early operations, setting the stage for its future growth.
Biggerstaff and Medearis identified a need for a bank that understood the tech industry. Their focus on this niche was the foundation of SVB's unique market position.
Early investors were a mix of entrepreneurs and investors. Their support was crucial for the bank's initial capital and operations.
The initial ownership was likely concentrated among the founders and early backers. Agreements like vesting schedules would have been in place.
SVB's specialization in the tech sector distinguished it. This focus drove its rapid expansion in subsequent decades.
SVB's early focus on the innovation economy shaped its ownership structure. This focus laid the groundwork for its rapid growth.
The bank's strategic vision, centered on the innovation economy, was linked to its ownership and decision-making.
During its early years, the SVB ownership structure was likely concentrated, typical of a startup financial institution. Agreements such as vesting schedules were probably in place to ensure the long-term commitment of the founders. The founders' strategic vision, centered on the specialized needs of the innovation economy, was intrinsically linked to the distribution of control among these initial stakeholders. This early focus laid the groundwork for SVB's unique market position and rapid growth. For more insights into the bank's strategies, you can explore the Growth Strategy of SVB.
Understanding the early ownership of SVB bank is crucial to understanding its trajectory.
- The founders, Bill Biggerstaff and Robert Medearis, identified a market gap.
- Early investors were crucial in providing seed capital.
- The ownership structure was likely concentrated in the early years.
- The focus on the tech sector was a key differentiator.
SVB SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format

How Has SVB’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of the ownership of the SVB company began with its initial public offering (IPO) on July 10, 1988, when it listed on the NASDAQ exchange. This transition from a private to a public entity allowed for wider investment and fueled the bank's expansion. Over time, institutional investors became key stakeholders, including mutual funds, index funds, and large asset management firms, which held significant portions of the publicly traded shares. This shift significantly impacted the SVB ownership structure, influencing its corporate governance and strategic direction.
Prior to its collapse in March 2023, major institutional investors held substantial stakes in SVB. For example, as of December 30, 2022, Vanguard Group Inc. held 10.84%, BlackRock Inc. held 8.94%, and State Street Corp. held 4.67%. The rapid decline and subsequent FDIC receivership dramatically altered this landscape, with common equity holders facing significant losses. Following the FDIC's intervention, First Citizens Bank acquired a substantial portion of SVB's assets and deposits in March 2023, effectively transferring the operational ownership of the banking entity.
| Key Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | July 10, 1988 | Transitioned from private to public ownership, enabling broader investment. |
| Institutional Investment | Ongoing | Increased influence of mutual funds, index funds, and asset management firms. |
| FDIC Receivership and Acquisition | March 2023 | Common equity holders faced significant losses; First Citizens Bank acquired assets. |
The ownership of SVB bank has seen significant changes, especially after the bank's collapse. The FDIC's intervention and subsequent acquisition by First Citizens Bank marked a pivotal moment. For more details on the bank's history, you can refer to the article about the history of SVB ownership.
The ownership of SVB evolved significantly from its IPO to its acquisition by First Citizens Bank.
- Institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock were major stakeholders before the collapse.
- The FDIC played a crucial role in the bank's restructuring.
- First Citizens Bank now holds the operational ownership of the banking entity.
- The SVB ownership structure shifted dramatically in March 2023.
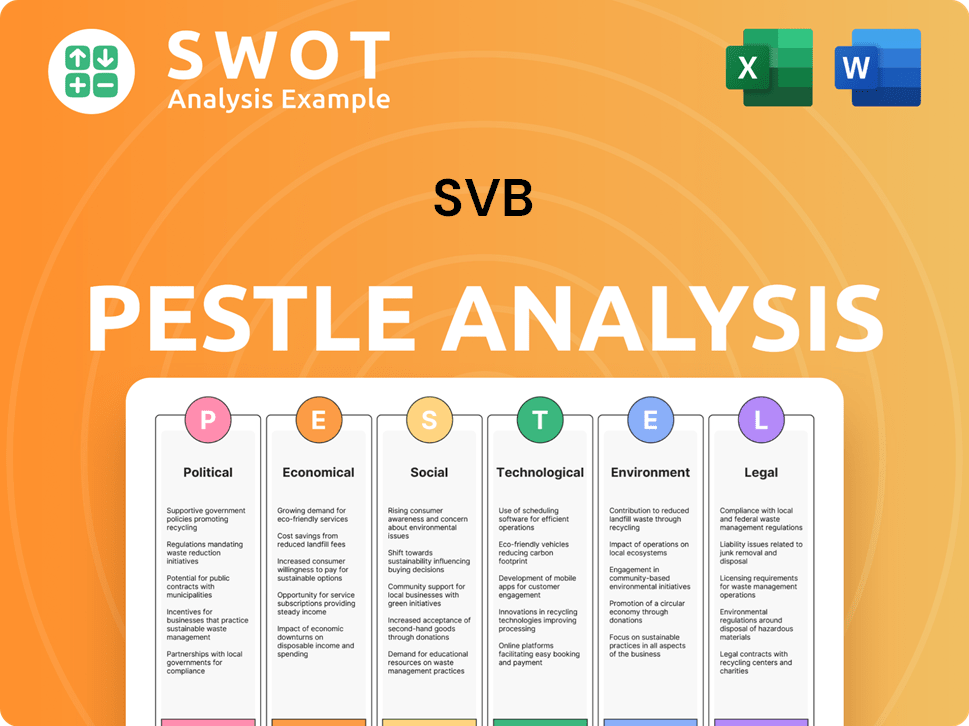
SVB PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on SVB’s Board?
Prior to its collapse, the Board of Directors of the SVB Financial Group, the SVB parent company, was responsible for overseeing the company's strategy and risk management. The board included a mix of independent directors and those with financial or industry expertise. While specific details on which board members directly represented major shareholders are not always explicitly stated, it's common for large institutional investors to engage with or influence the selection of board members. Understanding the dynamics of SVB ownership is crucial for assessing the decisions made during the bank's operation.
The voting structure of SVB Financial Group, the SVB company, was based on a one-share-one-vote principle for its common stock, typical for publicly traded companies. Each share of common stock entitled its holder to one vote on matters brought before shareholders. There were no publicly known special voting rights, golden shares, or founder shares that would have given certain individuals or entities outsized control beyond their proportional equity stake. If you want to learn more about the bank's past, you can read a Brief History of SVB.
| Board Member | Title (Pre-Collapse) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Greg Becker | President and CEO | Led the company through the period leading up to the collapse. |
| Garen Staglin | Lead Independent Director | Played a key role in board oversight. |
| Other Directors | Various | Included individuals with expertise in finance, technology, and venture capital. |
In the period leading up to its failure, there were no widely publicized proxy battles or activist investor campaigns that significantly shaped decision-making within the company. However, post-collapse analyses have scrutinized the board's oversight of the bank's interest rate risk management and its response to the changing economic environment. The composition of the board, and the expertise of its members, became a point of contention in the aftermath, with questions raised about the adequacy of their oversight in light of the rapid and unexpected downfall of the institution. Understanding who owns SVB and who was responsible for its operations is vital for understanding the events that led to its failure.
The Board of Directors oversaw SVB's operations, with a mix of independent and expert members. The voting structure followed a standard one-share-one-vote system. Post-collapse, the board's oversight of risk management came under scrutiny.
- The board's role was critical in overseeing strategy and risk.
- The voting structure was straightforward, based on equity ownership.
- The board's actions and expertise were questioned after the bank's failure.
- The government seized SVB.
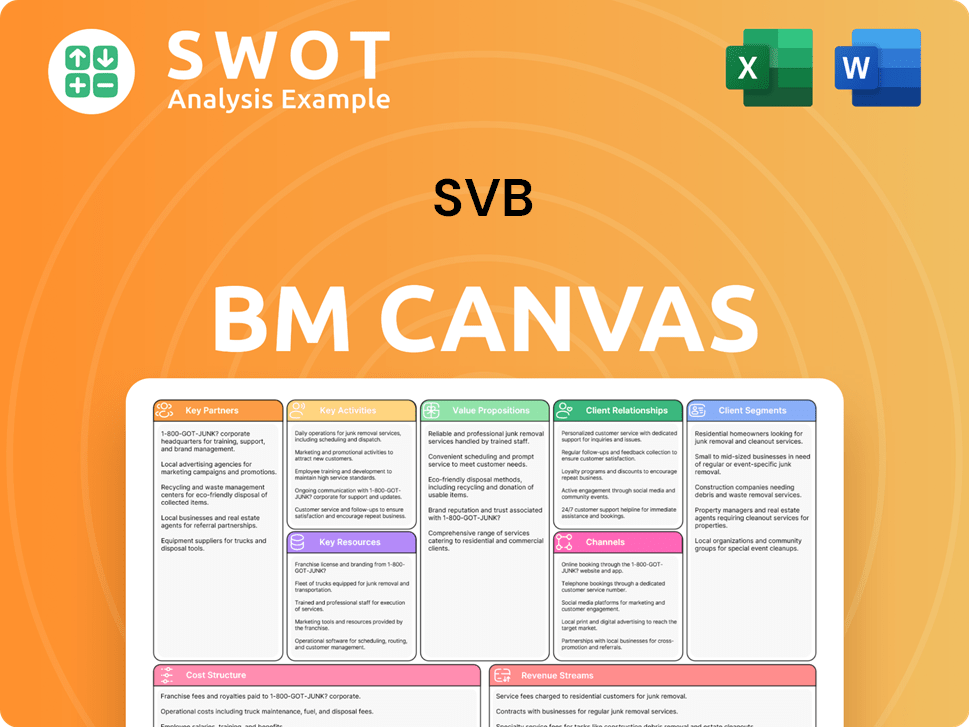
SVB Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped SVB’s Ownership Landscape?
The most significant recent development in the SVB ownership profile is its dramatic collapse in March 2023. Following a rapid bank run, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) stepped in as receiver for Silicon Valley Bank. On March 27, 2023, First Citizens Bank acquired substantially all loans and deposits of Silicon Valley Bridge Bank, N.A., the entity created by the FDIC to temporarily hold SVB's assets. This acquisition fundamentally altered the ownership structure of the operational banking entity, transferring control to First Citizens Bank.
This event reflects broader industry trends of consolidation within the banking sector. For the former SVB Financial Group shareholders, the outcome was severe, with common stock rendered worthless. The event has led to increased scrutiny from regulators on bank risk management practices, particularly regarding interest rate risk and liquidity. The focus has shifted to First Citizens Bank's integration of the acquired assets and its strategy for serving the innovation economy clientele that SVB once dominated. This highlights the potential for rapid shifts in ownership within the financial sector, driven by market forces and regulatory intervention. To understand the bank's operations, you can read about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of SVB.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Event | SVB Collapse and FDIC Intervention | Loss of shareholder value, regulatory scrutiny |
| Acquirer | First Citizens Bank | Control of SVB's core banking business |
| Shareholder Outcome | SVB Financial Group common stock rendered worthless | Significant financial loss for former shareholders |
The acquisition by First Citizens Bank has reshaped the banking landscape. The regulatory response and the subsequent sale underscore the risks associated with concentrated client bases and interest rate risk, particularly in mid-sized banks. The focus now is on First Citizens Bank's ability to manage and grow the acquired assets, including serving the innovation economy clients that SVB previously served. The future of SVB is now tied to First Citizens Bank's strategic direction and operational performance.
First Citizens Bank acquired the core banking assets of Silicon Valley Bank. The FDIC facilitated the sale after the bank's collapse. The former SVB Financial Group is no longer the owner.
Shareholders of the former SVB Financial Group saw their common stock become worthless. The collapse led to significant financial losses for investors. The FDIC's intervention resulted in this outcome.
The FDIC acted as receiver for Silicon Valley Bank after its failure. The FDIC created a bridge bank to manage assets temporarily. The FDIC facilitated the sale of SVB's assets to First Citizens Bank.
The focus is now on First Citizens Bank's integration and strategy. Increased regulatory scrutiny of bank risk management is expected. The incident highlights the potential for rapid ownership changes.
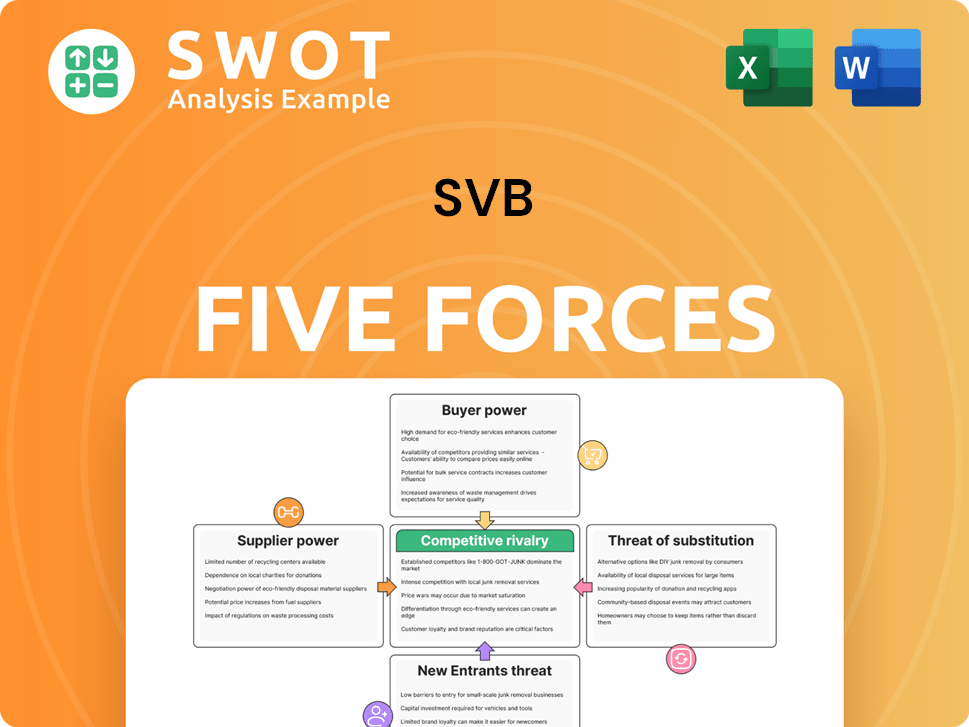
SVB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of SVB Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of SVB Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of SVB Company?
- How Does SVB Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of SVB Company?
- What is Brief History of SVB Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of SVB Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.